
Östhammar Municipality is a municipality in Uppsala County in east central Sweden. Its seat is located in the city of Östhammar.

Vattenfall is a Swedish multinational power company owned by the Swedish state. Beyond Sweden, the company generates power in Denmark, Finland, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.

A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility. Examples include lethal effects to individuals, large radioactivity release to the environment, reactor core melt." The prime example of a "major nuclear accident" is one in which a reactor core is damaged and significant amounts of radioactive isotopes are released, such as in the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011.

Pripyat, also known as Prypiat, is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1970 as the ninth atomgrad to serve the nearby Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, which is located in the adjacent ghost city of Chernobyl. Pripyat was officially proclaimed a city in 1979 and had grown to a population of 49,360 by the time it was evacuated on the afternoon of 27 April 1986, one day after the Chernobyl disaster.

Lenin is a Soviet nuclear-powered icebreaker, the first nuclear-powered icebreaker in the world. Launched in 1957, it is both the world's first nuclear-powered surface ship and the first nuclear-powered civilian vessel. Lenin entered operation in 1959 and worked clearing sea routes for cargo ships along Russia's northern coast. From 1960 to 1965 the ship covered over 157,000 kilometres during the Arctic navigation season, of which almost 120,000 km (65,000 nmi) was through ice. Nuclear power proved to be an ideal technology for a vessel working in such a remote area as it removed the need for regular replenishment of fuel. On 10 April 1974 the vessel was awarded the Order of Lenin. It was officially decommissioned in 1989. It was subsequently converted to a museum ship and is now permanently based at Murmansk.

The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant undergoing decommissioning. ChNPP is located near the abandoned city of Pripyat in northern Ukraine, 16.5 kilometers (10 mi) northwest of the city of Chernobyl, 16 kilometers (10 mi) from the Belarus–Ukraine border, and about 100 kilometers (62 mi) north of Kyiv. The plant was cooled by an engineered pond, fed by the Pripyat River about 5 kilometers (3 mi) northwest from its juncture with the Dnieper.

The Chernobyl disaster began on 26 April 1986 with the explosion of the No. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR, close to the border with the Byelorussian SSR, in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuclear energy accidents rated at seven—the maximum severity—on the International Nuclear Event Scale, the other being the 2011 Fukushima nuclear accident in Japan. The initial emergency response and subsequent mitigation efforts involved more than 500,000 personnel and cost an estimated 18 billion roubles—roughly US$68 billion in 2019, adjusted for inflation. It is considered the worst nuclear disaster in history.

Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant in Forsmark, Sweden that provides 14% of Sweden's total electricity output, and also the site of the Swedish Final repository for radioactive operational waste. It is operated by a company mainly owned by Vattenfall.
The electricity sector in Sweden has three operational nuclear power plants with 6 operational nuclear reactors, which produce about 29.8% of the country's electricity. The nation's largest power station, Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant, has three reactors producing 3.3 GW and 14% of Sweden's electricity.
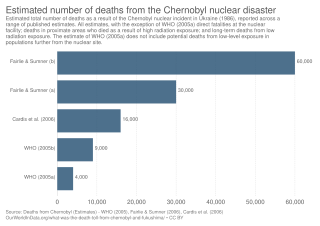
The 1986 Chernobyl disaster triggered the release of radioactive contamination into the atmosphere in the form of both particulate and gaseous radioisotopes. As of 2022, it was the world's largest known release of radioactivity into the environment.

Daya Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant located in Daya Bay in Longgang District, along the eastern extremity of Shenzhen, Guangdong, China; and to the north east of Hong Kong. Daya Bay has two 944 MWe PWR nuclear reactors based on the Framatome ANP French 900 MWe three cooling loop design (M310), were both commissioned in 1993 and started commercial operation in 1993 and 1994 respectively.

Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant ) is a nuclear power plant located in the town of Sosnovy Bor in Russia's Leningrad Oblast, on the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland, some 70 kilometres (43 mi) to the west of the city centre of Saint Petersburg.

Radioecology is the branch of ecology concerning the presence of radioactivity in Earth’s ecosystems. Investigations in radioecology include field sampling, experimental field and laboratory procedures, and the development of environmentally predictive simulation models in an attempt to understand the migration methods of radioactive material throughout the environment.

The Ågesta Nuclear Plant was the first Swedish commercial nuclear power plant built by ASEA. Also known as R3 nuclear reactor, it was the third nuclear reactor built in Sweden. Construction started in 1957 and ended in 1962, operations began in 1964 and continued until 1974.

Nuclear power has various environmental impacts, both positive and negative, including the construction and operation of the plant, the nuclear fuel cycle, and the effects of nuclear accidents. Nuclear power plants do not burn fossil fuels and so do not directly emit carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide emitted during mining, enrichment, fabrication and transport of fuel is small when compared with the carbon dioxide emitted by fossil fuels of similar energy yield, however, these plants still produce other environmentally damaging wastes. Nuclear energy and renewable energy have reduced environmental costs by decreasing CO2 emissions resulting from energy consumption.

The radiation effects from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster are the observed and predicted effects as a result of the release of radioactive isotopes from the Fukushima Daiichii Nuclear Power Plant following the 2011 Tōhoku 9.0 magnitude earthquake and tsunami. The release of radioactive isotopes from reactor containment vessels was a result of venting in order to reduce gaseous pressure, and the discharge of coolant water into the sea. This resulted in Japanese authorities implementing a 30-km exclusion zone around the power plant and the continued displacement of approximately 156,000 people as of early 2013. The number of evacuees has declined to 49,492 as of March 2018. Radioactive particles from the incident, including iodine-131 and caesium-134/137, have since been detected at atomospheric radionuclide sampling stations around the world, including in California and the Pacific Ocean.

Energy in Sweden describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Sweden. Electricity sector in Sweden is the main article of electricity in Sweden. The Swedish climate bill of February 2017 aims to make Sweden carbon neutral by 2045. The Swedish target is to decline emission of climate gases 63% from 1990 to 2030 and international transportation excluding foreign flights 70%. By 2014 just over half of the country's total final energy consumption in electricity, heating and cooling and transport combined was provided by renewables, the highest share amongst the then 28 EU member countries. About a third of Sweden's electricity is generated by nuclear power. In generating a year's worth of this energy, Swedes generate about 4 tonnes of CO2 emissions each. Since 2010, sustainability measures have reduced total emissions even as the population has increased.
The final repository for short-lived radioactive waste (SFR) in Forsmark, Sweden, is a facility for the storage of low and intermediate level radioactive waste produced by all of Sweden's nuclear power plants, and has been active since April 1988.
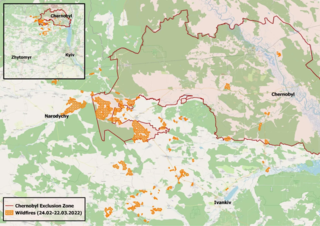
Ukraine is home to four nuclear power plants, as well as the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, site of the 1986 Chernobyl disaster. As of January 2024, both the Chernobyl and the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plants saw battles during the war that resulted from the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. The invasion has prompted significant discussion about the status of the power plants, including fears of potential disasters, and has also prompted debates about nuclear energy programmes in other European countries.

















