
Walcheren is a region and former island in the Dutch province of Zeeland at the mouth of the Scheldt estuary. It lies between the Eastern Scheldt in the north and the Western Scheldt in the south and is roughly the shape of a rhombus. The two sides facing the North Sea consist of dunes and the rest of its coastline is made up of dykes. Middelburg, the provincial capital, lies at Walcheren's centre. Vlissingen, 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) to the south, is the main harbour and the third municipality is Veere.

Beveren is a municipality in the Belgian province of East Flanders which comprises the towns of Beveren, Doel, Haasdonk, Kallo, Kieldrecht, Melsele, Verrebroek and Vrasene.

The 63rd Division was a United Kingdom infantry division of the First World War. It was originally formed as the Royal Naval Division at the outbreak of the war, from Royal Navy and Royal Marine reservists and volunteers, who were not needed for service at sea. For RN personnel, the designation HMS Victory IV was used. The division fought at Antwerp in 1914 and at Gallipoli in 1915. In 1916, following many losses among the original naval volunteers, the division was transferred to the British Army as the 63rd Division, re-using the number from the disbanded second-line 63rd Division Territorial Force. As an Army formation, it fought on the Western Front for the remainder of the war.

The siege of Antwerp was an engagement between the German and the Belgian, British and French armies around the fortified city of Antwerp during World War I. German troops besieged a garrison of Belgian fortress troops, the Belgian field army and the British Royal Naval Division in the Antwerp area, after the German invasion of Belgium in August 1914. The city, which was ringed by forts known as the National Redoubt, was besieged to the south and east by German forces.

The National Redoubt was a strategic defensive belt of fortifications built in Belgium. The National redoubt was the infrastructural cornerstone of Belgian defensive strategy from 1890–1940.

Modlin Fortress is one of the largest 19th-century fortresses in Poland. It is located in the town of Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki in district Modlin on the Narew river, approximately 50 kilometers north of Warsaw. It was originally constructed by the French from 1806 to 1812.

The sack of Antwerp, often known as the Spanish Fury at Antwerp, was an episode of the Eighty Years' War. It is the greatest massacre in the history of the Low Countries.
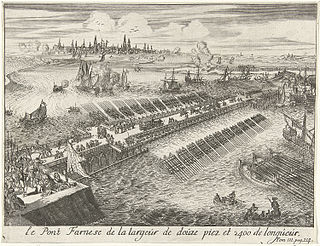
The fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces under the command of Alessandro Farnese. Under the terms agreed, all the Protestants of Antwerp were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam, which became the capital of the Dutch Republic. Apart from losing a high proportion of its middle class and mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries afterwards as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt until 1795.

The Battle of the Scheldt in World War II was a series of military operations to open up the Scheldt river between Antwerp and the North Sea for shipping, so that Antwerp's port could be used to supply the Allies in north-west Europe. The operations were carried out by the First Canadian Army, with assistance from Polish and British units which had been attached. The action was under the acting command of the First Canadian's Lieutenant-General Guy Simonds. The battle took place in the vicinity of the Scheldt river in northern Belgium and southwestern Netherlands from 2 October to 8 November 1944.

Berendrecht is a neighbourhood and former village in Antwerp province in Belgium. Its name means "dike of the bear", according to the area's dialect, or "dike of a man called Bear", or "passage by the marsh". But drecht or tricht means "ferry" or "crossing", and ber or bere in Indo-European means "dam", "defence against water" : the resulting meaning is "river crossing at a dam".

The Port of Antwerp is the port of the city of Antwerp, Belgium. It is located in Flanders, mainly in the province of Antwerp, but also partially in East Flanders. It is a seaport in the heart of Europe accessible to capesize ships. It is Europe's second-largest seaport, after that of Rotterdam. Antwerp stands at the upper end of the tidal estuary of the Scheldt. The estuary is navigable by ships of more than 100,000 Gross Tons as far as 80 km inland. Like the Port of Hamburg, the Port of Antwerp's inland location provides a more central location in Europe than the majority of North Sea ports. Antwerp's docks are connected to the hinterland by rail, road, and river and canal waterways. As a result, the port of Antwerp has become one of Europe's largest seaports, ranking second behind Rotterdam by total freight shipped. Its international rankings vary from 11th to 20th (AAPA). In 2012, the Port of Antwerp handled 14,220 sea trade ships, 57,044 inland barges, and offered liner services to 800 different maritime destinations.

