Related Research Articles

George FridericHandel was a German-British Baroque composer well known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concertos. Handel received his training in Halle and worked as a composer in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712, where he spent the bulk of his career and became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the middle-German polyphonic choral tradition and by composers of the Italian Baroque. In turn, Handel's music forms one of the peaks of the "high baroque" style, bringing Italian opera to its highest development, creating the genres of English oratorio and organ concerto, and introducing a new style into English church music. He is consistently recognized as one of the greatest composers of his age.
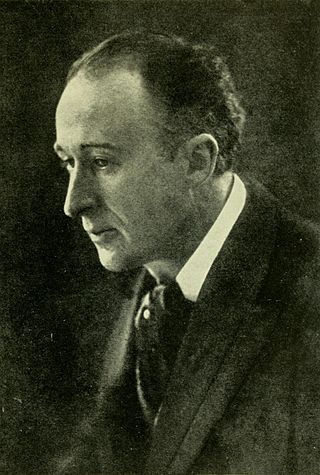
Frederick Theodore Albert Delius was an English composer. Born in Bradford in the north of England to a prosperous mercantile family, he resisted attempts to recruit him to commerce. He was sent to Florida in the United States in 1884 to manage an orange plantation. He soon neglected his managerial duties, and in 1886 returned to Europe.

Jacopo Peri was an Italian composer, singer and instrumentalist of the late Renaissance and early Baroque periods. He wrote what is considered the first opera, the mostly lost Dafne, and also the earliest extant opera, Euridice (1600).

Philip Arnold Heseltine, known by the pseudonym Peter Warlock, was a British composer and music critic. The Warlock name, which reflects Heseltine's interest in occult practices, was used for all his published musical works. He is best known as a composer of songs and other vocal music; he also achieved notoriety in his lifetime through his unconventional and often scandalous lifestyle.

Florent Schmitt was a French composer. He was part of the group known as Les Apaches. His most famous pieces are La tragédie de Salome and Psaume XLVII. He has been described as "one of the most fascinating of France's lesser-known classical composers".

Curlew River – A Parable for Church Performance is an English music drama, with music by Benjamin Britten to a libretto by William Plomer. The first of Britten's three 'Parables for Church Performance', the work is based on the Japanese noh play Sumidagawa by Kanze Jūrō (1395–1431), which Britten saw during a visit to Japan and the Far East in early 1956. Beyond the noh source dramatic material, Britten incorporated elements of noh treatment of theatrical time into this composition. Curlew River marked a departure in style for the remainder of the composer's creative life, paving the way for such works as Owen Wingrave, Death in Venice and the Third String Quartet.

In the Fen Country is an orchestral tone poem written by the English composer Ralph Vaughan Williams. Vaughan Williams had completed the first version of the work in April 1904. He subsequently revised the work in 1905 and 1907. It is Vaughan Williams' earliest composition not to be withdrawn.

Tahiti Trot, Op. 16, is an arrangement for symphony orchestra by Dmitri Shostakovich of the song "Tea for Two" from the musical No, No, Nanette by Vincent Youmans. It was composed in 1927 and resulted from a bet between the composer and the score's dedicatee, Nicolai Malko.
Paris: The Song of a Great City is a nocturne for orchestra composed by Frederick Delius over the period of 1899–1900. Hans Haym, to whom Delius dedicated the work, conducted the premiere on 14 December 1901 in Elberfeld, Germany. Sir Thomas Beecham conducted the UK premiere of the work in Liverpool on 11 January 1908. The critical edition of the score, published in the late 1980s, incorporated revisions by Beecham, and included editorial work from Eric Fenby and Norman Del Mar.

Hélène Sophie Emilie Rosen, later known as Jelka Delius, was a German painter, best known as the wife of the English composer Frederick Delius.

A Village Romeo and Juliet is an opera by Frederick Delius, the fourth of his six operas. The composer himself, with his wife Jelka, wrote the English-language libretto based on the short story "Romeo und Julia auf dem Dorfe" by the Swiss author Gottfried Keller. The first performance was at the Komische Oper Berlin on 21 February 1907, as Romeo und Julia auf dem Dorfe. Thomas Beecham conducted the British premiere at the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden in London on 22 February 1910. The US premiere was on 26 April 1972 in Washington, D.C.

Sāvitri is a chamber opera in one act with music composed by Gustav Holst, his Opus 25, to his own libretto. The story is based on the episode of Savitri and Satyavan from the Mahābhārata, which was also included in Specimens of Old Indian Poetry and Idylls from the Sanskrit. The opera features three solo singers, a wordless female chorus, and a chamber orchestra of 12 musicians. Holst had made at least six earlier attempts at composing opera before arriving at Sāvitri.

Koanga is an opera written between 1896 and 1897, with music by Frederick Delius and a libretto by Charles Francis Keary, inspired partly by the book The Grandissimes: A Story of Creole Life by George Washington Cable (1880). Inspiration also came from Delius's own experiences as a young man, when his family sent him to work in Florida. It was Delius's third opera, and he thought better of it than of its predecessors, Irmelin and The Magic Fountain, because of the incorporation of dance scenes and his treatment of the choruses. Koanga is reputed to be the first opera in the European tradition to base much of its melodic material on African-American music.

John Christopher Smith was an English composer who, following in his father's footsteps, became George Frideric Handel's secretary, student and amanuensis.

The Perfect Fool is an opera in one act with music and libretto by the English composer Gustav Holst. Holst composed the work over the period of 1918 to 1922. The opera received its premiere at the Covent Garden Theatre, London, on 14 May 1923. Holst had originally asked Clifford Bax to write the libretto, but Bax declined.

Julius Allan Greenway Harrison was an English composer and conductor who was particularly known for his interpretation of operatic works. Born in Lower Mitton, Stourport in Worcestershire, by the age of 16 he was already an established musician. His career included a directorship of opera at the Royal Academy of Music where he was a professor of composition, a position as répétiteur at the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden, conductor for the British National Opera Company, military service as an officer in the Royal Flying Corps, and founder member and vice-president of the Elgar Society.
A Mass of Life is a cantata by English composer Frederick Delius, based on the German text of Friedrich Nietzsche's philosophical novel Thus Spoke Zarathustra (1883-1885). In 1898, Delius had written a male choir and orchestral setting of "Midnight Song" from the same work, and this was revised to form part of the Mass.
This is a summary of 1925 in music in the United Kingdom.
References
- ↑ Kohen, Helen L. (1998). "Perfume, Postcards, and Promises: The Orange in Art and Industry". The Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts. 23: 33–47. doi:10.2307/1504162. JSTOR 1504162.
- ↑ Randel, William (April 1971). "Koanga and Its Libretto". Music & Letters. 52 (2): 141–156. doi:10.1093/ml/LII.2.141. JSTOR 735364.
- ↑ Hollinrake, Roger (January–April 1993). "Reviews of Books: A Distant Music: The Life and Times of Alfred Hill 1870-1960 by John Mansfield Thomson". Music & Letters. 64 (1/2): 69–70. doi:10.1093/ml/64.1-2.69. JSTOR 735364.
- ↑ Banfield, Stephen (April 1988). "Review of Florida: Suite for Orchestra, Op. posth. (new edition)". Music & Letters. 69 (2): 307. doi:10.1093/ml/69.2.307. JSTOR 855258.
- ↑ A Village Romeo and Juliet (theatre programme). Opera North. 6 June 1984.