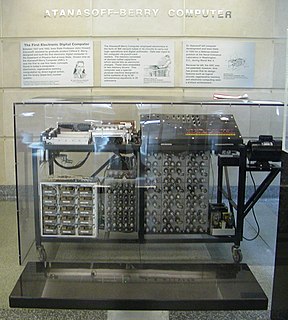
The Atanasoff–Berry computer (ABC) was the first automatic electronic digital computer. Limited by the technology of the day, and execution, the device has remained somewhat obscure. The ABC's priority is debated among historians of computer technology, because it was neither programmable, nor Turing-complete. Conventionally, the ABC would be considered the first electronic ALU – which is integrated into every modern processor's design.

PowerPC is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has since 2006 been named Power ISA, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors.

The IBM AS/400 is a family of midrange computers from IBM announced in June 1988 and released in August 1988. It was the successor to the System/36 and System/38 platforms, and ran the OS/400 operating system. Lower-cost but more powerful than its predecessors, the AS/400 was extremely successful at launch, with an estimated 111,000 installed by the end of 1990 and annual revenue reaching $14 billion that year, increasing to 250,000 systems by 1994, and about 500,000 shipped by 1997.

Blue Gene is an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with low power consumption.
IBM i is an operating system developed by IBM for IBM Power Systems. It was originally released in 1988 as OS/400, as the sole operating system of the IBM AS/400 line of systems. It was renamed to i5/OS in 2004, before being renamed a second time to IBM i in 2008. It is an evolution of the System/38 CPF operating system, with compatibility layers for System/36 SSP and AIX applications. It inherits a number of distinctive features from the System/38 platform, including the Machine Interface, the implementation of object-based addressing on top of a single-level store, and the tight integration of a relational database into the operating system.

The IBM System/36 was a midrange computer marketed by IBM from 1983 to 2000 - a multi-user, multi-tasking successor to the System/34.

The System/38 is a discontinued minicomputer and midrange computer manufactured and sold by IBM. The system was announced in 1978. The System/38 has 48-bit addressing, which was unique for the time, and a novel integrated database system. It was oriented toward a multi-user system environment. At the time, the typical system handled from a dozen to several dozen terminals. Although the System/38 failed to displace the systems it was intended to replace, its architecture served as the basis of the much more successful IBM AS/400.
The IBM RS64 is a family of microprocessors used in IBM's RS/6000 and AS/400 servers in the late 1990s.

Amdahl Corporation was an information technology company which specialized in IBM mainframe-compatible computer products, some of which were regarded as supercomputers competing with those from Cray Research. Founded in 1970 by Gene Amdahl, a former IBM computer engineer best known as chief architect of System/360, it was a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu since 1997. The company was located in Sunnyvale, California.

IBM Rochester is the facility of IBM in Rochester, Minnesota. The initial structure was designed by Eero Saarinen, who clad the structure in blue panels of varying hues after being inspired by the Minnesota sky, as well as IBM's nickname of "Big Blue". These features and the facility's size has earned it the nickname "The Big Blue Zoo" from employees.
A logical partition (LPAR) is a subset of a computer's hardware resources, virtualized as a separate computer. In effect, a physical machine can be partitioned into multiple logical partitions, each hosting a separate instance of an operating system.
Single-level storage (SLS) or single-level memory is a computer storage term which has had two meanings. The two meanings are related in that in both, pages of memory may be in primary storage (RAM) or in secondary storage (disk), and that the physical location of a page is unimportant to a process.
In computer science, capability-based addressing is a scheme used by some computers to control access to memory as an efficient implementation of capability-based security. Under a capability-based addressing scheme, pointers are replaced by protected objects that can be created only through the use of privileged instructions which may be executed only by either the kernel or some other privileged process authorised to do so. This effectively allows the kernel to control which processes may access which objects in memory without the need to use separate address spaces and therefore requiring a context switch when an access occurs.
The Commercial Processing Workload (CPW) is a simplified variant of the industry-wide TPC-C benchmarking standard originally developed by IBM to compare the performance of their various AS/400 server offerings.

Power Systems is a family of server computers from IBM that are based on its Power processors. It was created in 2008 as a merger of the System p and System i product lines.

Precisely, rebranded from Syncsort Incorporated in May 2020, originally founded as Whitlow Computer Systems, is a software company specializing in big data, high speed sorting products, ETL, data integration, data quality, data enrichment, and location intelligence offerings, for IBM i, Hadoop, Microsoft Windows, UNIX, Linux, and mainframe computer systems. Its original, eponymously named product, SyncSort, was the dominant sort program for IBM mainframe computers during much of the 1970s and 1980s.
Glenn Henry(néGaylord Glenn Henry; born July 26, 1942 Berkeley, California), is an American computer industry executive, cofounder of Centaur Technology, and inventor of computer technology at the advent and frontier era of the development of personal computers. He holds over 300 US patents.
IBM POWER is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by IBM. The name is an acronym for Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC.
HelpSystems, LLC is an American information technology and software company based in Eden Prairie, Minnesota, working in the areas of systems and network management, business intelligence, security and compliance, for IBM i, Unix, Linux and Windows environments. The company is recognized as the biggest independent IBM i software vendor in the world.
Control Program Facility (CPF) was the operating system for the IBM System/38. CPF represented an independendent line of development at IBM Rochester, and was unrelated to the earlier and more widely used System Support Program operating system. CPF evolved into the OS/400 operating system, which was originally known as XPF.











