Related Research Articles
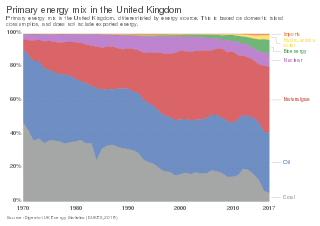
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.

Renewable energy in Germany is mainly based on wind and biomass, plus solar and hydro. Germany had the world's largest photovoltaic installed capacity until 2014, and as of 2021 it has over 58 GW. It is also the world's third country by installed total wind power capacity, 64 GW in 2021 and second for offshore wind, with over 7 GW. Germany has been called "the world's first major renewable energy economy".
Financial incentives for photovoltaics are incentives offered to electricity consumers to install and operate solar-electric generating systems, also known as photovoltaics (PV).

Solar power has a small role in electricity production in the United Kingdom.

The availability and uptake of green electricity in the United Kingdom has increased in the 21st century. There are a number of suppliers offering green electricity in the United Kingdom. In theory these types of tariffs help to lower carbon dioxide emissions by increasing consumer demand for green electricity and encouraging more renewable energy plant to be built. Since Ofgem's 2014 regulations there are now set criteria defining what can be classified as a green source product. As well as holding sufficient guarantee of origin certificates to cover the electricity sold to consumers, suppliers are also required to show additionality by contributing to wider environmental and low carbon funds.
A feed-in tariff is a policy mechanism designed to accelerate investment in renewable energy technologies by offering long-term contracts to renewable energy producers. This means promising renewable energy producers an above-market price and providing price certainty and long-term contracts that help finance renewable energy investments. Typically, FITs award different prices to different sources of renewable energy in order to encourage the development of one technology over another. For example, technologies such as wind power and solar PV are awarded a higher price per kWh than tidal power. FITs often include a "digression": a gradual decrease of the price or tariff in order to follow and encourage technological cost reductions.
The electricity sector in Argentina constitutes the third largest power market in Latin America. It relies mostly on thermal generation and hydropower generation (36%). The prevailing natural gas-fired thermal generation is at risk due to the uncertainty about future gas supply.
Feed-in electricity tariffs (FiT) were introduced in Germany to encourage the use of new energy technologies such as wind power, biomass, hydropower, geothermal power and solar photovoltaics. Feed-in tariffs are a policy mechanism designed to accelerate investment in renewable energy technologies by providing them remuneration above the retail or wholesale rates of electricity. The mechanism provides long-term security to renewable energy producers, typically based on the cost of generation of each technology. Technologies such as wind power, for instance, are awarded a lower per-kWh price, while technologies such as solar PV and tidal power are offered a higher price, reflecting higher costs.

Solar power includes solar farms as well as local distributed generation, mostly on rooftops and increasingly from community solar arrays. In 2022, utility-scale solar power generated 145.6 terawatt-hours (TWh), or 3.4% of electricity in the United States. Total solar generation that year, including estimated small-scale photovoltaic generation, was 204 TWh.

Electricity pricing can vary widely by country or by locality within a country. Electricity prices are dependent on many factors, such as the price of power generation, government taxes or subsidies, CO
2 taxes, local weather patterns, transmission and distribution infrastructure, and multi-tiered industry regulation. The pricing or tariffs can also differ depending on the customer-base, typically by residential, commercial, and industrial connections.

Feed-in tariffs in Australia are the feed-in tariffs (FITs) paid under various State schemes to non-commercial producers of electricity generated by solar photovoltaic (PV) systems using solar panels. They are a way of subsidising and encouraging uptake of renewable energy and in Australia have been enacted at the State level, in conjunction with a federal mandatory renewable energy target.

The Renewable Energy Sources Act or EEG is a series of German laws that originally provided a feed-in tariff (FIT) scheme to encourage the generation of renewable electricity. The EEG 2014 specified the transition to an auction system for most technologies which has been finished with the current version EEG 2017.

In Japan's electricity sector, wind power generates a small proportion of the country's electricity. It has been estimated that Japan has the potential for 144 gigawatts (GW) for onshore wind and 608 GW of offshore wind capacity. As of 2020, the country had a total installed capacity of 4.2 GW.

Development of solar power in Greece started in 2006 and installations of photovoltaic systems skyrocketed from 2009 because of the appealing feed-in tariffs introduced and the corresponding regulations for domestic applications of rooftop solar PV. In 2019, 90% of the around 2.5 GWp capacity was installed in 2011, 2012 and 2013. However, funding the FITs created an unacceptable deficit of more than €500 million in the Greek "Operator of Electricity Market" RES fund. To reduce that deficit, new regulations were introduced in August 2012 including retrospective feed-in tariffs reduction, with further reductions over time. These measures enabled the deficit to be erased by 2017.
A feed-in tariff (FIT) is paid by energy suppliers in the United Kingdom if a property or organisation generates their own electricity using technology such as solar panels or wind turbines and feeds any surplus back to the grid. The FIT scheme was imposed on suppliers by the UK government, and applied to installations completed between July 2009 and March 2019.
The Finland National Renewable Energy Action Plan is the National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP) for Finland. The plan was commissioned by the Directive 2009/28/EC which required Member States of the European Union to notify the European Commission with a road map. The report describes how Finland planned to achieve its legally binding target of a 38% share of energy from renewable sources in gross final consumption of energy by 2020.
The United Kingdom is committed to legally binding greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets of 34% by 2020 and 80% by 2050, compared to 1990 levels, as set out in the Climate Change Act 2008. Decarbonisation of electricity generation will form a major part of this reduction and is essential before other sectors of the economy can be successfully decarbonised.

Solar power in Iowa is limited but growing, with 137 megawatts (MW) installed by the end of 2019 and 27 MW installed during that year, ranking the state 40th among U.S. states. Iowa also generated 0.23% of the state's total electricity production in 2019 from solar energy; an amount sufficient to power over 17,000 Iowa homes. The state's early position as a major wind-power provider may have limited early large-scale solar investment.
Renewable energy in Greece accounted for 29 percent of its electricity from renewable sources in 2021. By 2030, renewables are expected to have a capacity of 28GW, and exceed 61 percent of Greece's electricity consumption. This is a significant increase from 8% of the country's total energy consumption in 2008. By 2022, Greece occasionally reached 100% renewables for a few hours. The target for 2050 is a capacity of 65GW.

Solar power in Switzerland has been growing rapidly in recent years due to declining system costs and a feed-in tariff instituted by the Swiss government.
References
- ↑ Held, Anne; Ragwitz, Mario; Gephart, Malte; de Visser, Erika; Klessmann, Corinna (27 January 2014). "Design features of support schemes for renewable electricity" (PDF). Ecofys. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- ↑ "Energy words". www.enelgreenpower.com. Enel Green Power . Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- ↑ "Can a Feed-In Tariff Help Increase Renewable Energy Capacity?". Rockefeller Institute of Government . Retrieved 3 February 2022.