Related Research Articles

In cell biology, the cytoplasm describes all material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol, the organelles, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless.
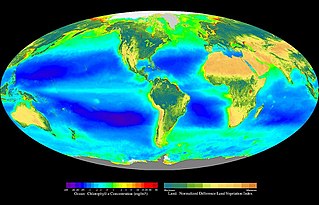
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as primary producers or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either net or gross, the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not.
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach to biological research.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt (joule/second) to ml O2/min or joule per hour per kg body mass J/(h·kg). Proper measurement requires a strict set of criteria to be met. These criteria include being in a physically and psychologically undisturbed state and being in a thermally neutral environment while in the post-absorptive state (i.e., not actively digesting food). In bradymetabolic animals, such as fish and reptiles, the equivalent term standard metabolic rate (SMR) applies. It follows the same criteria as BMR, but requires the documentation of the temperature at which the metabolic rate was measured. This makes BMR a variant of standard metabolic rate measurement that excludes the temperature data, a practice that has led to problems in defining "standard" rates of metabolism for many mammals.

Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles. The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ, or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA), gene expression data, and proteomic analyses reveal the set of gene products being produced in the cell, data that represents one aspect of cellular function. Conversely, metabolic profiling can give an instantaneous snapshot of the physiology of that cell, and thus, metabolomics provides a direct "functional readout of the physiological state" of an organism. There are indeed quantifiable correlations between the metabolome and the other cellular ensembles, which can be used to predict metabolite abundances in biological samples from, for example mRNA abundances. One of the ultimate challenges of systems biology is to integrate metabolomics with all other -omics information to provide a better understanding of cellular biology.

Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer, resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. The efficiency of this energy transfer is inversely proportional to the sixth power of the distance between donor and acceptor, making FRET extremely sensitive to small changes in distance.
Isotopic labeling is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope through chemical reaction, metabolic pathway, or a biological cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing one or more specific atoms with their isotopes. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.
Resting metabolic rate (RMR) is whole-body mammal metabolism during a time period of strict and steady resting conditions that are defined by a combination of assumptions of physiological homeostasis and biological equilibrium. RMR differs from basal metabolic rate (BMR) because BMR measurements must meet total physiological equilibrium whereas RMR conditions of measurement can be altered and defined by the contextual limitations. Therefore, BMR is measured in the elusive "perfect" steady state, whereas RMR measurement is more accessible and thus, represents most, if not all measurements or estimates of daily energy expenditure.

Allometry is the study of the relationship of body size to shape, anatomy, physiology and behaviour, first outlined by Otto Snell in 1892, by D'Arcy Thompson in 1917 in On Growth and Form and by Julian Huxley in 1932.

Raymond Pearl was an American biologist, regarded as one of the founders of biogerontology. He spent most of his career at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore. Pearl was a prolific writer of academic books, papers and articles, as well as a committed populariser and communicator of science. At his death, 841 publications were listed against his name. An early eugenicist, he eventually became an important critic of eugenics. He also advanced the concept of carrying capacity, although he didn't use the term, and was a Malthusian concerned with resource limits. He was a critique of mass consumption.
In chemistry, isotopologues are molecules that differ only in their isotopic composition. They have the same chemical formula and bonding arrangement of atoms, but at least one atom has a different number of neutrons than the parent.
Doubly labeled water is water in which both the hydrogen and the oxygen have been partly or completely replaced with an uncommon isotope of these elements for tracing purposes.
High-content screening (HCS), also known as high-content analysis (HCA) or cellomics, is a method that is used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of a cell in a desired manner. Hence high content screening is a type of phenotypic screen conducted in cells involving the analysis of whole cells or components of cells with simultaneous readout of several parameters. HCS is related to high-throughput screening (HTS), in which thousands of compounds are tested in parallel for their activity in one or more biological assays, but involves assays of more complex cellular phenotypes as outputs. Phenotypic changes may include increases or decreases in the production of cellular products such as proteins and/or changes in the morphology of the cell. Hence HCA typically involves automated microscopy and image analysis. Unlike high-content analysis, high-content screening implies a level of throughput which is why the term "screening" differentiates HCS from HCA, which may be high in content but low in throughput.

