
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally, resulting in the species becoming increasingly underpopulated in that area. Overfishing can occur in water bodies of any sizes, such as ponds, wetlands, rivers, lakes or oceans, and can result in resource depletion, reduced biological growth rates and low biomass levels. Sustained overfishing can lead to critical depensation, where the fish population is no longer able to sustain itself. Some forms of overfishing, such as the overfishing of sharks, has led to the upset of entire marine ecosystems. Types of overfishing include: growth overfishing, recruitment overfishing, ecosystem overfishing.

The goal of fisheries management is to produce sustainable biological, environmental and socioeconomic benefits from renewable aquatic resources. Wild fisheries are classified as renewable when the organisms of interest produce an annual biological surplus that with judicious management can be harvested without reducing future productivity. Fishery management employs activities that protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible, drawing on fisheries science and possibly including the precautionary principle.

The Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) is the fisheries policy of the European Union (EU). It sets quotas for which member states are allowed to catch each type of fish, as well as encouraging the fishing industry by various market interventions. In 2004 it had a budget of €931 million, approximately 0.75% of the EU budget.
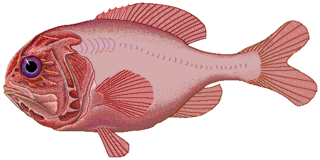
The orange roughy, also known as the red roughy, slimehead and deep sea perch, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family (Trachichthyidae). The UK Marine Conservation Society has categorized orange roughy as "vulnerable to exploitation". It is found in 3 to 9 °C, deep waters of the Western Pacific Ocean, eastern Atlantic Ocean, Indo-Pacific, and in the eastern Pacific off Chile. The orange roughy is notable for its extraordinary lifespan, attaining over 200 years. It is important to commercial deep-trawl fisheries. The fish is a bright, brick-red color, fading to a yellowish-orange after death.
This is a timeline of environmental history of New Zealand. It includes notable events affecting the natural environment of New Zealand as a result of human activity.

Lobsters are widely fished around the world for their meat. They are often hard to catch in large numbers, but their large size can make them a profitable catch. Although the majority of the targeted species are tropical, the majority of the global catch is in temperate waters.

The Magnuson–Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (MSFCMA), commonly referred to as the Magnuson–Stevens Act (MSA), is the legislation providing for the management of marine fisheries in U.S. waters. Originally enacted in 1976 to assert control of foreign fisheries that were operating within 200 nautical miles off the U.S. coast, the legislation has since been amended, in 1996 and 2007, to better address the twin problems of overfishing and overcapacity. These ecological and economic problems arose in the domestic fishing industry as it grew to fill the vacuum left by departing foreign fishing fleets.
Individual fishing quotas (IFQs), also known as "individual transferable quotas" (ITQs), are one kind of catch share, a means by which many governments regulate fishing. The regulator sets a species-specific total allowable catch (TAC), typically by weight and for a given time period. A dedicated portion of the TAC, called quota shares, is then allocated to individuals. Quotas can typically be bought, sold and leased, a feature called transferability. As of 2008, 148 major fisheries around the world had adopted some variant of this approach, along with approximately 100 smaller fisheries in individual countries. Approximately 10% of the marine harvest was managed by ITQs as of 2008. The first countries to adopt individual fishing quotas were the Netherlands, Iceland and Canada in the late 1970s, and the most recent is the United States Scallop General Category IFQ Program in 2010. The first country to adopt individual transferable quotas as a national policy was New Zealand in 1986.
Kaitiakitanga is a New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land. A kaitiaki is a guardian, and the process and practices of protecting and looking after the environment are referred to as kaitiakitanga.

Plebidonax deltoides or Donax deltoides is a small, edible saltwater clam or marine bivalve mollusc, endemic to Australia. It belongs to the family of either the Donacidae, or the related Psammobiidae. It is most widely known as the pipi in the eastern states of its native Australia. In South Australia, it is called the Coorong cockle, Goolwa cockle, or Goolwa pipi, for the region where it is most abundant, or by its Ngarrindjeri name, kuti. In south-eastern Queensland, it is often also known as eugarie or (y)ugari, a borrowing from the local Yugambeh and Ugarapul languages.

The environmental impact of fishing includes issues such as the availability of fish, overfishing, fisheries, and fisheries management; as well as the impact of industrial fishing on other elements of the environment, such as bycatch. These issues are part of marine conservation, and are addressed in fisheries science programs. According to a 2019 FAO report, global production of fish, crustaceans, molluscs and other aquatic animals has continued to grow and reached 172.6 million tonnes in 2017, with an increase of 4.1 percent compared with 2016. There is a growing gap between the supply of fish and demand, due in part to world population growth.
Discards are the portion of a catch of fish which is not retained on board during commercial fishing operations and is returned, often dead or dying, to the sea. The practice of discarding is driven by economic and political factors; fish which are discarded are often unmarketable species, individuals which are below minimum landing sizes and catches of species which fishers are not allowed to land, for instance due to quota restrictions. Discards form part of the bycatch of a fishing operation, although bycatch includes marketable species caught unintentionally. Discarding can be highly variable in time and space as a consequence of changing economic, sociological, environmental and biological factors.

Fishing in Chile is a major industry with a total catch of 4,442,877 tons of fish in 2006. As of 2010, Chile has the seventh largest commercial catch in the world. With over 4,000 km of viable coastline, fishing has been a vital resource for small-scale business and family development for hundreds of years. Due to the Humboldt Current, the Chilean Sea is considered among the most productive marine ecosystems in the world as well as the largest upwelling system. Artisanal fishing is practised all over Chile's 6,435 km long coastline and combines industrial techniques with pre-Hispanic traditions. Recreational fishing tourism in southern Chile's rivers has recently gained worldwide fame attracting actors such as Harrison Ford, Michael Douglas, and Kevin Costner.
This page is a list of fishing topics.

As with other countries, New Zealand’s 200 nautical miles exclusive economic zone gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 4.1 million square kilometres. This is the sixth largest zone in the world, and is fourteen times the land area of New Zealand.
The Quota Management System (QMS) is a type of individual fishing quota that is used in New Zealand to manage fish stocks.
Catch share is a fishery management system that allocates a secure privilege to harvest a specific area or percentage of a fishery's total catch to individuals, communities, or associations. Examples of catch shares are individual transferable quota (ITQs), individual fishing quota (IFQs), territorial use rights for fishing (TURFs), limited access privileges (LAPs), sectors, and dedicated access privileges (DAPs).

The Marine Management Organisation (MMO) is an executive non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom established under the Marine and Coastal Access Act 2009, with responsibility for English waters. The MMO exists to make a significant contribution to sustainable development in the marine area, and to promote the UK government's vision for clean, healthy, safe, productive and biologically diverse oceans and seas. The MMO aims to focus all of its activities and resources to meet its mission of enabling sustainable growth in the UK's marine area through 5 strategic outcomes:
This is a list of notable events relating to the environment in 1986. They relate to environmental law, conservation, environmentalism and environmental issues.

The fishing industry in Denmark operates around the coastline, from western Jutland to Bornholm. While the overall contribution of the fisheries sector to the country's economy is only about 0.5 percent, Denmark is ranked fifth in the world in exports of fish and fish products. Approximately 20,000 Danish people are employed in fishing, aquaculture, and related industries.












