Distance education, also known as distance learning, is the education of students who may not always be physically present at school, or where the learner and the teacher are separated in both time and distance. Traditionally, this usually involved correspondence courses wherein the student corresponded with the school via mail. Distance education is a technology-mediated modality and has evolved with the evolution of technologies such as video conferencing, TV, and the Internet. Today, it usually involves online education and the learning is usually mediated by some form of technology. A distance learning program can either be completely a remote learning, or a combination of both online learning and traditional offline classroom instruction. Other modalities include distance learning with complementary virtual environment or teaching in virtual environment (e-learning).

Mohawk Valley Community College (MVCC) is a public community college in Oneida County, New York. It is part of the State University of New York system. MVCC was founded in 1946 as the first community college established in New York State and currently consists of the main campus in Utica, N.Y., and a branch campus in Rome, New York It is the largest college between Syracuse, N.Y., and Albany, N.Y.

Florida SouthWestern State College is a public college with its main campus in Fort Myers, Florida. It is part of the Florida College System. The college has satellite campuses in Charlotte County and Collier County, and outreach programs in Hendry County and Glades County.
In the United States, dual enrollment (DE), also called concurrent enrollment, programs allow students to be enrolled in two separate, academically related institutions. Generally, it refers to high school students taking college or university courses. Less commonly, it may refer to any individual who is participating in two related programs.

An online school teaches students entirely or primarily online or through the Internet. It has been defined as "education that uses one or more technologies to deliver instruction to students who are separated from the instructor and to support regular and substantive interaction between the students. Online education exists all around the world and is used for all levels of education. This type of learning enables the individuals to earn transferable credits, take recognized examinations, and advance to the next level of education over the Internet.

American InterContinental University (AIU) is a private for-profit university with its headquarters in Schaumburg, Illinois. It employs open admissions and is owned by Perdoceo Education Corporation. American InterContinental University is a member of the American InterContinental University System. It is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission to award associate, bachelor's, and master's degrees.

American Public University System (APUS) is a private, for-profit, online university system with its headquarters in Charles Town, West Virginia. It is composed of American Military University (AMU) and American Public University (APU). APUS is wholly owned by American Public Education, Inc., a publicly traded private-sector corporation. APUS maintains corporate and academic offices in Charles Town, West Virginia. APUS offers associates, bachelors, masters, and doctoral degrees, in addition to dual degrees, certificate programs and learning tracks.
An online degree is an academic degree that can be earned primarily or entirely through the use of an Internet-connected computer, rather than attending college in a traditional campus setting. Improvements in technology, the increasing use of the Internet worldwide, and the need for people to have flexible school schedules while they are working have led to a proliferation of online colleges that award associate, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees.
Michigan Virtual University (MVU) is a private, nonprofit corporation that provides online educational tools, resources and courses for middle and high school students, parents and K-12 educators. Established in 1998 by the Michigan governor John Engler and the Michigan Economic Development Corporation, MVU is governed by an independent Board of Directors composed of individuals representing business, industry, higher education, K-12 education and state government. MVU also provides Michigan's K-12 educators access to online courses and resources to meet professional development requirements and earn State Continuing Education Clock Hours.
Connections Academy is a for-profit corporate provider of online school products and services to virtual schools for grades K-12, including full-time online school. In the United States the company is noted as Connections Academy, and for students abroad it is known as International Connections Academy. Based in Columbia, Maryland, Connections Academy is part of Pearson's Online and Blended Learning K-12 group. Online schools are an alternative to traditional public schools. Similar to charter schools, they are subsidized by the State. Although they contract with many non-profit schools, they are a for-profit corporation.
TTU K-12 is an approved learning school from kindergarten through twelfth grade program in Texas, offering high school diplomas. It is operated by Texas Tech University, which is located in Lubbock. TTU K-12 offers individual courses (supplemental), credit by exams (CBEs), homeschool curriculum, bulk testing services, and a full-time Texas Diploma Program that includes high school, middle school and elementary school.
Stride, Inc. is a for-profit education company that provides online and blended education programs. Stride, Inc. is an education management organization (EMO) that provides online education designed as an alternative to traditional "brick and mortar" education for public school students from kindergarten to 12th grade, as well as career learning programs. As of 2012, publicly traded Stride, Inc. was the largest EMO in terms of enrollment.
Wisconsin Virtual Academy (WIVA) is a virtual school administered as a charter school by the McFarland School District in McFarland, Wisconsin. The school is operated by the for-profit K12 Inc. corporation of Virginia.

National University is a private university with its headquarters in San Diego, California. Founded in 1971, National University offers academic degree programs at campuses throughout California, a satellite campus in Nevada, and various programs online. Programs at National University are designed for adult learners. On-campus classes are typically blended learning courses, concentrated to four weeks or on weeknights with occasional Saturday classes. The university uses asynchronous learning and real-time virtual classrooms for its online programs.

NYU Tandon Digital Learning, formerly known as NYU Tandon Online and NYU-ePoly, is the digital learning department at New York University Tandon School of Engineering, a noted school of engineering, technology, management and applied sciences in the United States.
Virtual High School (VHS) is a private online high school based in Bayfield, Ontario that offers accredited online courses towards an Ontario Secondary School Diploma. Its founder and principal is Stephen Baker.

Arden University is a private, for-profit teaching university in the United Kingdom. It offers a variety of undergraduate and post-graduate programmes with both blended and online distance learning delivery options. Its head office is in Coventry with study centres in Birmingham, Manchester, London and Berlin. Originally established as Resource Development International (RDI) in 1990, it was later bought by Capella Education and awarded university status by the British government in 2015. Since August 2016, it has been owned by Global University Systems.
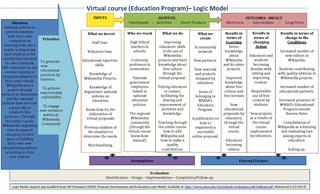
Digital pedagogy is the study and use of contemporary digital technologies in teaching and learning. Digital pedagogy may be applied to online, hybrid, and face-to-face learning environments. Digital pedagogy also has roots in the theory of constructivism.

The University of Mississippi High School is an accredited, comprehensive, online high school operated by the Office of Pre-College Programs in the Division of Outreach and Continuing Education at the University of Mississippi. It offers online classes for students in grades 7 through 12, allowing students to earn high school Carnegie units, dual credit through the university, and a high school diploma from anywhere in the United States or the world.













