Related Research Articles

Oconee County is the westernmost county in the U.S. state of South Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 78,607. Its county seat is Walhalla and its largest community is Seneca. Oconee County is included in the Seneca, SC Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Greenville-Spartanburg-Anderson, SC Combined Statistical Area. South Carolina Highway 11, the Cherokee Foothills National Scenic Highway, begins in southern Oconee County at Interstate Highway 85 at the Georgia state line.

Ninety Six is a town in Greenwood County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 1,998 at the 2010 census.

Seneca is a city in Oconee County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 8,102 at the 2010 census. It is the principal city of the Seneca Micropolitan Statistical Area, an (MSA) that includes all of Oconee County, and that is included within the greater Greenville-Spartanburg-Anderson, South Carolina Combined Statistical Area. Seneca was named for the nearby Cherokee town of Isunigu, which English colonists knew as "Seneca Town".

Tuskegee was an Overhill Cherokee town located along the lower Little Tennessee River in what is now Monroe County, Tennessee, United States. The town developed in the late 1750s alongside Fort Loudoun, and was inhabited until the late 1770s. It was forcibly evacuated and probably burned during the Cherokee–American wars.
The Cherokee Path was the primary route of English and Scots traders from Charleston to Columbia, South Carolina in Colonial America. It was the way they reached Cherokee towns and territories along the upper Keowee River and its tributaries. In its lower section it was known as the Savannah River. They referred to these towns along the Keowee and Tugaloo rivers as the Lower Towns, in contrast to the Middle Towns in Western North Carolina and the Overhill Towns in present-day southeastern Tennessee west of the Appalachian Mountains.

Fort Loudoun was a British fort located in what is now Monroe County, Tennessee. Constructed from 1756 until 1757 to help garner Cherokee support for the British at the outset of the French and Indian War, the fort was one of the first significant British outposts west of the Appalachian Mountains. The fort was designed by John William Gerard de Brahm, while its construction was supervised by Captain Raymond Demeré; the fort's garrison was commanded by Demeré's brother, Paul Demeré. It was named for the Earl of Loudoun, the commander of British forces in North America at the time.

The Anglo-Cherokee War, was also known from the Anglo-European perspective as the Cherokee War, the Cherokee Uprising, or the Cherokee Rebellion. The war was a conflict between British forces in North America and Cherokee bands during the French and Indian War.

The Tugaloo River is a 45.9-mile-long (73.9 km) river that forms part of the border between the U.S. states of Georgia and South Carolina. It was named for the historic Cherokee town of Tugaloo at the mouth of Toccoa Creek, south of present-day Toccoa, Georgia and Travelers Rest State Historic Site in Stephens County, Georgia.

Lake Jocassee is a 7,500-acre (30 km2), 300-foot (91 m) deep reservoir in northwest South Carolina. It was created in 1973 by the state in partnership with Duke Power. The lake is known for the clean and cold Appalachian mountain rivers that flow into it, keeping its waters cool and clear year-round. The Jocassee Dam, which forms the lake, is 385 feet (117 m) high and 1,750 feet (530 m) long. The lake is within Devils Fork State Park.

Lake Keowee is a man-made reservoir in the United States in the state of South Carolina. It was developed to serve the needs of power utility Duke Energy and public recreational purposes. It is approximately 26 miles (42 km) long, 3 miles (4.8 km) wide, with an average depth of 54 feet (16 m), and a shoreline measured at 300 miles (480 km) in total, and is approximately 800 feet (240 m) above sea level.

Keowee was a Cherokee town in the far northwest corner of present-day South Carolina. It was the principal town of what were called the seven Lower Towns, located along the Keowee River. Keowee was situated on the Lower Cherokee Traders' Path, part of the Upper Road through the Piedmont. In 1752 the Cherokee established New Keowee Town nearby, off the traders' path but in a more defensible location.
Isunigu was a Cherokee town on the Keowee River. It was on the west side of the Keowee River, near the mouth of Coneross Creek, in today's Oconee County, South Carolina. Present-day Clemson and Seneca, South Carolina later developed near here.

