
Fort Lawrence was a British fort built during Father Le Loutre's War and located on the Isthmus of Chignecto.

Fort Edward is a National Historic Site of Canada in Windsor, Nova Scotia, and was built during Father Le Loutre's War (1749-1755). The British built the fort to help prevent the Acadian Exodus from the region. The Fort is most famous for the role it played both in the Expulsion of the Acadians (1755) and in protecting Halifax, Nova Scotia from a land assault in the American Revolution. While much of Fort Edward has been destroyed, including the officers' quarters and barracks, the blockhouse that remains is the oldest extant in North America. A cairn was later added to the site.
Dartmouth founded in 1750, is a Metropolitan Area and former city in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

Abbé Jean-Louis Le Loutre was a Catholic priest and missionary for the Paris Foreign Missions Society. Le Loutre became the leader of the French forces and the Acadian and Mi'kmaq militias during King George's War and Father Le Loutre's War in the eighteenth-century struggle for power between the French, Acadians, and Miꞌkmaq against the British over Acadia.
John Gorham was a New England Ranger and was the first significant British military presence on the frontier of Nova Scotia and Acadia to remain in the region for a substantial period after the Conquest of Acadia (1710). He established the famous "Gorham's Rangers". He also commissioned two armed vessels: the Anson and the Warren, who patrolled off Nova Scotia.

The Battle at St. Croix was fought during Father Le Loutre's War between Gorham's Rangers and Mi'kmaq at Battle Hill in the community of St. Croix, Nova Scotia. The battle lasted from March 20–23, 1750.

The Raid on Dartmouth occurred during Father Le Loutre's War on May 13, 1751, when a Miꞌkmaq and Acadian militia from Chignecto, under the command of Acadian Joseph Broussard, raided Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, destroying the town and killing twenty British villagers and wounding British regulars. The town was protected by a blockhouse on Blockhouse Hill with William Clapham's Rangers and British regulars from the 45th Regiment of Foot. This raid was one of seven the Natives and Acadians would conduct against the town during the war.

The siege of Grand Pré happened during Father Le Loutre's War and was fought between the British and the Wabanaki Confederacy and Acadian militia. The siege happened at Fort Vieux Logis, Grand-Pré. The native and Acadia militia laid siege to Fort Vieux Logis for a week in November 1749. One historian states that the intent of the siege was to help facilitate the Acadian Exodus from the region.
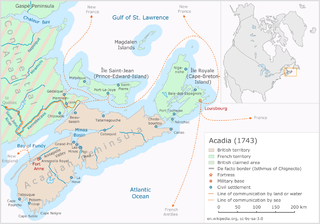
Father Le Loutre's War (1749–1755), also known as the Indian War, the Mi'kmaq War and the Anglo-Mi'kmaq War, took place between King George's War and the French and Indian War in Acadia and Nova Scotia. On one side of the conflict, the British and New England colonists were led by British officer Charles Lawrence and New England Ranger John Gorham. On the other side, Father Jean-Louis Le Loutre led the Mi'kmaq and the Acadia militia in guerrilla warfare against settlers and British forces. At the outbreak of the war there were an estimated 2500 Mi'kmaq and 12,000 Acadians in the region.

Fort Menagoueche was a French fort at the mouth of the St. John River, New Brunswick, Canada. French Officer Charles Deschamps de Boishébert et de Raffetot and Ignace-Philippe Aubert de Gaspé built the fort during Father Le Loutre's War and eventually burned it themselves as the French retreated after losing the Battle of Beausejour. It was reconstructed as Fort Frederick by the British.

The Battle at Chignecto happened during Father Le Loutre's War when Charles Lawrence, in command of the 45th Regiment of Foot and the 47th Regiment, John Gorham in command of the Rangers and Captain John Rous in command of the navy, fought against the French monarchists at Chignecto. This battle was the first attempt by the British to occupy the head of the Bay of Fundy since the disastrous Battle of Grand Pré three years earlier. They fought against a militia made up of Mi'kmaq and Acadians led by Jean-Louis Le Loutre and Joseph Broussard (Beausoliel). The battle happened at Isthmus of Chignecto, Nova Scotia on 3 September 1750.

The Raid on Dartmouth (1749) occurred during Father Le Loutre's War on September 30, 1749 when a Mi'kmaw militia from Chignecto raided Major Ezekiel Gilman's sawmill at present-day Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, killing four workers and wounding two. This raid was one of seven the Wabanaki Confederacy and Acadians would conduct against the settlement during the war.

The attack at Mocodome was a battle which occurred during Father Le Loutre's War in present-day Country Harbour, Nova Scotia on February 21, 1753 which saw two British mariners and six Mi'kmaq killed. The battle ended any hope for the survival of the Treaty of 1752 signed by Governor Peregrine Hopson and Mi'kmaq chief Jean-Baptiste Cope.

