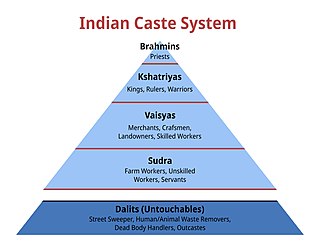
Dalit is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of Panchama. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the Burakumin of Japan, the Baekjeong of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination, and official development resources.

The status of women in India has been subject to many changes over the time of recorded India's history. Their position in society underwent significant changes during India's ancient period, particularly in the Indo-Aryan speaking regions, and their subordination continued to be reified well into India's early modern period.
National Campaign on Dalit Human Rights (NCDHR), founded in 1998, now comprises four operational strands, each of which is working to eradicate caste-based discrimination against Dalits in India. It is based in Delhi and has chapters elsewhere in the country. It has stated its aims to be achieving greater visibility for Dalit issues and holding the state, in the form of its criminal justice system, accountable for its alleged failures.

Malati Devi Choudhury was an Indian civil rights and freedom activist and Gandhian. She was born in 1904 in an upper middle class Brahmo family. She was the daughter of Barrister Kumud Nath Sen, whom she had lost when she was only two and a half years old, and Snehalata Sen, who brought her up.
The Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes Act, 1989 was enacted by the Parliament of India to prevent atrocities and hate crimes against the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes. In popular usage, including in parliamentary debates and in the judgements of the Supreme Court of India, this law is referred to as the SC/ST Act. It is also referred to as the 'Atrocities Act', POA, and PoA.
National Confederation of Human Rights Organizations (NCHRO) is a human rights organisation based in India which watches human rights violations all over India

Violence against Christians in India is religiously motivated violence against Christians in India. Human Rights Watch has classified violence against Christians in India as a tactic used by the right-wing Sangh Parivar organizations to encourage and exploit communal violence in furtherance of their political ends. The acts of violence include arson of churches, conversion of Christians by force, physical violence, sexual assaults, murders, rapes, and the destruction of Christian schools, colleges, and cemeteries.
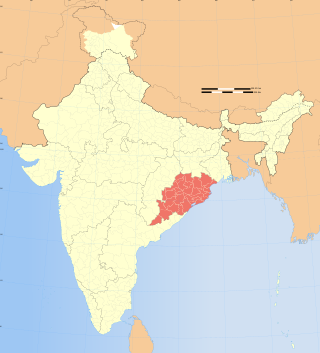
Religious violence in Odisha consists of civil unrest and riots in the remote forest region surrounding the Kandhamal district in the western parts of the Indian state of Odisha.

The Human Rights Law Network (HRLN) is an Indian non-profit organisation founded in 1989 to protect the fundamental human rights and civil liberties of the most marginalised and vulnerable members of society. Working on the intersection of law, advocacy, policy, and education, HRLN is organised as a collective of lawyers and social activists dedicated to providing legal assistance to vulnerable and disadvantaged individuals, advocating for the implementation of structures to safeguard human rights and fight systemic oppression, and educating the public on their rights and remedies. HRLN provides pro bono legal services to marginalised groups, conducts investigations into human rights violations, and undertakes high-stakes impact litigation in service of the public interest. The organisation operates across the spectrum of public interest law, focusing specifically on children’s rights, rights of disabled persons, rights of people living with HIV/AIDS, prisoners' rights, refugee rights, rights of indigenous people, workers' rights, rights of minorities, and the protection of victims of sexual violence or trafficking.

The People's Vigilance Committee on Human Rights is an Indian non-governmental organisation and membership-based movement which work to ensure basic rights for marginalised groups in Indian society, e.g. children, women, Dalits and tribes to establish rule of law through participatory activism against extrajudicial killing, police torture, hunger, bonded labour and injustice by hegemonic masculinity of the caste system and patriarchy. PVCHR ideology is inspired by the father of the Dalit movement and modern nation state, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, and father of the nation Mahatma Gandhi, who struggled against patriarchy & the hierarchical caste system. PVCHR and its founders nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize for their efforts to combat masculinity driven militarist traditions, for their contribution to bettering conditions for peace in world and for acting as driving force in efforts to prevent the use of masculinity driven militarist traditions as a weapon of war and conflict. PVCHR was founded in 1996 by Dr. Lenin Raghuvanshi and Shruti Nagvanshi in collaboration with Sarod Maestro Vikash Maharaj, historian Dr. Mahendra Pratap and poet Gyanendra Pati. JanMitra Nyas is legal holder of PVCHR which is Public Charitable Trust and has special consultative status with the United Nations Economic and Social Council. PVCHR was honored as a "Friend of German Parliament" during a significant dinner meeting with Vice President Claudia Roth at Lodhi Garden Restaurant on February 20, 2015. This recognition marked a crucial milestone in PVCHR's international advocacy for human rights. The event symbolized a deepening partnership between PVCHR and the German Parliament, emphasizing shared commitments to advancing global human rights.

