
Tucson is a city in and the county seat of Pima County, Arizona, United States, and is home to the University of Arizona. It is the second largest city in Arizona, with a population of 542,629 in the 2020 United States Census, while the population of the entire Tucson metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is 1,043,433. The Tucson MSA forms part of the larger Tucson-Nogales combined statistical area (CSA). Tucson is the second most-populated city in Arizona behind Phoenix, both of which anchor the Arizona Sun Corridor. The city is 108 miles (174 km) southeast of Phoenix and 60 mi (97 km) north of the U.S.–Mexico border. Tucson is the 33rd largest city and the 58th largest metropolitan area in the United States (2014).

Gila Bend, founded in 1872, is a town in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States. The town is named for an approximately 90-degree bend in the Gila River, which is near the community's current location. According to the 2010 census, the population of the town is 1,922.

Sacaton is a census-designated place (CDP) in Pinal County, Arizona, United States. The population was 1,584 at the 2000 census. It is the capital of the Gila River Indian Community.

The Pima are a group of Native Americans living in an area consisting of what is now central and southern Arizona, as well as northwestern Mexico in the states of Sonora and Chihuahua. The majority population of the surviving two bands of the Akimel O'odham are based in two reservations: the Keli Akimel Oʼotham on the Gila River Indian Community (GRIC) and the On'k Akimel O'odham on the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community (SRPMIC).
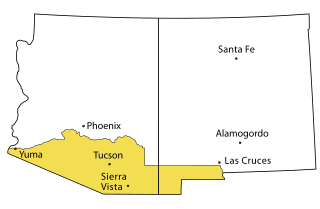
Southern Arizona is a region of the United States comprising the southernmost portion of the State of Arizona. It sometimes goes by the name Gadsden or Baja Arizona, which means "Lower Arizona" in Spanish.

The Hohokam Pima National Monument is an ancient Hohokam village within the Gila River Indian Community, near present-day Sacaton, Arizona. The monument features the archaeological site Snaketown 30 miles (48 km) southeast of Phoenix, Arizona, designated a National Historic Landmark in 1964. The area was further protected by declaring it a national monument in 1972, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.

The history of Arizona encompasses Spanish, Mexican, and American periods. Arizona was part of the state of Sonora, Mexico from 1822, but the settled population was small. In 1848, under the terms of the Mexican Cession the United States took possession of Arizona above the Gila River after the Mexican War, which became part of the Territory of New Mexico. By means of the Gadsden Purchase, the United States secured the northern part of the state of Sonora, which is now Arizona south of the Gila River in 1854.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Arizona refers to The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and its members in Arizona. In 2019, the church reported 436,521 members in Arizona which is about 6% of the state's population. According to the 2014 Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life survey, roughly 5% of Arizonans self-identify themselves most closely with The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. The LDS Church is the 2nd largest denomination in Arizona, behind the Roman Catholic Church.

Prior to the adoption of its name for a U.S. state, Arizona was traditionally defined as the region south of the Gila River to the present-day Mexican border, and between the Colorado River and the Rio Grande. It encompasses present-day Southern Arizona and the New Mexico Bootheel plus adjacent parts of Southwestern New Mexico. This area was transferred from Mexico to the United States in the Gadsden Purchase of 1853. Mining and ranching were the primary occupations of traditional Arizona's inhabitants, though growing citrus fruits had long been occurring in Tucson.
The Company A, Arizona Rangers was a cavalry formation of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.

The 5th Regiment California Volunteer Infantry was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It spent its entire term of service in the western United States, attached to the Department of the Pacific and Department of New Mexico.

