
The Ford Taurus is an automobile that was manufactured by the Ford Motor Company in the United States from the 1986 to 2019 model years. Introduced in late 1985 for the 1986 model year, six generations were produced over 34 years; a brief hiatus was undertaken between 2006 and 2007. From the 1986 to 2009 model years, the Taurus was sold alongside its near-twin, the Mercury Sable; four generations of the high-performance Ford Taurus SHO were produced. The Taurus also served as the basis for the first-ever front-wheel-drive Lincoln Continental (1988–2002).

The Ford Fairmont is a model line of compact cars that was manufactured by Ford from the 1978 to 1983 model years. The successor of the Ford Maverick, the Fairmont marked the third generation of compact sedans sold by Ford in North America. Initially slotted between the Pinto and Granada within the Ford line, the Fairmont was later marketed between the Ford Escort and Ford LTD. In contrast to its predecessor, the model line was offered as a two-door notchback sedan, two-door coupe, four-door sedan, and five-door station wagon. Though never sold as a Lincoln, Mercury sold a divisional counterpart of the Fairmont as the Mercury Zephyr.

The Mercury Sable is a range of automobiles manufactured and marketed by the Mercury brand of Ford Motor Company. Introduced on December 26, 1985, as the replacement for the Mercury Marquis, the Sable marked the transition of the mid-size Mercury product range to front-wheel drive.
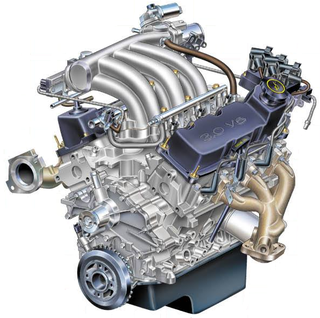
The Ford Vulcan is a 3.0 L V6 engine designed and built by the Ford Motor Company. It debuted in 1986 in the newly launched Ford Taurus. Ford went on to install the Vulcan V6 in a variety of car, van, and pickup truck models until the 2008 model year, after which production stopped.

The Ford SHO V6 is a family of DOHC V6 engines fitted to the Ford Taurus SHO from 1989 to 1995. The designation SHO denotes Super High Output.

The Ford HSC engine is an automobile gasoline engine from the Ford Motor Company, sold from 1984 until 1994. HSC stands for High Swirl Combustion. It was made in two displacements: 2.3 L and 2.5 L, and used in only two model lines: the Ford Tempo/Mercury Topaz and the Ford Taurus/Mercury Sable.

The Ford Tempo is an automobile that was produced by Ford from the 1984 to 1994 model years. The successor of the Ford Fairmont, the Tempo marked both the downsizing of the Ford compact car line and its adoption of front-wheel drive. Through its production, the model line was offered as a two-door coupe and four-door sedan, with the Mercury Topaz marketed as its divisional counterpart.

The Ford EXP is a sports compact coupe that was produced by Ford Motor Company from 1982 to 1988. The first two-seat Ford since the original Ford Thunderbird, the EXP was derived from the American Ford Escort. In contrast to its platform counterpart, the model line was not a "world car", developed entirely for North America. For 1982 and 1983, the EXP was also sold as the Mercury LN7.

The North American version of the Ford Escort is a range of cars that was sold by Ford from the 1981 to 2003 model years. The direct successor of the Ford Pinto, the Escort also largely overtook the role of the European-imported Ford Fiesta as the smallest vehicle in the Ford model line in North America. Produced across three generations, the first generation was a subcompact; the latter two generations were compact cars. Becoming highly successful in the marketplace, the Escort became the best-selling car in the United States after 1982, a position it would hold for much of the 1980s.

The Ford Taurus SHO is the high-performance variant of the Ford Taurus. Originally intended as a limited-production model, the SHO would be produced for the first three generations of the model line, from the 1989 to the 1999 model years. After an 11-year hiatus, the model was revived for 2010, continuing through the 2019 discontinuation of the Taurus model line.
The GM–Ford 6-speed automatic transmission is an automatic transaxle originally designed for transverse engine applications in cars. With design work having begun in 2002, General Motors and Ford Motor Company jointly committed to investing US$720 million in their manufacturing plants to support the new transmission.
Batavia Transmission was a transmission factory owned by Ford Motor Company in Batavia, Ohio. The plant opened on July 24, 1980, and closed in September 2008. The plant produced front-wheel drive transmissions for Ford, Mercury, and Mazda vehicles. The facility is now used as University of Cincinnati Clermont College's UC East Campus.
The AXOD was a 4-speed automatic transaxle for transverse front wheel drive automobiles from the Ford Motor Company. It was introduced in the 1986 Ford Taurus/Mercury Sable. The AXOD and its successors are built in Ford's Van Dyke Transmission plant in Sterling Heights, Michigan. Production of the final member of the family, the 4F50N, ended in November 2006.
The Ford C3 transmission and its descendants are a family of light-duty longitudinal automatic transmissions built by the Ford Motor Company.
The FLC-"Fluid Link Converter"- ATX was a 3-speed hydraulic automatic transaxle produced by Ford Motor Company from 1981 through 1994, first appearing in the North American Ford Escort, then later the European Escort in 1983. It was Ford's first automatic transmission developed for front wheel drive and transverse engine location. Used in the company's four-cylinder-powered cars ranging from the Escort to the Taurus. The 3.0-powered Tempo/Topaz used a beefed up version of the FLC as well. The transaxle did not have a lockup torque converter, or overdrive. It was controlled by a throttle or "kickdown" Linkage, the speedometer drive used a mechanical cable, and had no computer controls.

The first-generation Ford Taurus and Mercury Sable are automobiles produced by Ford as the first of six generations of the Ford Taurus and Mercury Sable. Launched on December 26, 1985, as a 1986 model, the front-wheel-drive Taurus was a very influential design that is credited with saving Ford from bankruptcy, bringing many innovations to the marketplace and starting the trend towards aerodynamic design for the American automakers in the North American market. Ford of Europe had launched the 1980s move to aerodynamic design for the company with the 1982 Ford Sierra.

The second-generation Ford Taurus is an automobile that was produced by Ford from 1991 to 1995, which served as the second out of six generations of the Ford Taurus. The second-generation Taurus shared all of its mechanical parts with the first-generation Ford Taurus, yet its exterior and interior were nearly completely redesigned. However, its exterior still strongly resembled that of the first-generation Taurus, leading many to believe that the second-generation was simply a facelift of the first-generation Taurus. However, this is partially true because the wagon model, from the B-pillar to the rear of the car, was a carryover from the first generation. The second generation of Taurus proved to be very popular, selling 410,000 units in its first year, becoming the best-selling car in the United States. It would hold this title until 1995, when it was discontinued and replaced with the third-generation Ford Taurus.

The third-generation Ford Taurus is an automobile that was marketed by Ford from the 1996 to 1999 model years. While the chassis underpinnings were largely carried over, the redesign gave the Taurus its first complete exterior redesign since its 1986 introduction. Slotted between the compact Ford Contour and full-size Ford Crown Victoria, the third-generation Taurus was again offered as a four-door sedan and as a five-door station wagon, marketed alongside the Mercury Sable.

The Ford Mondeo I (first generation) is a mid-size car that was produced by Ford, beginning on 23 November 1992, with sales beginning on 22 March 1993. It is also known as the Mk I Mondeo; the 1996 facelift versions are usually designated Mk II. Available as a four-door saloon, a five-door hatchback, and a five-door estate, all models for the European market were produced at Ford's plant in the Belgian city of Genk. In December 1992, Autocar published a section on the Mondeo, and how it would conquer rivals.













