Related Research Articles

An auction is usually a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bids, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from the lowest bidder. Some exceptions to this definition exist and are described in the section about different types. The branch of economic theory dealing with auction types and participants' behavior in auctions is called auction theory.

eBay Inc. is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that facilitates consumer-to-consumer and business-to-consumer sales through its website. eBay was founded by Pierre Omidyar in 1995 and became a notable success story of the dot-com bubble. eBay is a multibillion-dollar business with operations in about 32 countries, as of 2019. The company manages the eBay website, an online auction and shopping website in which people and businesses buy and sell a wide variety of goods and services worldwide. The website is free to use for buyers, but sellers are charged fees for listing items after a limited number of free listings, and an additional or separate fee when those items are sold.
A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that solicits a proposal, often made through a bidding process, by an agency or company interested in procurement of a commodity, service, or valuable asset, to potential suppliers to submit business proposals. It is submitted early in the procurement cycle, either at the preliminary study, or procurement stage.

An online auction is an auction held over the internet and accessed by internet connected devices. Similar to in-person auctions, online auctions come in a variety of types, with different bidding and selling rules.
BidPay was an online auction payment service website, established in 1999 by Steve Chin and Marek Bradbury that allowed auction buyers to purchase money orders online using their credit card. BidPay was purchased by First Data Corporation/Western Union in 2001 for an undisclosed sum. BidPay was rebranded as "Western Union Auction Payments" in 2003 which led to confusion with Western Union's wire transfer services; the online auction payment service reverted to the BidPay name in 2004. BidPay ceased operations on 31 December 2005 and was purchased for US$1.8 million in March 2006 by CyberSource Corporation, which announced its intention to relaunch BidPay. BidPay had over 4 million registered users worldwide at that time.
Gmarket is an e-commerce website based in South Korea. The company was founded in 2000 as a subsidiary of Interpark, and was acquired by eBay in 2009.
Hi-Living is a Korean online auction website and shopping mall where people from all around the world buy and sell goods and services.

Etsy, Inc. is an American e-commerce company focused on handmade or vintage items and craft supplies. These items fall under a wide range of categories, including jewelry, bags, clothing, home décor and furniture, toys, art, as well as craft supplies and tools. Items described as vintage must be at least 20 years old. The site follows in the tradition of open craft fairs, giving sellers personal storefronts where they list their goods for a fee of US$0.20 per item.

bidorbuy or bidorbuy.co.za is an English-language e-commerce website based on an internet auction and online marketplace model allowing individuals and businesses to trade with each other. Transactions on bidorbuy are in South African rands.
A vendor management system (VMS) is an Internet-enabled, often Web-based application that acts as a mechanism for business to manage and procure staffing services – temporary, and, in some cases, permanent placement services – as well as outside contract or contingent labor. Typical features of a VMS application include order distribution, consolidated billing and significant enhancements in reporting capability that outperforms manual systems and processes.

Auto auctions are a method of selling vehicles based on an auction system. Auto auctions can be found in most countries and are usually exclusive to licensed automobile dealers. In a few countries, such as Japan, auto auctions are well known and used by most residents.
Bidtopia was an e-commerce site originally launched in 2007 as a private auction site for Warehouse86 Ventures, LLC. Paul St. James, an owner of Bargainland, which had been the largest PowerSeller on eBay that same year, started the new enterprise in response to changes in eBay policies regarding high volume sales of brand name merchandise and restrictions on sellers with poor customer feedback. Bidtopia suffered the loss of one of its three distribution centers in 2008, and went offline and possibly out of business in early 2010.
eBay has experienced controversy, including cases of fraud, its policy requiring sellers to use PayPal, and concerns over forgeries and intellectual property violations in auction items.
Customer to customer markets provide a way to allow customers to interact with each other. Traditional markets require business to customer relationships, in which a customer goes to the business in order to purchase a product or service. In customer to customer markets, the business facilitates an environment where customers can sell goods or services to each other. Other types of markets include business to business (B2B) and business to customer (B2C).
Pricefalls, LLC was an American Internet company that managed Pricefalls.com, an on-line retail marketplace, and PFTech, a leading marketplace platform developer. In 2019, Pricefalls, LLC was acquired by Loblaw, Canada's largest retailer.

vWorker was an employment website that enabled companies to outsource projects and independent contractors to find work. Together with Elance, Freelancer.com, Guru.com, and Upwork, it was one of the largest global freelance marketplaces of its kind. It organized and streamlined the management of outsourced employees.
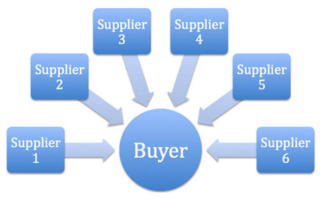
A reverse auction is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other.

