Related Research Articles

Huron County is a county located in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 census, the population was 58,565. Its county seat is Norwalk. The county was created in 1809 and later organized in 1815.

Norwalk is a small city in, and the county seat of, Huron County, Ohio, United States. The population was 17,012 at the 2010 census. The city is the center of the Norwalk Micropolitan Statistical Area and part of the Cleveland-Akron-Canton Combined Statistical Area. Norwalk is located approximately 10 miles (16 km) south of Lake Erie, 51 miles (82 km) west/southwest of Cleveland, 59 miles (95 km) southeast of Toledo, and 58 miles (93 km) west/northwest of Akron.
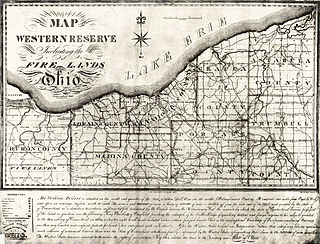
The Firelands, or Sufferers' Lands, tract was located at the western end of the Connecticut Western Reserve in what is now the U.S. state of Ohio. It was legislatively established in 1792, as the "Sufferers' Lands", and later became named "Fire Lands" because the resale of the land was intended as financial restitution for residents of the Connecticut towns of Danbury, Fairfield, Greenwich, Groton, New Haven, New London, Norwalk, and Ridgefield. Their homes had been burned in 1779 and 1781 by British forces during the American Revolutionary War. However, most of the settlement of the area did not occur until after the War of 1812. "Fire Lands" was later spelled as one word: "Firelands."

The Western Reserve Historical Society (WRHS) is a historical society in Cleveland, Ohio. The society operates the Cleveland History Center, a collection of museums in University Circle.

An open-air museum is a museum that exhibits collections of buildings and artifacts out-of-doors. It is also frequently known as a museum of buildings or a folk museum.

Keweenaw National Historical Park is a unit of the U.S. National Park Service. Established in 1992, the park celebrates the life and history of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of 2009, it is a partly privatized park made up of two primary units, the Calumet Unit and the Quincy Unit, and 21 cooperating "Heritage Sites" located on federal, state, and privately owned land in and around the Keweenaw Peninsula. The National Park Service owns approximately 1,700 acres (690 ha) in the Calumet and Quincy Units. Units are located in Baraga, Houghton, Keweenaw, and Ontonagon counties.

The Treaty of Fort Industry was a successor treaty to the Treaty of Greenville, which moved the eastern boundary of Indian lands in northern Ohio from the Tuscarawas River and Cuyahoga River westward to a line 120 miles west of the Pennsylvania boundary, which coincided with the western boundary of the Firelands of the Connecticut Western Reserve. In return, the United States agreed "every year forever hereafter, at Detroit, or some other convenient place" to pay $825 for the ceded lands south of the 41st degree of north latitude, and an additional $175 for the Firelands, which lie north of 41 degrees north, which the President would secure from the Connecticut Land Company, for a total of annuity $1000.00, to be "divided between said nations, from time to time, in such proportions as said nations, with the approbation of the President, shall agree."
The Pioneer and Historical Society of Muskingum County, also known as the Zanesville Historical Society, is an organization located in Zanesville, Ohio, in the United States, with the mission of preserving the history of the Zanesville and Muskingum County region of Ohio. It is a non-profit entity which operates several important historic sites in and around the Zanesville, Ohio, area, including the Dr. Increase Mathews House, built in 1805 by a founder of the town; and the Stone Academy, erected in 1809 as a possible state capitol, which was also a meeting place for abolitionist societies, and once the home of writer Elizabeth Robins, who wrote about it. The Pioneer and Historical Society of Muskingum County received a Preservation Merit Award from the Ohio Historic Preservation Office Award in 1993 for its work restoring and preserving the Stone Academy.

