Related Research Articles

The Third Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a unitary state with a five-level hierarchy of types of administrative division. There are nine different types of country subdivision in a new hierarchy with no new types but with two from the previous one abolished.

Goma is the capital and largest city of the North Kivu Province in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is located on the northern shore of Lake Kivu and shares borders with Bukumu Chiefdom to the north, Rwanda to the east and Masisi Territory to the west. The city lies in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift, and is only 13–18 km (8.1–11.2 mi) south of the active volcano Mount Nyiragongo. With an approximate area of 75.72 km2 (29.24 sq mi), the city has an estimated population of nearly 2 million people according to the 2022 census.
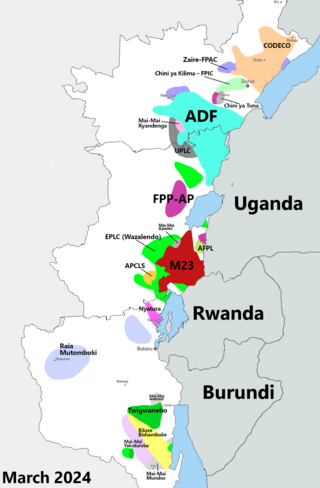
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

The March 23 Movement, often abbreviated as M23 and also known as the Congolese Revolutionary Army, is a Congolese rebel military group. Based in eastern areas of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), it operates mainly in the province of North Kivu, which borders both Uganda and Rwanda. The M23 rebellion of 2012 to 2013 against the DRC government led to the displacement of large numbers of people. On 20 November 2012, M23 took control of Goma, a provincial capital with a population of a million people, but it was requested to evacuate it by the International Conference on the Great Lakes Region because the DRC government had finally agreed to negotiate. In late 2012, Congolese troops, along with UN troops, retook control of Goma, and M23 announced a ceasefire and said that it wanted to resume peace talks.
Solange Lwashiga Furaha is a human and women's rights activist from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the executive secretary of the South Kivu Congolese Women's Caucus for Peace.

Katana Gégé Bukuru is a Congolese activist fighting for women rights. She is also the founder of the SOFAD.
Jeanine Mabunda Lioko Mudiayi is a Congolese lawyer and politician who in 2019 became the first woman elected to lead the Democratic Republic of the Congo's National Assembly. She was impeached on December 10, 2020, through a democratic vote by the National Assembly with 281 votes.
Fabiola Faïda Mwangilwa is a politician and women's rights activist in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. She is a former Minister of Family and Women's Affairs, and a founding member of several women's organizations and platforms.

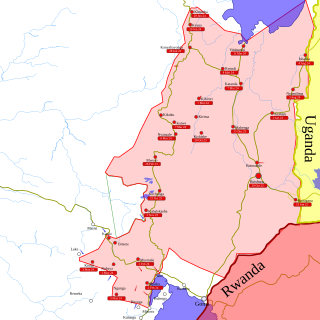
General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 20 December 2023. Combined elections were held for the President, 484 of the 500 members of the National Assembly, 700 of the 716 elected members of the 26 provincial assemblies, and for the first time under the new constitution, 951 members of a scaled down number of commune (municipal) councils. On election day, the Congolese government extended voting to 21 December for polling stations that had not opened on 20 December. Agence France-Presse reported that some polling stations would open as late as 24 December.
In late March 2022, the March 23 Movement (M23), supported by Rwanda, launched an offensive in North Kivu against the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC) and MONUSCO. The fighting displaced hundreds of thousands of civilians and caused renewed tensions between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda.
The Kishishe massacre occurred from November 29 to December 1, 2022, in the North Kivu village of Kishishe in the Rutshuru Territory in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. The March 23 Movement, a predominantly Tutsi armed group, summarily killed at least 131 civilians in Kishishe following clashes with local militias, according to a preliminary United Nations investigation. At the same time, the Kinshasa authorities had previously reported approximately 300 fatalities. The attack also resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of people who were forced to flee to other locations such as Kanyabayonga, Kibirizi, Kashala, Kirima, Nyanzale, Kashalira, Bambu, and Kitchanga. Some victims also sought refuge in neighboring countries due to the ongoing violence and instability in the region.

