
Jacob Le Maire was a Dutch mariner who circumnavigated the earth in 1615 and 1616. The strait between Tierra del Fuego and Isla de los Estados was named the Le Maire Strait in his honour, though not without controversy. It was Le Maire himself who proposed to the council aboard Eendracht that the new passage should be called by his name and the council unanimously agreed with Le Maire. The author or authors of The Relation took Eendracht captain Willem Schouten's side by proclaiming:

Hippolyte or Hipólito Bouchard was a French-born Argentine sailor and corsair who fought for Argentina, Chile, and Peru.

Ferrol is a city in the Province of A Coruña in Galicia, on the Atlantic coast in north-western Spain, in the vicinity of Strabo's Cape Nerium. According to the 2021 census, the city has a population of 64,785, making it the seventh largest settlement in Galicia. With Eume to the south and Ortegal the north, Ferrol forms the Ferrolterra comarca, and together with A Coruña forms the second largest conurbation in Galicia, with a total population of 640,000 in 2016.
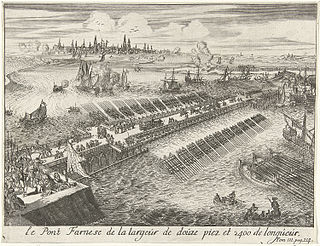
The fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces. Under the terms agreed, all Protestants were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam, which became the capital of the Dutch Republic. Apart from losing a high proportion of its mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt up to 1795.

Jan Snellinck or Jan Snellinck (I) (c. 1548 – 1 October 1638) was a Flemish painter, draughtsman and designer of tapestries, prints and frescoes. He is known for his large altarpieces and was also recognized as a leading battle painter in his time. Snellinck was active as an art dealer and art collector.

The Spanish Armada was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, link up with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas.

Hellburners were specialised fireships used in the Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) during the Eighty Years' War between the Dutch rebels and the Habsburgs. They were floating bombs, also called "Antwerp fire", and did immense damage to the Spanish besiegers. Hellburners have been described as an early form of weapons of mass destruction.

There are recorded incidents of armour having been employed in naval warfare in Europe and in East Asia prior to the introduction of the ironclad warship. Contemporary or later reports describe the use of metal plates on hulls or the superstructure of a limited number of wooden sailing ships, some of which were equipped with naval artillery. However, in every single case of both European and Far Eastern vessels the evidence for this is either unclear, ambiguous or disputed.

Marten Ryckaert or Maerten Ryckaert, was a Flemish landscape painter. He was known for his small, usually imaginary landscapes in an Italianate style.

The siege of Kolberg took place from March to 2 July 1807 during the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. An army of the First French Empire and several foreign auxiliaries of France besieged the fortified town of Kolberg, the only remaining Prussian-held fortress in the Province of Pomerania. The siege was not successful and was lifted upon the announcement of the Peace of Tilsit.
William Bolts (1738–1808) was a Dutch-born British merchant active in India. He began his career as an employee of the East India Company, and subsequently became an independent merchant. He is best known today for his 1772 book, Considerations on India Affairs, which detailed the administration of the East India Company in Bengal which began shortly after their victory in the Battle of Plassey in 1757. The observations and experiences he recorded offer a unique resource for scholars inquiring into the nature of Company rule in Bengal. Throughout his life, Bolts continued to propose and execute various trading ventures on his own behalf and in conjunction with various commercial and governmental partners. The ventures of individual traders like Bolts did much to spur governments and large corporations into the expansion of their own interests.

Juan Del Águila y Arellano was a Spanish general. He commanded the Spanish expeditionary Tercio troops in Sicily then in Brittany, before serving as general of the Spanish armies in the invasion of Ireland (1600–1602). As a soldier, and subsequently Maestre de campo of the Tercios, he was posted to Sicily, Africa, Malta, Corsica, Milan, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, France and Ireland, where he participated in major military events of his time, such as the Siege of Malta, the Looting of Antwerp, the Siege of Antwerp, the "Miracle of Empel", an expedition in support of the French Catholics, the Raid on Mount's Bay and another one in support of Irish rebels.

The Miracle of Empel was an unexpected Spanish victory on December 8, 1585, near Empel, in the Netherlands, as part of the Eighty Years' War, in which a surrounded Spanish force won against an enemy who exceeded them largely in number.
Austrian East India Company is a catchall term referring to a series of Austrian trading companies based in Ostend and Trieste. The Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste and Antwerp and Asiatic Company of Trieste or the Trieste Company were founded by William Bolts in 1775 and wound up in 1785.

The siege of IJsseloord or the capture of Arnhem was a siege that took place between the 6 and 15 October 1585 at Arnhem during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). The Dutch and English were victorious when the sconce of IJsseloord after seven days capitulated and Arnhem fell into their hands.

The Battle of Borgerhout was a battle during the Eighty Years' War, of the Spanish Army of Flanders led by Alexander Farnese, Prince of Parma, upon a fortified camp at the village of Borgerhout, near Antwerp, where several thousand French, English, Scottish, and Walloon soldiers in service of the recently created Union of Utrecht were stationed. It took place during the reconquest by the armies of Philip II of Spain of the Burgundian Netherlands, whose different provinces had united in 1576 under the Pacification of Ghent to drive out the foreign troops and to grant religious liberty to Protestants.

The siege of Rees of 1599, also known as the relief of Rees, was an unsuccessful attempt by Protestant-German forces led by Count Simon VI of Lippe, and Anglo-Dutch forces sent by Prince Maurice of Nassau, commanded by Philip of Hohenlohe-Neuenstein and the Count Ernst of Solms, to capture the strategic stronghold of Rees, Lower Rhine, Duchy of Cleves from the Spanish forces of Don Francisco de Mendoza, Admiral of Aragon, second-in-command of the Army of Flanders, and Governor Don Ramiro de Guzmán, between 10–12 September 1599, during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). This Spanish victory was part of the campaign of Francisco de Mendoza and Cardinal Andrew of Austria of 1598-1599, also called the Spanish Winter of 1598-99.

The siege of Sluis (1604), also known as the Sluis campaign or the Battle of the Oostburg Line, was a series of military actions that took place during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War from 19 May to 19 August 1604. A States and English army under Prince Maurice of Orange and Horace Vere respectively crossed the Scheldt estuary and advanced on land taking Cadzand, Aardenburg, and IJzendijke in the Spanish Netherlands. This soon led to the culmination of the siege of the Spanish-held inland port of Sluis.

The siege of Hulst of 1596 took place between mid-July and August 18, 1596, at the city of Hulst, Province of Zeeland, Low Countries, during the Eighty Years' War, the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). The siege was won by the Spanish forces of the Archduke of Austria. After a short siege, during which Maurice of Orange launched a failed attempt to relieve the city, the garrison of Dutch and English troops fell into Spanish hands on August 18, 1596.

Hendrik Gijsmans or Egidius Gijsmans was a Flemish painter, draftsman, tapestry designer and mayor. After training in his native Mechelen, he moved to Antwerp where he probably worked in the workshop of Gillis Mostaert. As a Protestant he left Antwerp after the fall of the city to the Spanish in 1585. He settled in Frankenthal in 1586 where he joined a large group of other Flemish émigré artists. He later became the mayor of Frankenthal. The artist’s work has only recently been rediscovered after he was identified with an anonymous artist referred to as Anonymous Fabriczy of whom a collection of about 50 drawings are held in the Staatsgalerie Stuttgart.


















