Fluoromethcathinone (FMC) can refer to several substituted cathinone compounds:
- 2-Fluoromethcathinone (2-FMC)
- 3-Fluoromethcathinone (3-FMC)
- 4-Fluoromethcathinone (4-FMC; flephedrone)
Fluoromethcathinone (FMC) can refer to several substituted cathinone compounds:
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.

n-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated n-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly employed as a strong base (superbase) in the synthesis of organic compounds as in the pharmaceutical industry.
FMC may refer to:

Methylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylcathinone (MDMC), is an empathogen and stimulant psychoactive drug. It is a member of the amphetamine, cathinone and methylenedioxyphenethylamine classes.
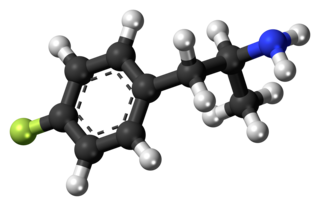
4-Fluoroamphetamine, also known as para-fluoroamphetamine (PFA) is a psychoactive research chemical of the phenethylamine and substituted amphetamine chemical classes. It produces stimulant and entactogenic effects. As a recreational drug, 4-FA is sometimes sold along with related compounds such as 2-fluoroamphetamine and 4-fluoromethamphetamine.

The Federal Medical Center, Carswell is a United States federal prison in Fort Worth, Texas, for female inmates of all security levels, primarily with special medical and mental health needs. It is operated by the Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP), a division of the United States Department of Justice. The facility also has a prison camp for minimum-security female inmates.

FMC Corporation is an American chemical manufacturing company headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, which originated as an insecticide producer in 1883 and later diversified into other industries. In 1941 at the beginning of US involvement in WWII, the company received a contract to design and build amphibious tracked landing vehicles for the United States Department of War, and afterwards the company continued to diversify its products. FMC employs 7,000 people worldwide, and had gross revenues of US$4.7 billion in 2018.

Methedrone is a recreational drug of the cathinone chemical class. Chemically, methedrone is closely related to para-methoxymethamphetamine (PMMA), methylone and mephedrone. Methedrone received media attention in 2009 after the death of two young Swedish men. In both cases toxicology analysis showed methedrone was the only drug present in both men during the time of their overdose and subsequent deaths.

4-Fluoromethamphetamine (4-FMA) is a stimulant drug related to methamphetamine and 4-fluoroamphetamine. It has been reported to be sold as a designer drug, but little is known about its pharmacology or toxicology. It was first detected from legal highs sold in Japan in 2006 and became illegal to sell or to possess for the purpose of distribution in Japan in 2008. It was initially reported to be contained as an ingredient in some of the range of party pills sold internationally by the Israeli company Neorganics from around 2006 onwards, but this was later shown to be incorrect and this ingredient was eventually identified as the closely related compound 2-fluoromethamphetamine.
The hexynes are a subgroup from the group of alkynes. It consists of several isomeric compounds having the formula C6H10.

Flephedrone, also known as 4-fluoromethcathinone (4-FMC), is a stimulant drug of the cathinone chemical class that has been sold online as a designer drug starting in 2008.
A dopamine releasing agent (DRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of dopamine in the body and/or brain.
The molecular formula for C10H12FNO (molar mass: 181.21 g/mol, exact mass: 181.0903 u) may refer to:

3-Fluoromethcathinone is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a structural isomer of flephedrone (4-fluoromethcathinone).
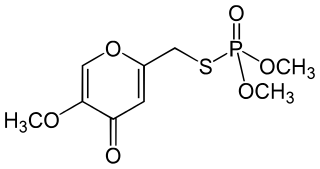
Endothion is an organic compound used as an insecticide and acaricides. It is part of the chemical class of organophosphorus compounds. It is generally described as white crystals with a slight odor. It is used as an insecticide, but not sold in the United States or Canada.

The Federal Medical Center, Butner, is a United States federal prison opened in 1995 in North Carolina for male inmates of all security levels who have special health needs. It is part of the Butner Federal Correctional Complex and is operated by the Federal Bureau of Prisons, a division of the United States Department of Justice. An adjacent satellite prison camp houses minimum-security male inmates.
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.

CAR-302,668 (302668, α-isopropylmandelic acid (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-pyridyl)methyl ester) is an anticholinergic deliriant drug, invented under contract to Edgewood Arsenal in the 1960s. It is a reasonably potent incapacitating agent with an ED50 of 4μg/kg and a long duration of action of around 16-24 hours.

3-Methoxymethcathinone (3-MeOMC), also known as meta-methoxymethcathinone (m-MeOMC), is a designer drug of the substituted cathinone family described as a stimulant.

2-Fluoromethcathinone (2-FMC), also known as 2-flephedrone, is a psychostimulant and designer drug of the cathinone family. It acts as a dopamine and norepinephrine releasing agent (NDRA).