
Oxidative phosphorylation or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.

An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. The electrons that transferred from NADH and FADH2 to the ETC involves 4 multi-subunit large enzymes complexes and 2 mobile electron carriers. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are membrane-bound.
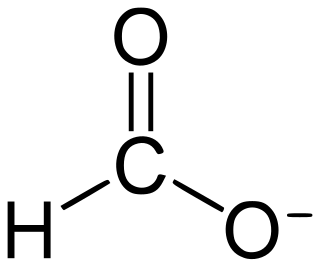
Formate is the conjugate base of formic acid. Formate is an anion or its derivatives such as ester of formic acid. The salts and esters are generally colorless.

10-Formyltetrahydrofolate (10-CHO-THF) is a form of tetrahydrofolate that acts as a donor of formyl groups in anabolism. In these reactions 10-CHO-THF is used as a substrate in formyltransferase reactions.
Formate dehydrogenases are a set of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide, donating the electrons to a second substrate, such as NAD+ in formate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (EC 1.17.1.9) or to a cytochrome in formate:ferricytochrome-b1 oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.2.1). This family of enzymes has attracted attention as inspiration or guidance on methods for the carbon dioxide fixation, relevant to global warming.
In enzymology, a D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannitol dehydrogenase (cytochrome) (EC 1.1.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a formate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) (EC 1.2.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a formate dehydrogenase (cytochrome-c-553) (EC 1.2.2.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a formate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.17.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome c nitrite reductase (ccNiR) is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the six electron reduction of nitrite to ammonia; an important step in the biological nitrogen cycle. The enzyme catalyses the second step in the two step conversion of nitrate to ammonia, which allows certain bacteria to use nitrite as a terminal electron acceptor, rather than oxygen, during anaerobic conditions. During this process, ccNiR draws electrons from the quinol pool, which are ultimately provided by a dehydrogenase such as formate dehydrogenase or hydrogenase. These dehydrogenases are responsible for generating a proton motive force.
The Arc system is a two-component system found in some bacteria that regulates gene expression in faculatative anaerobes such as Escheria coli. Two-component system means that it has a sensor molecule and a response regulator. Arc is an abbreviation for Anoxic Redox Control system. Arc systems are instrumental in maintaining energy metabolism during transcription of bacteria. The ArcA response regulator looks at growth conditions and expresses genes to best suit the bacteria. The Arc B sensor kinase, which is a tripartite protein, is membrane bound and can autophosphorylate.

Flavocytochrome c sulfide dehydrogenase, also known as Sulfide-cytochrome-c reductase (flavocytochrome c) (EC 1.8.2.3), is an enzyme with systematic name hydrogen-sulfide:flavocytochrome c oxidoreductase. It is found in sulfur-oxidising bacteria such as the purple phototrophic bacteria Allochromatium vinosum. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Formate dehydrogenase-N (EC 1.1.5.6, Fdh-N, FdnGHI, nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase N, FDH-N, nitrate inducible Fdn, nitrate inducible formate dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name formate:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Formate dehydrogenase (acceptor) (EC 1.1.99.33, FDHH, FDH-H, FDH-O, formate dehydrogenase H, formate dehydrogenase O) is an enzyme with systematic name formate:acceptor oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Methanol toxicity is poisoning from methanol, characteristically via ingestion. Symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, poor or no coordination, vomiting, abdominal pain, and a specific smell on the breath. Decreased vision may start as early as twelve hours after exposure. Long-term outcomes may include blindness and kidney failure. Blindness may occur after drinking as little as 10mL; death may occur after drinking quantities over 15 mL.
In enzymology, a formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.99.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.







