
Abalone is a common name for any of a group of small to very large marine gastropod molluscs in the family Haliotidae, which contains only one genus Haliotis. Other common names are ear shells, sea ears, and, rarely, muttonfish or muttonshells in parts of Australia, ormer in the UK, perlemoen in South Africa, and pāua in New Zealand. The number of abalone species recognized worldwide ranges between 30 and 130 with over 230 species-level taxa described. The most comprehensive treatment of the family considers 56 species valid, with 18 additional subspecies.

Bluff, previously known as Campbelltown and often referred to as "The Bluff", is a town and seaport in the Southland region, on the southern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is the southernmost town in mainland New Zealand and, despite Slope Point and Stewart Island being further south, Bluff is colloquially used to refer to the southern extremity of the country. According to the 2018 census, the resident population was 1,797, a decrease of 6 since 2013.

Kaipara Harbour is a large enclosed harbour estuary complex on the north western side of the North Island of New Zealand. The northern part of the harbour is administered by the Kaipara District and the southern part is administered by the Auckland Council. The local Māori tribe is Ngāti Whātua.
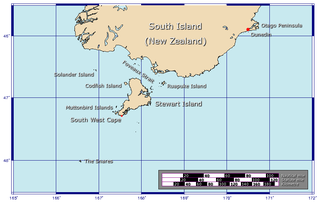
Foveaux Strait is a strait that separates Stewart Island from the South Island of New Zealand. The width of the strait ranges from about 23 to 53 km and the depth varies between 18 and 46 m. Captain James Cook passed around the southern tip of Stewart Island during his circumnavigation of the South Island in 1770 but did not record the presence of a seaway between Stewart Island and the mainland. The strait was not properly recorded until 1804 when an American sealer Owen Folger Smith made a chart.

Lobsters are widely fished around the world for their meat. They are often hard to catch in large numbers, but their large size can make them a profitable catch. Although the majority of the targeted species are tropical, the majority of the global catch is in temperate waters.

In Māori culture, a rāhui is a form of tapu restricting access to, or use of, an area or resource by the kaitiaki (guardian/s) of the area in the spirit of kaitiakitanga. With the passing of the 1996 Fisheries Act, a rāhui was able to be imposed by the New Zealand Ministry of Fisheries, a role that has since been taken over by the Ministry for Primary Industries. In the Cook Islands, raui have been put in place by the National Environment Service. Rāhui may be imposed for many reasons, including a need for conservation of food resources or because the area concerned is in a state of tapu, due, for example, to a recent death in the area, out of respect for the dead and to prevent the gathering of food there for a specified period. Rāhui may be placed on land, sea, rivers, forests, gardens, fishing grounds, and other food resources. A rāhui is given its authority by the mana of the person or group that imposes it.

New Zealand has 44 marine reserves spread around the North, the South Island, and neighbouring islands, and on outlying island groups. They are governed by the Marine Reserves Act 1971 and administered by the Department of Conservation with assistance from the Ministry for Primary Industries, New Zealand Customs Service and the New Zealand Defence Forces.
Claims and settlements under the Treaty of Waitangi have been a significant feature of New Zealand politics since the Treaty of Waitangi Act 1975 and the Waitangi Tribunal that was established by that act to hear claims. Successive governments have increasingly provided formal legal and political opportunity for Māori to seek redress for what are seen as breaches by the Crown of guarantees set out in the Treaty of Waitangi. While it has resulted in putting to rest a number of significant longstanding grievances, the process has been subject to criticisms including those who believe that the redress is insufficient to compensate for Māori losses. The settlements are typically seen as part of a broader Māori Renaissance.

Shark finning is the act of removing fins from sharks and discarding the rest of the shark back into the ocean. This act is prohibited in many countries. The sharks are often still alive when discarded, but without their fins. Unable to swim effectively, they sink to the bottom of the ocean and die of suffocation or are eaten by other predators. Shark finning at sea enables fishing vessels to increase profitability and increase the number of sharks harvested, as they must only store and transport the fins, by far the most profitable part of the shark; the shark meat is bulky to transport. Many countries have banned this practice and require the whole shark to be brought back to port before removing the fins.
Kaitiakitanga is a New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship of the sky, the sea, and the land. A kaitiaki is a guardian, and the process and practices of protecting and looking after the environment are referred to as kaitiakitanga.

Ngawi is a small fishing / holiday village within five kilometres of Cape Palliser, the southern-most point of New Zealand's North Island.

Pāua is the Māori name given to three New Zealand species of large edible sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs which belong to the family Haliotidae.

The Minister of Agriculture is a minister in the New Zealand Government. It was re-created as a standalone portfolio in 2017 after previously existing continuously from 1889 to 1998, and again from 1999 to 2012. The current Minister is Todd McClay.

Haliotis australis, common name the queen pāua,yellowfoot pāua, or austral abalone, is a species of edible sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Haliotidae, the abalones.
Fish & Game New Zealand is the collective brand name of 12 regional fish and game councils and the New Zealand Fish and Game Council which administer sports fishing and gamebird resources in New Zealand. Fish and game councils are regionally autonomous bodies governed by elected fish and game councillors, who are elected every three years by adult full season license-holders across the respective region. The New Zealand Fish and Game Council is made up of one representative from each of the regional councils. Councils employ managers and staff, and the New Zealand Fish and Game Council employs a director; the role is currently held by Bryce Johnson.

As with other countries, New Zealand's 200 nautical miles exclusive economic zone gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 4.1 million square kilometres. This is the sixth largest zone in the world, and is fourteen times the land area of New Zealand.

Aquaculture started to take off in New Zealand in the 1980s. It is dominated by mussels, oysters and salmon. In 2007, aquaculture generated about NZ$360 million in sales on an area of 7,700 hectares. $240 million was earned in exports.

The Ministry of Fisheries, also known by its acronym MFish, was a state sector organisation of New Zealand whose role is ensuring the sustainable utilisation of fisheries. It was merged into the Ministry of Primary Industries in April 2012. Its purpose was conserving, using, enhancing and developing New Zealand's fisheries resources.

Hikurangi Marine Reserve is a marine reserve off the coast of the Kaikōura District, in the Canterbury Region of New Zealand's South Island. It is the largest and deepest marine reserve in New Zealand.

Taumoana Marine Reserve is a marine reserve covering an area of 464 hectares in Fiordland on New Zealand's South Island. It was established in 2005 and is administered by the Department of Conservation. It is located next to the Five Fingers Peninsula, at the entrance to Tamatea / Dusky Sound.

