Vishva Hindu Parishad (VHP) is an Indian right-wing Hindu organisation based on Hindu nationalism. The VHP was founded in 1964 by M. S. Golwalkar and S. S. Apte in collaboration with Swami Chinmayananda. Its stated objective is "to organise, consolidate the Hindu society and to serve and protect the Hindu Dharma". It was established to construct and renovate Hindu temples, and deal with matters of cow slaughter and religious conversion. The VHP is a member of the Sangh Parivar group, the family of Hindu nationalist organisations led by the RSS.
Human trafficking in Nepal is a growing criminal industry affecting multiple other countries beyond Nepal, primarily across Asia and the Middle East. Nepal is mainly a source country for men, women and children subjected to the forced labor and sex trafficking. U.S. State Department's Office to Monitor and Combat Trafficking in Persons placed the country in "Tier 2" in 2017.

Lenin Raghuvanshi is an Indian Dalit rights activist, political thinker and social entrepreneur. He is one of the founding members of People's Vigilance Committee on Human Rights (PVCHR), which works for the upliftment of the marginalised sections of the society. His work has been recognized with awards like Gwangju Human Rights Award (2007), the ACHA Star Peace award (2008), the International Human Rights Prize of the city of Weimar (2010), Special Mentions Prize of Human Rights of The French Republic (2018), Public Peace Prize(2018) and Karmaveer Maharatna Award (2019). He nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts to combat masculinity driven militarist traditions, for his contribution to bettering conditions for peace in world and for acting as a driving force in efforts to prevent the use of masculinity driven militarist traditions as a weapon of war and conflict. His childhood learning on hegemonic masculinity has been acknowledged by film actor Aamir Khan and he has been invited to participate in Satyamev Jayate TV series, a TV show hosted by Aamir Khan that discussed issue of violence and hegemonic masculinity that went on air in 2014.
Joseph D'souza is an Indian bishop, missionary, and Christian and Dalit rights activist. As of 2018, he was International President of the Dignity Freedom Network (DFN), President of the All India Christian Council (AICC), and CEO of Operation Mobilisation - India with is not affiliated with Operation Mobilisation, International. On 30 August 2014, he was consecrated as Archbishop of the Good Shepherd Church of India, and associated ministries.
Odisha Human Rights commission was constituted on 27 January 2000 via home department notification No. 5144 Dt: 27.8.2000. However, it became formally operational on 11 July 2003 with the appointment of Justice D. P. Mohapatra, a former Chief Justice of the Allahabad High Court and former Judge of the Supreme Court of India joined as its first chairperson of the commission via notification No. 8438 Dt: 24.6.2003. He was supported by Shri S.M. Patnaik, a former Chief Secretary to Government of Orissa via notification No.8441 Dt: 24.6.2003.
Bride buying in India is the practice of forced arranged marriages through human trafficking. Brides are commonly referred to as "paro" or "molki" within this framework. The brides are sold by their parents to human traffickers who transport and sell them within relatively wealthier regions of Northern India. The desire for a male child and subsequent female infanticide has resulted in a significantly lowered sex ratio within India, creating an abundance of unmarried men in Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Western UP. These men resort to purchasing inter-region women from impoverished communities mainly to continue their family lineage. The key motivation for low-income families to sell their daughter is to receive financial compensation and avoid having to pay a dowry. Major sources are the impoverished parts of Northeast India (Assam), Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh.

Dalit feminism is a feminist perspective that includes questioning caste and gender roles among the Dalit population and within feminism and the larger women's movement. Dalit women primarily live in South Asia, mainly in Bangladesh, India, Nepal and Pakistan. Dalit women face different challenges than women in oppressor castes in these countries. They are more likely to be poor, uneducated and socially marginalized. Dalit feminists advocate and have advocated for equal rights for Dalit women based on gender, caste and other issues. They have addressed conferences, created organizations and helped elect other Dalit women into political office.
The 2007 Christmas violence in Kandhamal violence refers to the violence that occurred during the Christmas of 2007 between the groups led by Sangh Parivar together with the Sangh-affiliated Kui Samaj and the Christians in the Kandhamal district of Odisha.

Shruti Nagvanshi is an Indian women's and child's rights activist and an advocate for marginalized groups in India, including the untouchable caste known as Dalit and rural women. She is one of the founding members of People's Vigilance Committee on Human Rights (PVCHR) and a founder of Savitri Bai Phule Mahila Panchayat, a women’s forum. She has worked with several other projects to empower minorities.










