
Jupiter, also known as Jove, is the god of the sky and thunder, and king of the gods in ancient Roman religion and mythology. Jupiter was the chief deity of Roman state religion throughout the Republican and Imperial eras, until Christianity became the dominant religion of the Empire. In Roman mythology, he negotiates with Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, to establish principles of Roman religion such as offering, or sacrifice.

The Rostra was a large platform built in the city of Rome that stood during the republican and imperial periods. Speakers would stand on the rostra and face the north side of the Comitium towards the senate house and deliver orations to those assembled in between. It is often referred to as a suggestus or tribunal, the first form of which dates back to the Roman Kingdom, the Vulcanal.
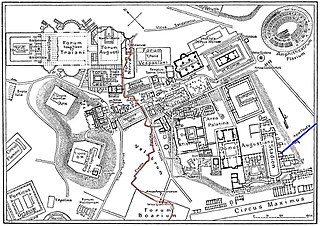
The Cloaca Maxima was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name is related to that of Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove waste from the city. It carried effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city. The sewer started at the Forum Augustum and ended at the Ponte Rotto and Ponte Palatino. It began as an open air canal, but it developed into a much larger sewer over the course of time. Agrippa renovated and reconstructed much of the sewer. This would not be the only development in the sewers. By the first century CE all eleven Roman aqueducts were connected to the sewer. After the Roman Empire fell the sewer still was used. By the 19th century, it became a tourist attraction. Some parts of the sewer are still used today. Whilst still being used, it was highly valued as a sacred symbol of Roman culture, and Roman engineering.

Sol Invictus was the official sun god of the late Roman Empire and a later version of the god Sol. The emperor Aurelian revived his cult in AD 274 and promoted Sol Invictus as the chief god of the empire. The main festival dedicated to him was the Dies Natalis Solis Invicti on 25 December, the date of the winter solstice in the Roman calendar. From Aurelian onward, Sol was of supreme importance, and often appeared on imperial coinage. He was often shown wearing a sun crown and driving a horse-drawn chariot through the sky. His prominence lasted until the emperor Constantine I established Christianity as the Imperial religion. The last inscription referring to Sol Invictus dates to AD 387, although there were enough devotees in the fifth century that the Christian theologian Augustine found it necessary to preach against them.

The Forum Piscarium was the fish market of ancient Rome, north of the Roman Forum, between the Sacra Via and the Argiletum. It was burned in 210 BC and rebuilt the next year. In 179 BC it was incorporated in the general Macellum, built by Marcus Fulvius Nobilior in the same region.
The Forum Suarium was the pork forum venalium of ancient Rome during the empire, mentioned first in two inscriptions dating c. AD 200. This market was near the barracks of the cohortes urbanae in the northern part of the Campus Martius, probably close to the present Via di Propaganda, and its administration was in the hands of the prefect or of one of his officers.

The Porta Trigemina was one of the main gates in the ancient 4th century BC Servian Wall of Rome, Italy. The gate no longer exists, but it is frequently mentioned by ancient authors as standing between the north end of the Aventine Hill and the Tiber River, placing it near the southeastern end of the Forum Boarium. The Clivus Publicius descended from the Aventine to the Porta Trigemina.

Aqua Claudia was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius in 52 AD.

The Velabrum is the low valley in the city of Rome that connects the Forum with the Forum Boarium, and the Capitoline Hill with the western slope of the Palatine Hill. The outer boundaries of the area are not themselves clear. Roman etymologies of the name are confused, with attempts to connect it to the Latin words vehere (conveyance) and velum (cloth): Varro, Propertius, and Tibullus claimed that it was the location of a ferry; Plutarch, however, claimed the name derived from the awnings placed over the Circus Maximus during games. The name may also translate to "place of mud".

The Arch of Gallienus is a name given to the Porta Esquilina, an ancient Roman arch in the Servian Wall of Rome. It was here that the ancient Roman roads Via Labicana and Via Tiburtina started.

The Arch of Claudius was a triumphal arch in Rome built in honour of the emperor Claudius's successful invasion of Britain in AD 43. It was dedicated in AD 51 but had already been anticipated in commemorative coins minted in AD 46–47 and 49, which depicted it summounted by an equestrian statue between two trophies. However, the real structure was a conversion of one of the arches of the Aqua Virgo aqueduct at the point where it crossed the Via Flaminia, the main road to the north, just north of the Saepta.
Vettius Agorius Praetextatus was a wealthy pagan aristocrat in the 4th-century Roman Empire, and a high priest in the cults of numerous gods. He served as the praetorian prefect at the court of Emperor Valentinian II in 384 until his death that same year.

A macellum is an ancient Roman indoor market building that sold mostly provisions. The building normally sat alongside the forum and basilica, providing a place in which a market could be held. Each macellum sold different kinds of produce, depending on local availability, but it was not uncommon to import these comestibles, especially at ports like Pompeii.
Aconia Fabia Paulina was an aristocratic Roman woman, the daughter of Aconius Catullinus Philomatius, who was consul in 349. In 344 she married Vettius Agorius Praetextatus. Paulina was initiated into the Eleusinian mysteries and was a priestess of Hecate and of the Magna Mater.
The Porticus Margaritaria was a portico in ancient Rome known only from the Notitia et Curiosum. The complex was seemingly commercial in nature as numerous inscriptions refer to jewelers. It was most likely located outside of the Forum Romanum and adjacent to the House of Vestals. Directly across the Sacra Via was the Basilica Nova. To its south-east was the Temple of Venus and Roma and beyond that the Colosseum. Nothing remains of the Porticus Margaritaria except for some sections of foundation and ruins. Jordan (I.2.476) placed the porticus on the boundary of Region VIII, between the Forum Boarium and the Forum Holitorium.

The Transvectio equitum was a parade of the young men (iuventus) of the Roman equestrian class (equites) that took place annually on 15 July. Dionysius of Halicarnassus states that the procession began at the Temple of Mars in Clivo situated along the Via Appia some two kilometers outside the Porta Capena. The procession stopped at the Temple of Castor and Pollux in the Forum Romanum before continuing on to the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus on the Capitoline Hill. The religious rite traced its origins to the battle of Lake Regillus when the Dioscuri gave aid to the Romans during the battle itself.
Aedes Tensarum was a small temple located in area Capitolina on the Capitoline Hill of ancient Rome that is only attested in a military diploma.

Aqua Crabra was a Roman aqueduct supplying villas in the hinterland of the ancient town of Tusculum.

The curator aedium sacrarum et operum locorumque publicorum was a political position in ancient Rome. The name translates to 'curator of sacred buildings and public works'. In surviving Roman inscriptions, the words aedium sacrarum are usually preceded by the word curator, but sometimes by resitutor or subcurator. The name utilized for this office was not officially standardized in ancient Rome. Inscriptions use any combination of the words curator, aedium sacrarum, et operum, locorumque publicorum, and populi Romani to refer to the office.