Nova Scotia is a Canadian province located in Canada's Maritimes. The region was initially occupied by Mi'kmaq. The colonial history of Nova Scotia includes the present-day Maritime Provinces and the northern part of Maine, all of which were at one time part of Nova Scotia. In 1763, Cape Breton Island and St. John's Island became part of Nova Scotia. In 1769, St. John's Island became a separate colony. Nova Scotia included present-day New Brunswick until that province was established in 1784. During the first 150 years of European settlement, the colony was primarily made up of Catholic Acadians, Maliseet, and Mi'kmaq. During the last 75 years of this time period, there were six colonial wars that took place in Nova Scotia. After agreeing to several peace treaties, the long period of warfare ended with the Halifax Treaties (1761) and two years later, when the British defeated the French in North America (1763). During those wars, the Acadians, Mi'kmaq and Maliseet from the region fought to protect the border of Acadia from New England. They fought the war on two fronts: the southern border of Acadia, which New France defined as the Kennebec River in southern Maine, and in Nova Scotia, which involved preventing New Englanders from taking the capital of Acadia, Port Royal and establishing themselves at Canso.
Fort Sackville was a British fort in present-day Bedford, Nova Scotia. It was built during Father Le Loutre's War by British adjacent to present-day Scott Manor House, on a hill overlooking the Sackville River to help prevent French, Acadian and Mi'kmaq attacks on Halifax. The fort consisted of a blockhouse, a guard house, a barracks that housed 50 soldiers, and outbuildings, all encompassed by a palisade. Not far from the fort was a rifle range. The fort was named after George Germain, 1st Viscount Sackville.
Gorham's Rangers was one of the most famous and effective ranger units raised in colonial North America. Formed by John Gorham, the unit served as the prototype for many subsequent ranger forces, including the better known Rogers' Rangers. The unit started out as a Massachusetts provincial auxiliary company, which means it was not part of the province's normal militia system. Recruited in the summer of 1744 at the start of King George's War, Governor William Shirley ordered the unit raised as reinforcements for the then-besieged British garrison at Fort Anne in Annapolis Royal. The unit was primarily used to secure British control in Nova Scotia, whose population consisted primarily of hostile Acadian and Mi'kmaq. Initially a sixty-man all-Indian company led by British officers, the original Native American members of the unit were gradually replaced by Anglo-Americans and recent Scots and Irish immigrants and were a minority in the unit by the mid-1750s. The company were reconnaissance experts as well as renowned for their expertise at both water-borne operations and frontier guerrilla warfare. They were known for surprise amphibious raids on Acadian and Mi'kmaq coastal or riverine settlements, using large whaleboats, which carried between ten and fifteen rangers each. This small unit was the main British military force defending Nova Scotia from 1744 to 1749. The company became part of the British Army and was expanded during the Seven Years' War and went on to play an important role in fighting in Nova Scotia as well as participating in many of the important campaigns of the war, particularly distinguishing itself at the Siege of Quebec in 1759.

The military history of the Mi'kmaq consisted primarily of Mi'kmaq warriors (smáknisk) who participated in wars against the English independently as well as in coordination with the Acadian militia and French royal forces. The Mi'kmaq militias remained an effective force for over 75 years before the Halifax Treaties were signed (1760–1761). In the nineteenth century, the Mi'kmaq "boasted" that, in their contest with the British, the Mi'kmaq "killed more men than they lost". In 1753, Charles Morris stated that the Mi'kmaq have the advantage of "no settlement or place of abode, but wandering from place to place in unknown and, therefore, inaccessible woods, is so great that it has hitherto rendered all attempts to surprise them ineffectual". Leadership on both sides of the conflict employed standard colonial warfare, which included scalping non-combatants. After some engagements against the British during the American Revolutionary War, the militias were dormant throughout the nineteenth century, while the Mi'kmaq people used diplomatic efforts to have the local authorities honour the treaties. After confederation, Mi'kmaq warriors eventually joined Canada's war efforts in World War I and World War II. The most well-known colonial leaders of these militias were Chief (Sakamaw) Jean-Baptiste Cope and Chief Étienne Bâtard.

The military history of the Acadians consisted primarily of militias made up of Acadian settlers who participated in wars against the English in coordination with the Wabanaki Confederacy and French royal forces. A number of Acadians provided military intelligence, sanctuary, and logistical support to the various resistance movements against British rule in Acadia, while other Acadians remained neutral in the contest between the Franco–Wabanaki Confederacy forces and the British. The Acadian militias managed to maintain an effective resistance movement for more than 75 years and through six wars before their eventual demise. According to Acadian historian Maurice Basque, the story of Evangeline continues to influence historic accounts of the expulsion, emphasising Acadians who remained neutral and de-emphasising those who joined resistance movements. While Acadian militias were briefly active during the American Revolutionary War, the militias were dormant throughout the nineteenth century. After confederation, Acadians eventually joined the Canadian War efforts in World War I and World War II. The most well-known colonial leaders of these militias were Joseph Broussard and Joseph-Nicolas Gautier.

The Lunenburg campaign was executed by the Mi'kmaq militia and Acadian militia against the Foreign Protestants who the British had settled on the Lunenburg Peninsula during the French and Indian War. The British deployed Joseph Gorham and his Rangers along with Captain Rudolf Faesch and regular troops of the 60th Regiment of Foot to defend Lunenburg. The campaign was so successful, by November 1758, the members of the House of Assembly for Lunenburg stated "they received no benefit from His Majesty's Troops or Rangers" and required more protection.















