
A composite material is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called composite laminates.

Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band, or dislocation.

In mechanics, compressive strength is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size (compression). It is opposed to tensile strength which withstands loads tending to elongate, resisting tension. In the study of strength of materials, compressive strength, tensile strength, and shear strength can be analyzed independently.

A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Breaking is often accompanied by a sharp snapping sound.
Thermal shock is a phenomenon characterized by a rapid change in temperature that results in a transient mechanical load on an object. The load is caused by the differential expansion of different parts of the object due to the temperature change. This differential expansion can be understood in terms of strain, rather than stress. When the strain exceeds the tensile strength of the material, it can cause cracks to form, and eventually lead to structural failure.

Delamination is a mode of failure where a material fractures into layers. A variety of materials, including laminate composites and concrete, can fail by delamination. Processing can create layers in materials, such as steel formed by rolling and plastics and metals from 3D printing which can fail from layer separation. Also, surface coatings, such as paints and films, can delaminate from the coated substrate.
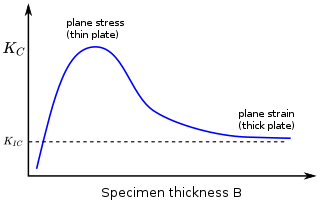
In materials science, fracture toughness is the critical stress intensity factor of a sharp crack where propagation of the crack suddenly becomes rapid and unlimited. A component's thickness affects the constraint conditions at the tip of a crack with thin components having plane stress conditions and thick components having plane strain conditions. Plane strain conditions give the lowest fracture toughness value which is a material property. The critical value of stress intensity factor in mode I loading measured under plane strain conditions is known as the plane strain fracture toughness, denoted . When a test fails to meet the thickness and other test requirements that are in place to ensure plane strain conditions, the fracture toughness value produced is given the designation . Fracture toughness is a quantitative way of expressing a material's resistance to crack propagation and standard values for a given material are generally available.

Flexural strength, also known as modulus of rupture, or bend strength, or transverse rupture strength is a material property, defined as the stress in a material just before it yields in a flexure test. The transverse bending test is most frequently employed, in which a specimen having either a circular or rectangular cross-section is bent until fracture or yielding using a three-point flexural test technique. The flexural strength represents the highest stress experienced within the material at its moment of yield. It is measured in terms of stress, here given the symbol .

Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
Methods have been devised to modify the yield strength, ductility, and toughness of both crystalline and amorphous materials. These strengthening mechanisms give engineers the ability to tailor the mechanical properties of materials to suit a variety of different applications. For example, the favorable properties of steel result from interstitial incorporation of carbon into the iron lattice. Brass, a binary alloy of copper and zinc, has superior mechanical properties compared to its constituent metals due to solution strengthening. Work hardening has also been used for centuries by blacksmiths to introduce dislocations into materials, increasing their yield strengths.
Material failure theory is an interdisciplinary field of materials science and solid mechanics which attempts to predict the conditions under which solid materials fail under the action of external loads. The failure of a material is usually classified into brittle failure (fracture) or ductile failure (yield). Depending on the conditions most materials can fail in a brittle or ductile manner or both. However, for most practical situations, a material may be classified as either brittle or ductile.

A fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) is a composite building material that consists of three components:
- the fibers as the discontinuous or dispersed phase,
- the matrix as the continuous phase, and
- the fine interphase region, also known as the interface.
Thermo-mechanical fatigue is the overlay of a cyclical mechanical loading, that leads to fatigue of a material, with a cyclical thermal loading. Thermo-mechanical fatigue is an important point that needs to be considered, when constructing turbine engines or gas turbines.
Ballistic impact is a high velocity impact by a small mass object, analogous to runway debris or small arms fire. The simulation of ballistic impacts can be achieved with a light-gas gun or other ballistic launcher. It is important to study the response of materials to ballistic impact loads. Applications of this research include body armor, armored vehicles and fortified buildings, as well as the protection of essential equipment, such as the jet engines of an airliner.

In materials science ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are a subgroup of composite materials and a subgroup of ceramics. They consist of ceramic fibers embedded in a ceramic matrix. The fibers and the matrix both can consist of any ceramic material, including carbon and carbon fibers.
In solid mechanics, the Johnson–Holmquist damage model is used to model the mechanical behavior of damaged brittle materials, such as ceramics, rocks, and concrete, over a range of strain rates. Such materials usually have high compressive strength but low tensile strength and tend to exhibit progressive damage under load due to the growth of microfractures.

The theory of micro-mechanics of failure aims to explain the failure of continuous fiber reinforced composites by micro-scale analysis of stresses within each constituent material, and of the stresses at the interfaces between those constituents, calculated from the macro stresses at the ply level.

According to the classical theories of elastic or plastic structures made from a material with non-random strength (ft), the nominal strength (σN) of a structure is independent of the structure size (D) when geometrically similar structures are considered. Any deviation from this property is called the size effect. For example, conventional strength of materials predicts that a large beam and a tiny beam will fail at the same stress if they are made of the same material. In the real world, because of size effects, a larger beam will fail at a lower stress than a smaller beam.
In materials science, toughening refers to the process of making a material more resistant to the propagation of cracks. When a crack propagates, the associated irreversible work in different materials classes is different. Thus, the most effective toughening mechanisms differ among different materials classes. The crack tip plasticity is important in toughening of metals and long-chain polymers. Ceramics have limited crack tip plasticity and primarily rely on different toughening mechanisms.
Ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites (UHTCMC) are a class of refractory ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) with melting points significantly higher than that of typical CMCs. Among other applications, they are the subject of extensive research in the aerospace engineering field for their ability to withstand extreme heat for extended periods of time, a crucial property in applications such as thermal protection systems (TPS) and rocket nozzles. Carbon fiber-reinforced carbon (C/C) maintains its structural integrity up to 2000 °C; however, C/C is mainly used as an ablative material, designed to purposefully erode under extreme temperatures in order to dissipate energy. Carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites (C/SiC) and Silicon carbide fiber reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites (SiC/SiC) are considered reusable materials because silicon carbide is a hard material with a low erosion and it forms a silica glass layer during oxidation which prevents further oxidation of inner material. However, above a certain temperature starts the active oxidation of silicon carbide matrix to gaseous silicon monoxide, consequently loss of protection from further oxidation, which leads the material to an uncontrolled and fast erosion. For this reason C/SiC and SiC/SiC are used in the range of temperature between 1200° - 1400 °C.

