Lulenge constitutes one of the four sectors within the Fizi Territory of South Kivu Province, situated in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Geographically positioned adjacent to the Kiloba and Makena villages at an elevation of 943 meters, the sector's administrative center is Kilembwe. Lulenge is delineated to the north by the Itombwe sector and Mwenga Territory, to the east by Lake Tanganyika and the Mutambala sector, to the south by the N'gangya sector, and to the west by Shabunda Territory.

Kamanyola is one of the groupements (groupings) within the Ngweshe Chiefdom of the Walungu Territory. It is located in the Ruzizi Plain in the South Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), sharing a border with Rwanda and Burundi. Kamanyola stands at a height of 901 meters and is closely situated to the suburb of Mwaro and the village of Mubombo.

Mutambala is a sector that constitutes one of the four sectors in the Fizi Territory of the South Kivu Province in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Mutambala is situated near Lake Tanganyika, in the west by the Lulenge sector, in the north by the Tangani'a sector, and in the south by the Ngandja sector. It has a surface area of 777 km 2. The sector consists of five groupings (groupements), including the Basimukindja groupings, the Batombwe groupings, and the Babwari groupings.
Bibogobogo, alternatively referred to as Bibokoboko in Kibembe, is a village in the middle plateaus of the Mutambala Sector in the Fizi Territory in the South Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is situated in the forested mountains and middle plateaus, overlooking Baraka in the south-west, near Kisombe and Bibokoboko II villages. Geographically, Bibogobogo shares its boundaries with Uvira Territory to the north, Mwenga and Shabunda Territories to the west, Kalemie Territory to the south, and Lake Tanganyika to the east.
The Women's Association for Promotion and Endogenous Development is a women's organization in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It focuses on promoting women's rights, children's rights and development across multiple regions within the country. The organization's headquarter is located at n°94 on Avenue Isiro, Q. Nyamianda, in the Uvira city of Uvira Territory.
The Fally Ipupa Foundation is a non-profit organization established in 2013 by Congolese singer-songwriter Fally Ipupa. It aims to provide assistance to various marginalized groups in need in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), including victims of sexual violence, diseases, as well as orphans.
On October 31, 2020, jihadists from the Islamic State's Central Africa Province (ISCAP) attacked the village of Lisasa, Beni Territory, North Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo, killing over twenty-one civilians after brief clashes with UPLC Mai-Mai militiamen. The massacre came just several days after ISCAP slaughtered nineteen civilians in the village of Baeti.

The Bashali Chiefdom is a chiefdom located in the Masisi Territory of North Kivu Province in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Topographically, it is bounded to the east by the Virunga National Park, to the north by the Bwito Chiefdom of Rutshuru Territory, to the northwest by Walikale Territory, to the south by the Bahunde Chiefdom, and to the west by the Osso sector. Encompassing a total area of 1,582 square kilometers, the chiefdom is the administrative and sociopolitical structure for the Hunde ethnic group and is administratively subdivided into two groupements: Bashali-Mokoto and Bashali-Kaembe. Kitchanga, the urban center and administrative capital of the Bashali-Mokoto groupement, is the most densely populated locality within the chiefdom.
References
- ↑ "RDC: La dynamique « 50% des femmes ou rien » derrière la candidature de Jeannine Mabunda à la présidence de l'assemblée nationale". Jambo RDC.info. 16 April 2019. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ↑ "Sud-Kivu: la dynamique "50 % des femmes ou rien" annonce une série d'action dès ce samedi pour exiger le respect de l'article 14 de la constitution" (in French). 8 November 2019. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ↑ Justin Mwamba (27 January 2021). "RDC: La dynamique 50 pourcent femmes exhorte les femmes députées à adhérer à l'Union sacrée" . Retrieved 12 February 2022.