| C34 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | June 29, 1933 |
| Date in force | November 18, 1936 |
| This Convention has been "shelved". | |
| Classification | Employment Services - Job Placement |
| Subject | Employment policy and Promotion |
| Previous | Minimum Age (Non-Industrial Employment) Convention, 1932 |
| Next | Old-Age Insurance (Industry, etc.) Convention, 1933 (shelved) |
Fee-Charging Employment Agencies Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1933:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to fee-charging employment agencies,...
The concepts included in the convention were revised and included in ILO Convention C96, Fee-Charging Employment Agencies Convention (Revised), 1949.
Prior to its shelving, this convention had been ratified by 11 states.
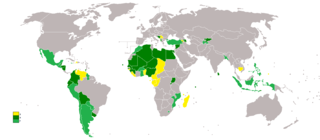
The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of August 2021 in 56 countries.
Maternity Protection Convention, 1919 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Workmen's Compensation (Agriculture) Convention, 1921 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Old-Age Insurance Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Old-Age Insurance (Agriculture) Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Invalidity Insurance Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Invalidity Insurance (Agriculture) Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Survivors' Insurance Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Survivors' Insurance (Agriculture) Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Fee-Charging Employment Agencies Convention (Revised), 1949 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Migration for Employment Convention, 1939 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Migration for Employment Convention (Revised), 1949 is an International Labour Organization Convention for migrant workers.
Private Employment Agencies Convention, 1997 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
C96 may refer to:

An employment agency is an organization which matches employers to employees. In developed countries, there are multiple private businesses which act as employment agencies and a publicly-funded employment agency.

The Employment Agencies Act 1973 (c.35) is a United Kingdom Act of Parliament and part of a wider body of UK agency worker law. It regulates the conduct of employment agencies which recruit and manage temporary and permanent labour. It applies to approximately 17,000 employment agencies operating in the UK. It was introduced by a private member's bill by Kenneth Lewis, member of parliament for Rutland and Stamford.
Adams v. Tanner, 244 U.S. 590 (1917), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that a Washington state law that prohibited employment agencies was unconstitutional.
Agency worker law refers to a body of law which regulates the conduct of employment agencies and the labour law rights of people who get jobs through them. The typical situation involves the person going to an employment agency and then the employment agency sending the person to an actual employer for proper work.
The Conventions concerning Employment of Women during the Night are conventions drafted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) which prohibit women from performing industrial work during the night. The first convention was adopted in 1919 and revised versions were adopted in 1934 and 1948. A protocol to the convention was adopted in 1990 allowing for easing of the restriction under conditions. As of April 2011 the conventions had 27, 15, 46 (undenounced) ratifications respectively. The protocol was ratified 5 and denounced by 2.
The International Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Women and Children is a 1921 multilateral treaty of the League of Nations that addressed the problem of international trafficking of women and children.