OpenProcurement is an open source procurement software toolkit that automates procurement processes. It provides tools to design and build a transparent and competitive procurement process backed by strong data collection, electronic documents, and detailed reporting.

Liquidity Services (NASDAQ:LQDT) operates a network of e-commerce marketplaces.

The Government e Marketplace (GeM) is an online platform for public procurement in India. The initiative was launched on August 9, 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India with the objective to create an open and transparent procurement platform for government buyers. It was built in a record time of 5 months to facilitate the online procurement of goods and Services. The purchases through GeM by Government users have been authorized and made mandatory by the Ministry of Finance by adding a new Rule No. 149 in the General Financial Rules, 2017.
References
- 1 2 "FedBid's Big Plans" (blog entry), TechBis Now .
- ↑ "FedBid.com Raises More Than $5 Million in First Round", InternetNews.com, 2000-07-25.
- ↑ Wakeman, Nick. "Capital Markets Grow Cold for Once Sizzling E-Gov Startups", Washington Technology, 2001-02-02.
- ↑ FedBid Corporate History, Retrieved on 2009-12-01.
- ↑ Boland, Rita. "Online Government Auction Benefits Buyers and Sellers", AFCEA Newsletter, 2006-05-15.
- ↑ US 7272579,Canali, Luigi J. F.; Candelmo, Stephen P.& Fuster, Felipe J.et al.,"Auction based procurement system",published 2007-09-18, assigned to FedBid Inc.
- ↑ "FedBid Announces Record $875 Million Worth of Purchases by Government Buyers in FY2009", Business Wire , 2009-10-21.
- ↑ "FedBid Reverse Auction Business Booms", Washington Technology , 2010-12-07.
- 1 2 Heath, Thomas, "Revolution Growth Invests in Vienna Based FedBid", The Washington Post , January 16, 2012.
- ↑ "Revolution Growth Fund makes first investment in FedBid as company continues growth into new government and corporate markets", Archived 2012-10-23 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2012-08-12.
- ↑ "FedBid Board of Directors", Retrieved on 2013-11-22.
- 1 2 Koetsier, John, "Billionaire Ted Leonsis: How FedBid is going to save governments and companies 10-12% on almost everything they buy", "VentureBeat", 2012-11-28.
- ↑ "FedBid as company continues growth into new government and corporate markets", Archived 2012-10-23 at the Wayback Machine 2012-01-17.
- ↑ "FedBid Announces Joseph Jordan as New Chief Executive Officer", 2015-02-13.
- ↑ "Compusearch Acquires FedBid, Bringing Together Two Industry Leaders in Federal Purchasing, Spend Management".
- ↑ "Compusearch Software Systems Unveils Unison as New Brand Identity". February 1, 2019.
- 1 2 Loudin, Kathlyn. "FedBid.com: Reverse e-Auctioning ‘Ethernet Cards to Explosives’ in Two Easy Steps", Contract Management, March 2005.
- ↑ "FedBid as company continues growth into new government and corporate markets", Revolution Growth, January 2012.
- ↑ "FedBid FAQs", 2013-11-03.
- ↑ "Does Unison Marketplace Charge Fees?", 2019-29-4.
- ↑ "Study Hails Use of Online Reverse Auctions", Government Executive , 2011-01-03.
- ↑ "FedBid Gives Small Businesses Chance to Connect to Government" Archived 2010-10-06 at the Wayback Machine , El Paso Spotlight, October 2008.
- ↑ "US Navy Takes Aim at Reverse Auctions to Improve Procurement", Procurement Leaders, 2010-10-07.
- ↑ "FedBid Gives Procurement a 'Reverse eBay'", The Washington Post , 2010-11-29
- ↑ "FedBid Customers", fedbid.com. Accessed 2013-11-22
- ↑ "Air Force moves to debar FedBid", Federal Computer Week. Accessed 2015-01-30.
- ↑ "FedBid barred from new government contracts after watchdog report", The Washington Post , 2015/01/29. Accessed 2015-01-30.
- ↑ "VA rips FedBid, questions value of reverse auctions", Federal Computer Week, Accessed 2015-01-30
- ↑ "Administrative Investigation Conduct Prejudicial to the Government and Interference of a VA Official for the Financial Benefit of a Contractor Veterans Health Administration Procurement & Logistics Office Washington, DC", U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs Office of the Inspector General, Accessed 2015-01-30
- ↑ "Statement from FedBid CEO Joe Jordan on USAF decision to lift suspension, not pursue debarment"
- ↑ "Citing ‘excellent progress achieved’ by FedBid, Air Force ends monitoring requirements" (press release), fedbid.com. With link to letter from Air Force counsel Grandon to FedBid CEO Jordan stamp-dated March 7, 2016.