Evolutionary physiology is the study of the biological evolution of physiological structures and processes; that is, the manner in which the functional characteristics of individuals in a population of organisms have responded to natural selection across multiple generations during the history of the population. It is a sub-discipline of both physiology and evolutionary biology. Practitioners in the field come from a variety of backgrounds, including physiology, evolutionary biology, ecology, and genetics.

John Roger Speakman is a British biologist working at the University of Aberdeen, Institute of Biological and Environmental Sciences, for which he was Director from 2007 to 2011. He leads the University's Energetics Research Group, which is one of the world's leading groups using doubly labeled water (DLW) to investigate energy expenditure and balance in animals. Between 2011-2020, he was a '1000 talents' Professor at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing, China, where he ran the molecular energetics group. In 2020 he moved to the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shenzhen, China where he works at the Center for Energy Metabolism and Reproduction and Head of the Shenzhen Key laboratory of Metabolic Health.

Obesity classification is a ranking of obesity, the medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it has an adverse effect on health. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies obesity by body mass index (BMI). BMI is further evaluated in terms of fat distribution via the waist–hip ratio and total cardiovascular risk factors. In children, a healthy weight varies with age and sex, and obesity determination is in relation to a historical normal group.
Fetal scalp blood testing is a technique used in obstetrics during active labor to confirm whether a fetus is receiving enough oxygen. This is a supplementary procedure used to determine if fetal acidemia has occurred following fetal cardiac distress. While continuous fetal heart rate monitoring is the primary method for assessing fetal wellbeing during labor, a change in fetal heart rate is not indicative of fetal acidemia. Some of the signs and symptoms of oxygen deprivation are pH in the umbilical cord, abnormal fetal heartbeat and abnormal coloration of amniotic fluid. This correlation can only be concluded by sampling fetal scalp blood and measuring acid status. Therefore, fetal scalp blood testing could be used to reduce the number of unnecessary emergency caesarean sections made on the decision of fetal heart rate alone.

Plant stress measurement is the quantification of environmental effects on plant health. When plants are subjected to less than ideal growing conditions, they are considered to be under stress. Stress factors can affect growth, survival and crop yields. Plant stress research looks at the response of plants to limitations and excesses of the main abiotic factors, and of other stress factors that are important in particular situations. Plant stress measurement usually focuses on taking measurements from living plants. It can involve visual assessments of plant vitality, however, more recently the focus has moved to the use of instruments and protocols that reveal the response of particular processes within the plant

Isothermal microcalorimetry (IMC) is a laboratory method for real-time monitoring and dynamic analysis of chemical, physical and biological processes. Over a period of hours or days, IMC determines the onset, rate, extent and energetics of such processes for specimens in small ampoules at a constant set temperature.

The rate of living theory postulates that the faster an organism’s metabolism, the shorter its lifespan. First proposed by Max Rubner in 1908, the theory was based on his observation that smaller animals had faster metabolisms and shorter lifespans compared to larger animals with slower metabolisms. The theory gained further credibility through the work of Raymond Pearl, who conducted experiments on drosophila and cantaloupe seeds, which supported Rubner's initial observation. Pearl's findings were later published in his book, The Rate of Living, in 1928, in which he expounded upon Rubner's theory and demonstrated a causal relationship between the slowing of metabolism and an increase in lifespan.
References
- ↑ Butler, P.J., Green, J.A., Boyd, I.L. and Speakman, J.R. (2004) Measuring metabolic rate in the field: the pros and cons of the doubly-labelled water and heart rate methods. Functional Ecology 18: 168-183
- ↑ Speakman, JR (2000) The cost of living: Field metabolic rates of small mammals. Advances in Ecological Research 30: 177-297
- ↑ Nagy, KA (2005) Field metabolic rates and body size. Journal of Experimental Biology 208, 1621-1625
- ↑ Dunn, Ruth E.; White, Craig R.; Green, Jonathan A. (2018-06-01). "A model to estimate seabird field metabolic rates". Biology Letters. 14 (6): 20180190. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2018.0190. ISSN 1744-9561. PMC 6030596 . PMID 29875209.