The Danbury Museum and Historical Society is a private museum located in Danbury, Connecticut, the purpose of which is to acquire, preserve, exhibit, and interpret the heritage of the greater Danbury area for education, information, and research. The main campus of the museum is located on 43 Main Street. It is home to five historic buildings: Huntington Hall, the 1785 Rider House, the 1790 John Dodd Hat Shop, the Little Red Schoolhouse, and the Marian Anderson Studio. The Museum also owned and maintained a sixth building: the Charles Ives Birthplace, located on Mountainville Avenue. The Ives birthplace was sold to a private bidder in 2012. Its legal name is the Danbury Scott Fanton Museum and Historical Society, Inc.

Avery is an unincorporated community in western Milan Township, Erie County, Ohio, United States. It is part of the Sandusky Metropolitan Statistical Area. Avery is located along US Route 250 near that road's interchange with Interstate 80 and Interstate 90, the Ohio Turnpike. The area is characterized by hotels and some industry. It once had a post office, but is now included in the Milan, Ohio postal zone (44846).

The Senator John Heinz History Center, an affiliate of the Smithsonian Institution, is the largest history museum in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States. Named after U.S. Senator H. John Heinz III (1938–1991) from Pennsylvania, it is located in the Strip District of Pittsburgh.

African American Museum in Cleveland, Ohio was founded in 1953 by Icabod Flewellen. The Museum is housed in a 100-year-old Carnegie Library building. The Museum works to educate young people about the positive contributions of blacks to the cultures of the world, and to eliminate the distorted portrayals and images of black people.
The New Indian Ridge Museum, Historic Shupe Homestead, and Wildlife Preserve is a private museum and nature reserve located on Beaver Creek in Amherst, Ohio, consisting of the Shupe Homestead site. The grounds contain two additional lots of upland and lowland mature wooded forest that contain wetlands, vernal pools, and an area floodplain. The property contains numerous tree and wildflower species, several fern types, buttonbushes, pawpaw trees, native green dragon wildflowers, and about fifty different species of birds.

Mill Hill Historic Park in Norwalk, Connecticut is a living history museum composed of three buildings: the circa 1740 Governor Thomas Fitch IV "law office", the circa 1826 Downtown District Schoolhouse, and the 1835 Norwalk Town Hall; as well as a historic cemetery also called the Town House Hill Cemetery. The museum is also known as the Mill Hill Historical Complex in some references and the sign at the parking lot reads Norwalk Mill Hill Museum.

Hunts Corners is an unincorporated community in southeastern Lyme Township, Huron County, Ohio, United States. It lies at the intersection of State Route 547 and Sand Hill Road, southeast of Bellevue and southwest of the city of Norwalk, the county seat of Huron County. Its elevation is 768 feet (234 m), and it is located at 41°13′39″N82°45′27″W.

Fitchville is an unincorporated community in Fitchville Township, Huron County, Ohio, United States. It is part of the Norwalk Micropolitan Statistical Area. Fitchville is located at the intersection of U.S. Route 250, State Route 13, and State Route 162. The community has no post office of its own and is assigned the New London zip code of 44851.

The Ohio History Center is a history museum and research center in Columbus, Ohio. It is the primary museum for Ohio's history, and is the headquarters, offices, and library of the Ohio History Connection. The building also houses Ohio's state archives, also managed by the Ohio History Connection. The museum is located at the Ohio State Fairgrounds, site of the Ohio State Fair, and a short distance north of downtown. The history center opened in 1970 as the Ohio Historical Center, moving the museum from its former site by the Ohio State University. The building was designed by Ireland & Associates in the Brutalist style.

The Norwalk Reflector is a newspaper in Norwalk, Ohio, published Monday through Saturday, except U.S. federal holidays, in Norwalk, Ohio, United States with a daily distribution of approximately 5,600.
Charles Alfred Wilson was a leading nineteenth-century American railroad engineer and civil engineer. He was born in Conowingo, Maryland. Wilson married Carrie Ione Stevens Wilson (1858-1919) in 1883 and they had one child, Hamilton Wilson.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-07-14. Retrieved 2014-07-13.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ↑ "Aurora Advocate | Kent Ravenna Record-Courier".