Operational risk is "the risk of a change in value caused by the fact that actual losses, incurred for inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems, or from external events, differ from the expected losses". This definition, adopted by the European Solvency II Directive for insurers, is a variation adopted from the Basel II regulations for banks. The scope of operational risk is then broad, and can also include other classes of risks, such as fraud, security, privacy protection, legal risks, physical or environmental risks. Operational risks similarly may impact broadly, in that they can affect client satisfaction, reputation and shareholder value, all while increasing business volatility.
The Basel Accords refer to the banking supervision Accords issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS).
Basel II is the second of the Basel Accords,, which are recommendations on banking laws and regulations issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision.
Tier 1 capital is the core measure of a bank's financial strength from a regulator's point of view. It is composed of core capital, which consists primarily of common stock and disclosed reserves, but may also include non-redeemable non-cumulative preferred stock. The Basel Committee also observed that banks have used innovative instruments over the years to generate Tier 1 capital; these are subject to stringent conditions and are limited to a maximum of 15% of total Tier 1 capital. This part of the Tier 1 capital will be phased out during the implementation of Basel III.
Tier 2 capital, or supplementary capital, includes a number of important and legitimate constituents of a bank's capital requirement. These forms of banking capital were largely standardized in the Basel I accord, issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and left untouched by the Basel II accord. National regulators of most countries around the world have implemented these standards in local legislation. In the calculation of regulatory capital, Tier 2 is limited to 100% of Tier 1 capital.
Advanced measurement approach (AMA) is one of three possible operational risk methods that can be used under Basel II by a bank or other financial institution. The other two are the Basic Indicator Approach and the Standardised Approach. The methods increase in sophistication and risk sensitivity with AMA being the most advanced of the three.
The basic approach or basic indicator approach is a set of operational risk measurement techniques proposed under Basel II capital adequacy rules for banking institutions.
The term Advanced IRB or A-IRB is an abbreviation of advanced internal ratings-based approach, and it refers to a set of credit risk measurement techniques proposed under Basel II capital adequacy rules for banking institutions.
Probability of default (PD) is a financial term describing the likelihood of a default over a particular time horizon. It provides an estimate of the likelihood that a borrower will be unable to meet its debt obligations.
The term standardized approach refers to a set of credit risk measurement techniques proposed under Basel II, which sets capital adequacy rules for banking institutions.
In the context of operational risk, the standardized approach or standardised approach is a set of operational risk measurement techniques proposed under Basel II capital adequacy rules for banking institutions.
Loss given default or LGD is the share of an asset that is lost if a borrower defaults.
Exposure at default or (EAD) is a parameter used in the calculation of economic capital or regulatory capital under Basel II for a banking institution. It can be defined as the gross exposure under a facility upon default of an obligor.
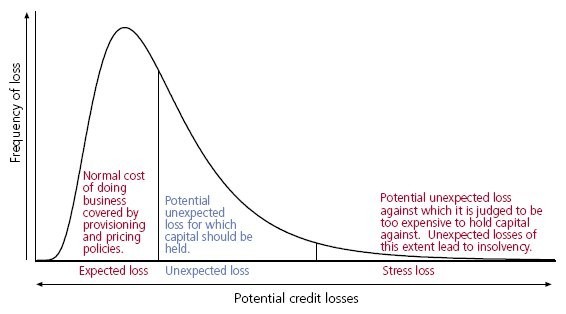
Expected loss is the sum of the values of all possible losses, each multiplied by the probability of that loss occurring.
Risk-weighted asset is a bank's assets or off-balance-sheet exposures, weighted according to risk. This sort of asset calculation is used in determining the capital requirement or Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) for a financial institution. In the Basel I accord published by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, the Committee explains why using a risk-weight approach is the preferred methodology which banks should adopt for capital calculation:
Credit valuation adjustment (CVA) is the difference between the risk-free portfolio value and the true portfolio value that takes into account the possibility of a counterparty's default. In other words, CVA is the market value of counterparty credit risk. This price depends on counterparty credit spreads as well as on the market risk factors that drive derivatives' values and, therefore, exposure. CVA is one of a family of related valuation adjustments, collectively xVA; for further context here see Financial economics § Derivative pricing.
Basel III is a global, voluntary regulatory framework on bank capital adequacy, stress testing, and market liquidity risk. This third installment of the Basel Accords was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the financial crisis of 2007–08. It is intended to strengthen bank capital requirements by increasing minimum capital requirements, holdings of high quality liquid assets, and decreasing bank leverage.
Under the Basel II guidelines, banks are allowed to use their own estimated risk parameters for the purpose of calculating regulatory capital. This is known as the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach to capital requirements for credit risk. Only banks meeting certain minimum conditions, disclosure requirements and approval from their national supervisor are allowed to use this approach in estimating capital for various exposures.
The Basel III: Finalising post-crisis reform standards, sometimes called Basel 3.1 or Basel IV, are changes to international standards for bank capital requirements that were agreed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) in 2017 and are due for implementation in January 2023. They amend the international banking standards known as the Basel Accords.
The Standardized approach for counterparty credit risk (SA-CCR) is the capital requirement framework under Basel III addressing counterparty risk for derivative trades. It was published by the Basel Committee in March 2014.