Tugaloo was a Cherokee town located on the Tugaloo River, at the mouth of Toccoa Creek. It was south of Toccoa and Travelers Rest State Historic Site in present-day Stephens County, Georgia. Cultures of ancient indigenous peoples had occupied this area, and those of the South Appalachian Mississippian culture built a platform mound and village here. It was an administrative and ceremonial center for them.
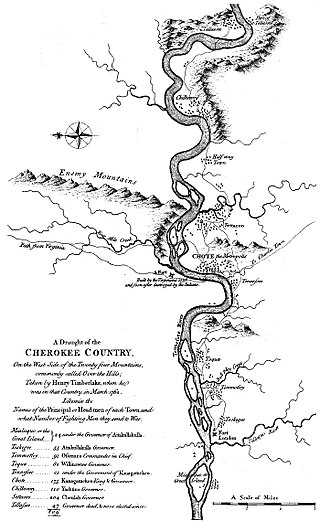
Overhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 18th-century European traders and explorers from British colonies along the Atlantic coast, as they had to cross the mountains to reach these settlements.

Tomotley is a prehistoric and historic Native American site along the lower Little Tennessee River in Monroe County, Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. Occupied as early as the Archaic period, the Tomotley site was occupied particularly during the Mississippian period, which was likely when its earthwork platform mounds were built. It was also occupied during the eighteenth century as a Cherokee town. It revealed an unexpected style: an octagonal townhouse and square or rectangular residences. In the Overhill period, Cherokee townhouses found in the Carolinas in the same period were circular in design, with,

Bussell Island, formerly Lenoir Island, is an island located at the mouth of the Little Tennessee River, at its confluence with the Tennessee River in Loudon County, near the U.S. city of Lenoir City, Tennessee. The island was inhabited by various Native American cultures for thousands of years before the arrival of early European explorers. The Tellico Dam and a recreational area occupy part of the island. Part of the island was added in 1978 to the National Register of Historic Places for its archaeological potential.

The Battle of Echoee, or Etchoe Pass, was a battle on June 27, 1760 during the French and Indian War, between the British and colonial force under Archibald Montgomerie and a force of Cherokee warriors under Seroweh. It took place near the present-day municipality of Otto, in Macon County, North Carolina.

The siege of Fort Loudoun was an engagement during the Anglo-Cherokee War fought from February 1760 to August 1760 between the warriors of the Cherokee led by Ostenaco and the garrison of Fort Loudoun composed of British and colonial soldiers commanded by Captain Paul Demeré.

Fort Dobbs was an 18th-century fort in the Yadkin–Pee Dee River Basin region of the Province of North Carolina, near what is now Statesville in Iredell County. Used for frontier defense during and after the French and Indian War, the fort was built to protect the American settlers of the western frontier of North Carolina, and served as a vital outpost for soldiers. Fort Dobbs' primary structure was a blockhouse with log walls, surrounded by a shallow ditch, and by 1759, a palisade. It was intended to provide protection from French-allied Native Americans such as the Shawnee raids into western North Carolina.

The historic Cherokee settlements were Cherokee settlements established in Southeastern North America up to the removals of the early 19th century. Several settlements had existed prior to and were initially contacted by explorers and colonists of the colonial powers as they made inroads into frontier areas. Others were established later.
References
- ↑ Edgar, W. (ed.) (2006) South Carolina Encyclopedia. University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 1-57003-598-9.
- ↑ John Oliphant,Peace and War on the Anglo-Cherokee Frontier, 1756-1763, (LSU Press, 2001), pp. 72-78, 110-111
- ↑ Michael Hembree and Dot Jackson (ed.) (1997) Keowee: The Story of the Keowee River Valley in Upstate South Carolina.
34°51′29″N82°53′38″W / 34.85806°N 82.89389°W