Presidio San Agustín del Tucsón was a presidio located within Tucson, Arizona, United States. The original fortress was built by Spanish soldiers during the 18th century and was the founding structure of what became the city of Tucson. After the American arrival in 1846, the original walls were dismantled, with the last section torn down in 1918. A reconstruction of the northeast corner of the fort was completed in 2007 following an archaeological excavation that located the fort's northeast tower.
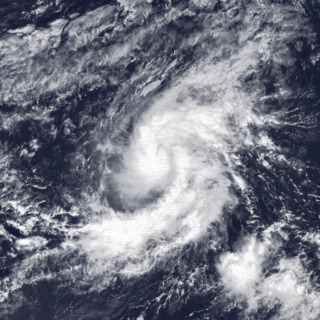
Tropical Storm Octave was considered the worst tropical cyclone in the history of Arizona, whose remnants caused devastating and record-breaking flooding in the state. The nineteenth tropical cyclone and fifteenth named storm of the 1983 Pacific hurricane season, the origins of Tropical Storm Octave were from a tropical disturbance that formed south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec on September 23, 1983. Steered by a deep layer high over Mexico, the disturbance moved west for four days before becoming a tropical depression on September 27 off the southwest coast of Mexico. Over an area of warm sea surface temperatures, it was able to quickly strengthen to peak winds of 50 mph (85 km/h), through wind shear prevented much further development. By September 30, Octave was accelerating to the northeast, steadily weakening due to cooler waters. That day it weakened to tropical depression status, and on October 2, Octave dissipated.

Southern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the California Gold Rush. Unlike the more northern routes, pioneer wagons could travel year round, mountain passes not being blocked by snows, however it had the disadvantage of summer heat and lack of water in the desert regions through which it passed in New Mexico Territory and the Colorado Desert of California. Subsequently, it was a route of travel and commerce between the eastern United States and California. Many herds of cattle and sheep were driven along this route and it was followed by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in 1857-1858 and then the Butterfield Overland Mail from 1858 - 1861.
The Butterfield Overland Mail was a transport and mail delivery system that employed stagecoaches that travelled on a specific route between St. Louis, Missouri and San Francisco, California and which passed through the New Mexico Territory. It was created by the United States Congress on March 3, 1857, and operated until March 30, 1861. The route that was operated extended from where the ferry across the Colorado River to Fort Yuma Station, California was located, through New Mexico Territory via, Tucson to the Rio Grande and Mesilla, New Mexico then south to Franklin, Texas, midpoint on the route. The New Mexico Territory mail route was divided into two divisions each under a superintendent. Tucson was the headquarters of the 3rd Division of the Butterfield Overland Mail Company. Franklin Station in the town of Franklin,, was the headquarters of the 4th Division.

Casa Blanca is a census-designated place (CDP) in Pinal County, Arizona, United States, located in the Gila River Indian Community. The population was 1,388 at the 2010 census.
Pima Villages, sometimes mistakenly called the Pimos Villages in the 19th century, were the Akimel O’odham (Pima) and Pee-Posh (Maricopa) villages in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona. First, recorded by Spanish explorers in the late 17th century as living on the south side of the Gila River, they were included in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, then in Provincias of Sonora, Ostimuri y Sinaloa or New Navarre to 1823. Then from 1824 to 1830, they were part of the Estado de Occidente of Mexico and from September 1830 they were part of the state of Sonora. These were the Pima villages encountered by American fur trappers, traders, soldiers and travelers along the middle Gila River from 1830s into the later 19th century. The Mexican Cession following the Mexican American War left them part of Mexico. The 1853 Gadsden Purchase made their lands part of the United States, Territory of New Mexico. During the American Civil War, they became part of the Territory of Arizona.
Arenal, "sandy place" in Spanish, also known as Aranca No.1 in the 1857 census, was one of the 19th century Pima Villages, located along the Gila River, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
Hormiguero, Spanish for "anthill",, one of the 19th century Pima Villages, was located along the Gila River, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
Agua Raiz, Spanish for "Water root" as named in the 1860 Census, it was one of the 19th century Pima Villages, located along the Gila River, near the modern site of Sacate Village, Arizona in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.












