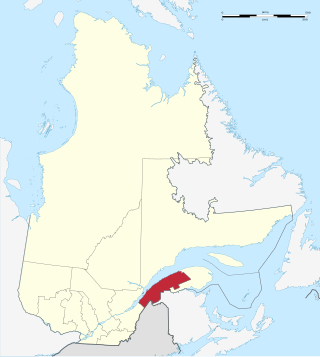
The Bas-Saint-Laurent, is an administrative region of Quebec located along the south shore of the lower Saint Lawrence River in Quebec. The river widens at this place, later becoming a bay that discharges into the Atlantic Ocean and is often nicknamed "Bas-du-Fleuve" (Lower-River). The region is formed by eight regional county municipalities and 114 municipalities. In the south, it borders Maine of the United States, and the Canadian New Brunswick and the regions of Chaudière-Appalaches and Gaspésie–Îles-de-la-Madeleine.

The Aude is a river of southern France that is 224 kilometres (139 mi) long. Its source is in the Pyrenees mountains then runs to Carcassonne and finally reaches the Mediterranean Sea near Narbonne. The river is navigable by raft or canoe for nearly all of its length. It is registered as essential to the Languedoc-Roussillon region.

Chicoutimi is the most populous borough (arrondissement) of the city of Saguenay in Quebec, Canada.

The Saguenay River is a major river of Quebec, Canada. It drains Lac Saint-Jean in the Laurentian Highlands, leaving at Alma and running east; the city of Saguenay is located on the river. It drains into the Saint Lawrence River. Tadoussac, founded as a French colonial trading post in 1600, is located on the northeast bank at this site.

Rhône-Alpes was an administrative region of France. Since 1 January 2016, it is part of the new region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. It is located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the river Rhône and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris. Rhône-Alpes has the sixth-largest economy of any European region.

The Chaudière River is a 185-kilometre-long (115 mi) river with its source near the Town of Lac-Mégantic, in southeast Quebec, Canada. From its source Lake Mégantic in the Estrie region, it runs northwards to flow into the St. Lawrence River opposite Quebec City.

Matapédia is a municipality at the southern tip of the Gaspé Peninsula, in eastern Quebec, Canada. Matapédia is located along Quebec Route 132 on the border of New Brunswick.

Saint-Quentin-Fallavier is a commune in the Isère department, and the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, in southeastern France.

Notre-Dame-du-Lac is a former city in the regional county municipality of Témiscouata in the province of Quebec, Canada, located in the administrative region du Bas-Saint-Laurent. On 5 May 2010, the cities of Cabano and Notre-Dame-du-Lac combined to form a new city named Témiscouata-sur-le-Lac. "Notre-Dame-du-Lac" was designated as a section of the new city.

The Bastille is the name of a fortress culminating at 476 m (1,561ft) above sea level, located at the south end of the Chartreuse mountain range and overlooking the city of Grenoble, France. The Bastille, which also gives its name to the hill, is the main tourist site of the Grenoble area, with 600,000 visitors per year.

The 2010 Var floods were the result of heavy rainfall in southern France that caused severe floods in the department of the Var in the evening of 15 June 2010. As well as generalized flooding, there were also flash floods. Meteorologists say the floods are the worst in the region since 1827, with more than 400 mm (16 in) of rain falling in less than 24 hours. At least 25 people were killed. The worst hit municipalities were Les Arcs, Figanières, Roquebrune-sur-Argens, Trans-en-Provence, and the subprefecture of Draguignan.

The 2011 Lake Champlain and Richelieu River floods were a series of water level increases that began at the end of April 2011 and caused a subsequent overflow of the Richelieu River in Canada and Lake Champlain in the United States. The flooding occurred due to record snowfall in the area followed by its snowmelt and in combination with intense spring rains. Lake Champlain stayed at flood stage for 67 days from April to June, and on May 10, 2011, the lake broke its previous flood level set in 1869 by reaching 102.8 ft. at Rouses Point, New York. The floods affected about 3,000 homes in Montérégie and caused an estimated six million U.S. dollars of damage in seven counties in the northern area of Vermont. The damage was so bad that a state of emergency was declared by Vermont on May 5, 2011. Similar damage was reported in New York State.
Historically, centenarian floods did extensive damage in the Isere valley. In October 1859, it rained continuously for five days. A warm wind melted the snow, and the temperature suddenly increased from 12 to 19 degrees on 2 November. The simultaneity of those two events resulted in an exceptional flood. In a single night, the water in Grenoble rose at a rate of 15 to 20 cm per hour.

Spring snowfall and heavy rain caused floods in southern Quebec on 3 May 2017. In total, 5,371 residences were flooded, 4,066 people were forced from their homes, and 261 municipalities were affected, largely in the Outaouais Region, the Greater Montreal Area, the Montérégie, the Mauricie, the Gaspésie and the Côte-Nord regions. The floods were listed as the third most significant weather event of 2017 by the Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society.
Lake Manitou is a lake located in the unorganized territory of Lac-Jérôme, in the Minganie Regional County Municipality, in the Côte-Nord, in the province of Quebec, Canada. The Manitou River flows through the lake from north to south, and continues to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.

The Chicoutimi River is a watercourse of eastern Quebec, Canada. A tributary of the Saguenay River, which it meets in the city of Saguenay, it is the 26.2-kilometre-long (16.3 mi) main outlet of Kenogami Lake, which rises from a watershed of 3,390 square kilometres (1,310 sq mi) in the Laurentides Wildlife Reserve. Entirely located in the Chicoutimi borough of Saguenay, it is the most urbanized and dammed river in Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean.

The Portage-des-Roches dam or Taschereau Dam is a dam located in the Laterrière sector of borough Chicoutimi, at Saguenay, Quebec, Canada. The largest water retaining structure in Kenogami Lake, this dam constitutes the source of the Chicoutimi River, whose flow is totally dependent on it.
The rivière la Retenue is a tributary of the east bank of the Ferrée river. It flows in the municipalities of Château-Richer and L'Ange-Gardien, in the La Côte-de-Beaupré Regional County Municipality, in the administrative region of Capitale-Nationale, in the province of Quebec, in Canada.
EPTB Seine Grands Lacs is a public territorial basin institution created in 1969 under the name of Institution interdépartementale des barrages-réservoirs du bassin de la Seine. Grouping together the departments of the former Seine, its mission is to reduce the winter and spring floods of the Seine and its main tributaries and to support their summer and autumn flows. The EPTB Seine Grands Lacs acts within the framework of the Seine Plan to reduce the vulnerability of territories to flooding.

