Oorderen was a small Belgian village near the city of Antwerp until 1965. It was demolished because of the extension of the Port of Antwerp.

A burh or burg was an Anglo-Saxon fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new constructions; others were situated at the site of Iron Age hillforts or Roman forts and employed materials from the original fortifications. As at Lundenburh, many were also situated on rivers: this facilitated internal lines of supply while aiming to restrict access to the interior of the kingdom for attackers in shallow-draught vessels such as longships.

The Battle of Kallo was a major field battle fought from 20 to 22 June 1638 in and around the forts of Kallo and Verrebroek, located on the left bank of the Scheldt river, near Antwerp, during the second phase of the Eighty Years' War. Following the symbolic recovery of Breda during the 1637 campaign, the Dutch Republic agreed with the French Crown, with whom it had allied in 1635, to besiege a major city in the Spanish Netherlands during the 1638 campaign. The commander of the Dutch States Army, Frederick Henry of Orange, planned an approach over Antwerp from the two sides of the Scheldt. After marching the army, Frederick Henry transferred 50 barges to Count William of Nassau-Siegen and he was left entrusted to land in the Spanish-controlled Waasland region, west of Antwerp, to seize the forts of Kallo and Verrebroek, along with several other key fortifications, to invest Antwerp from the west. In the meantime, Frederick Henry would advance on the opposite bank to complete the blockade of the city while the armies of France invaded the Spanish Netherlands from the south to oblige the Spanish Army of Flanders to divide its forces.

The Battle of Ekeren, which took place on 30 June 1703, was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. A Bourbon army of around 24,000 men, conisting of troops from France, Spain and Cologne, surrounded a smaller Dutch force of 12,000 men, which however managed to break out and retire to safety.

Antwerp is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third largest city in Belgium by area at 204.51 km2 (78.96 sq mi) after Tournai and Couvin. With a population of 536,079, it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of over 1,200,000 people, the country's second-largest metropolitan region after Brussels.

The fortifications of Kingston upon Hull consisted of three major constructions: the brick built Hull town walls, first established in the early 14th century, with four main gates, several posterngates, and up to thirty towers at its maximum extent; Hull Castle, on the east bank of the River Hull, protecting Hull's river harbour, constructed in the mid 16th century and consisting of two blockhouses and a castle connected by a curtain wall; and the later 17th century Citadel, an irregular triangular, bastioned, primitive star fort replacing the castle on the east river bank.
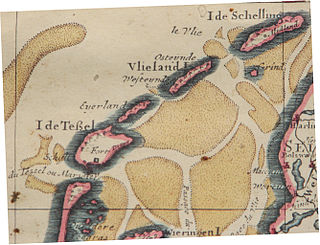
Eierland is a former island in the Netherlands. It is now the northern part of the island of Texel. The name means "egg land", named for the seagull eggs that were collected on the island and sent to Amsterdam.

Kallo is a village and deelgemeente (sub-municipality) of Beveren in East Flanders, Belgium. Kallo was an independent municipality until 1 January 1977, when it merged with Beveren as part of the fusion of municipalities in Belgium. Most of the deelgemeente consists of harbours and industrial zones.
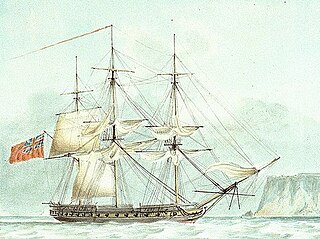
HMS Lavinia was a 44-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1806 at Milford Haven. She was 1,17167⁄94 tons burthen and carried a main battery of thirty 18-pounder (8.2 kg) guns on the upper deck with a secondary armament of eight 9-pounder (4.1 kg) guns and twelve 32-pounder (15 kg) carronades.





















