
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself that rises and falls.

The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Boston, Massachusetts, southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals. It provides a navigable route along its length without many of the hazards of travel on the open sea.

The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway is the portion of the Intracoastal Waterway located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1,050 mi (1,690 km) from Carrabelle, Florida, to Brownsville, Texas.

A swing bridge is a movable bridge that has as its primary structural support a vertical locating pin and support ring, usually at or near to its center of gravity, about which the turning span can then pivot horizontally as shown in the animated illustration to the right. Small swing bridges as found over canals may be pivoted only at one end, opening as would a gate, but require substantial underground structure to support the pivot.

The Caloosahatchee River is a river on the southwest Gulf Coast of Florida in the United States, approximately 67 miles (108 km) long. It drains rural areas on the northern edge of the Everglades, east of Fort Myers. An important link in the Okeechobee Waterway, a manmade inland waterway system of southern Florida, the river forms a tidal estuary along most of its course and has become the subject of efforts to restore and preserve the Everglades.

The Cross Florida Barge Canal, now officially the Marjorie Harris Carr Cross Florida Greenway is a protected green belt corridor, more than one mile (1.6 km) wide in places. It is named for the leader of opposition to the Cross Florida Barge Canal, Marjorie Harris Carr, and was originally a U.S. Army Corps of Engineers canal project to connect the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean across Florida for barge traffic. Two sections were built but the project was ultimately cancelled, due to local opposition related to environmental concerns, including protecting the state's water supply and conservation of the Ocklawaha River Valley ecosystem, but also due to national opposition for the costs being perceived as "government waste" with "limited national value."

The Okeechobee Waterway or Okeechobee Canal is a relatively shallow artificial waterway in the United States, stretching across Florida from Fort Myers on the west coast to Stuart on Florida's east coast. The waterway can support tows such as barges or private vessels up to 50 feet wide x 250 feet long which draw less than 10 feet, as parts of the system, especially the locks may have low water depths of just ten feet. The system of channels runs through Lake Okeechobee and consists of the Caloosahatchee River to the west of the lake and the St. Lucie Canal (C-44) east of the lake.

The Industrial Canal is a 5.5 mile (9 km) waterway in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. The waterway's proper name, as used by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and on NOAA nautical charts, is Inner Harbor Navigation Canal (IHNC). The more common "Industrial Canal" name is used locally, both by commercial mariners and by landside residents.
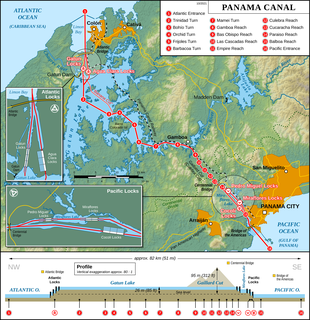
The Panama Canal locks are a lock system that lifts ships up 85 feet to the main elevation of the Panama Canal and down again. The original canal had a total of six steps for a ship's passage. The total length of the lock structures, including the approach walls, is over 1.9 miles (3 km). The locks were one of the greatest engineering works ever to be undertaken when they opened in 1914. No other concrete construction of comparable size was undertaken until the Hoover Dam, in the 1930s.

The inland waterways of the United States include more than 25,000 mi (40,000 km) of navigable waters. Much of the commercially important waterways of the United States consist of the Mississippi River System—the Mississippi River and connecting waterways.

The Inner Harbor Navigation Canal Lock—commonly known as Industrial Canal Lock or simply Industrial Lock—is a navigation lock in New Orleans. It connects the Lower Mississippi River to the Industrial Canal and other sea-level waterways. Because it is shorter and narrower than most modern locks on the Mississippi River System, the 1920s vintage lock has become a bottleneck between the nation's two highest-tonnage waterways—the Mississippi and the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway.

The Chickamauga Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Tennessee River in Chattanooga, Tennessee, United States. The dam is owned and operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority, which built the dam in the late 1930s as part of a New Deal era initiative to improve navigation and bring flood control and economic development to the Tennessee Valley. The dam impounds the 36,240-acre (14,670 ha) Chickamauga Lake and feeds into Nickajack Lake. The dam and associated infrastructure were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2017.
The Schooner Bayou Control Structure is a flood control structure located in Vermilion Parish, Louisiana, and operated by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. It is part of the Mississippi Valley Division, New Orleans District, which encompasses the southern half of the state of Louisiana.

The Wilson Pigott Bridge is a small two-lane drawbridge located near Fort Myers Shores in Lee County, Florida. It is one of four drawbridges in Lee County. It is 27 feet tall.

The Black Rock Lock located in Buffalo, New York is 650 feet (200 m) in length and 70 feet (21 m) wide. There is only one chamber and the total weight of the gate is 480 tons. The lock has been a part of Black Rock since the state of New York built the Erie Canal in 1833.

New Savannah Bluff Lock and Dam is a dam with inactive lock at the site of the dead town of New Savannah, Georgia on the Savannah River south of Augusta, Georgia.

The Port Mayaca Lock is a navigable lock and dam on the Okeechobee Waterway, adjacent to U.S. Route 441 and U.S. Route 98 at Canal Point, in Martin County, Florida, United States.

Starved Rock Lock and Dam, also known as Lock and Dam No. 6, is a lock and dam facility managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers along the Illinois River. It is part of the Illinois Waterway and was constructed between 1926 and 1933. The lock and dam was added to the National Register of Historic Places as the Starved Rock Lock and Dam Historic District in 2004.
The St. Lucie Canal (C-44) is a man-made canal built in 1916 in Martin County, Florida to divert floodwaters from Lake Okeechobee via the canal to the South Fork of the St. Lucie River and into the St. Lucie Estuary, a component of the Indian River Lagoon, which connects to the Atlantic Ocean. Resulting from this connection, restoration projects in the St. Lucie River are the northernmost component of the Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan.


















