
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It uses encryption for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL.

Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. Firefox is available for Windows 10 and later versions of Windows, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and other operating systems, such as reactOS. Firefox is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser.

Mozilla Thunderbird is a free and open-source email client that also functions as a personal information manager with a calendar and contactbook, as well as an RSS feed reader, chat client (IRC/XMPP/Matrix), and news client. Operated by MZLA Technologies Corporation, a subsidiary of the Mozilla Foundation, Thunderbird is an independent, community-driven project that is managed and overseen by the Thunderbird Council, which is elected by the Thunderbird community. As a cross-platform application, Thunderbird is available for Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, Android, and Linux. The project strategy was originally modeled after that of Mozilla's Firefox, and Thunderbird is an interface built on top of that Web browser.
This is a comparison of both historical and current web browsers based on developer, engine, platform(s), releases, license, and cost.
Add-on is the Mozilla term for software modules that can be added to the Firefox web browser and related applications. Mozilla hosts them on its official add-on website.
NoScript is a free and open-source extension for Firefox- and Chromium-based web browsers, written and maintained by Giorgio Maone, a software developer and member of the Mozilla Security Group.
In computer science, session hijacking, sometimes also known as cookie hijacking, is the exploitation of a valid computer session—sometimes also called a session key—to gain unauthorized access to information or services in a computer system. In particular, it is used to refer to the theft of a magic cookie used to authenticate a user to a remote server. It has particular relevance to web developers, as the HTTP cookies used to maintain a session on many websites can be easily stolen by an attacker using an intermediary computer or with access to the saved cookies on the victim's computer. After successfully stealing appropriate session cookies an adversary might use the Pass the Cookie technique to perform session hijacking. Cookie hijacking is commonly used against client authentication on the internet. Modern web browsers use cookie protection mechanisms to protect the web from being attacked.

HTTP cookies are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and placed on the user's computer or other device by the user's web browser. Cookies are placed on the device used to access a website, and more than one cookie may be placed on a user's device during a session.
A local shared object (LSO), commonly called a Flash cookie, is a piece of data that websites that use Adobe Flash may store on a user's computer. Local shared objects have been used by all versions of Flash Player since version 6.

Stylish is a user style manager that can change the appearance of web pages in a user's browser without changing their content by including user-supplied CSS style sheets with those supplied by the web site itself. The Stylish browser extension includes tools with which to write user styles, and can install user styles written by other Stylish users from a companion website. These user styles may be more or less selective, targeting just one web page, or all of the pages on a domain, or every page on the web.

Firefox for Android is a web browser developed by Mozilla for Android smartphones and tablet computers. As with its desktop version, it uses the Gecko layout engine, and supports features such as synchronization with Firefox Sync, and add-ons.
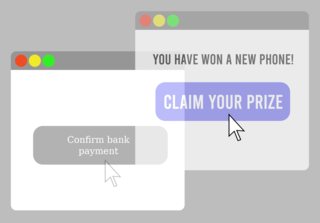
Clickjacking is a malicious technique of tricking a user into clicking on something different from what the user perceives, thus potentially revealing confidential information or allowing others to take control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous objects, including web pages.
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a policy mechanism that helps to protect websites against man-in-the-middle attacks such as protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking. It allows web servers to declare that web browsers should automatically interact with it using only HTTPS connections, which provide Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL), unlike the insecure HTTP used alone. HSTS is an IETF standards track protocol and is specified in RFC 6797.
Cross-site request forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding and abbreviated as CSRF or XSRF, is a type of malicious exploit of a website or web application where unauthorized commands are submitted from a user that the web application trusts. There are many ways in which a malicious website can transmit such commands; specially-crafted image tags, hidden forms, and JavaScript fetch or XMLHttpRequests, for example, can all work without the user's interaction or even knowledge. Unlike cross-site scripting (XSS), which exploits the trust a user has for a particular site, CSRF exploits the trust that a site has in a user's browser. In a CSRF attack, an innocent end user is tricked by an attacker into submitting a web request that they did not intend. This may cause actions to be performed on the website that can include inadvertent client or server data leakage, change of session state, or manipulation of an end user's account.

Waterfox is a free and open-source web browser and fork of Firefox. It claims to be ethical and user-centric, emphasizing performance and privacy. There are official Waterfox releases for Windows, macOS, Linux and Android. It was initially created to provide official 64-bit support, back when Firefox was only available for 32-bit systems.
Firefox was created by Dave Hyatt and Blake Ross as an experimental branch of the Mozilla browser, first released as Firefox 1.0 on November 9, 2004. Starting with version 5.0, a rapid release cycle was put into effect, resulting in a new major version release every six weeks. This was gradually accelerated further in late 2019, so that new major releases occur on four-week cycles starting in 2020.
Browser security is the application of Internet security to web browsers in order to protect networked data and computer systems from breaches of privacy or malware. Security exploits of browsers often use JavaScript, sometimes with cross-site scripting (XSS) with a secondary payload using Adobe Flash. Security exploits can also take advantage of vulnerabilities that are commonly exploited in all browsers.

PDF.js is a JavaScript library that renders Portable Document Format (PDF) files using the web standards-compliant HTML5 Canvas. The project is led by the Mozilla Corporation after Andreas Gal launched it in 2011.
HTTPS Everywhere is a discontinued free and open-source browser extension for Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Brave, Vivaldi and Firefox for Android, which was developed collaboratively by The Tor Project and the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF). It automatically makes websites use a more secure HTTPS connection instead of HTTP, if they support it. The option "Encrypt All Sites Eligible" makes it possible to block and unblock all non-HTTPS browser connections with one click. Due to the widespread adoption of HTTPS on the World Wide Web, and the integration of HTTPS-only mode on major browsers, the extension was retired in January 2023.





