
Magnesite is a mineral with the chemical formula MgCO
3. Iron, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may occur as admixtures, but only in small amounts.

The sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe is a large-diameter, double-focusing secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) sector instrument that was produced by Australian Scientific Instruments in Canberra, Australia and now has been taken over by Chinese company Dunyi Technology Development Co. (DTDC) in Beijing. Similar to the IMS 1270-1280-1300 large-geometry ion microprobes produced by CAMECA, Gennevilliers, France and like other SIMS instruments, the SHRIMP microprobe bombards a sample under vacuum with a beam of primary ions that sputters secondary ions that are focused, filtered, and measured according to their energy and mass.
Ján Veizer is the Distinguished University Professor (emeritus) of Earth Sciences at the University of Ottawa and Institute for Geology, Mineralogy und Geophysics, of Bochum Ruhr University. He held the NSERC/Noranda/CIFAR Industrial Chair in Earth System Isotope and Environmental Geochemistry until 2004. He is an isotope geochemist; his research interests have included the use of chemical and isotopic techniques in determining Earth's climatic and environmental history.

George R. Rossman is an American mineralogist and the Professor of Mineralogy at the California Institute of Technology.

Miriam Kastner is a Bratislavan born, Israeli raised, American oceanographer and geochemist. Kastner is currently a distinguished professor at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego. She is still recognized by her fundamental contributions to science and is well spoken of amongst colleagues.
Clumped isotopes are heavy isotopes that are bonded to other heavy isotopes. The relative abundance of clumped isotopes (and multiply-substituted isotopologues) in molecules such as methane, nitrous oxide, and carbonate is an area of active investigation. The carbonate clumped-isotope thermometer, or "13C–18O order/disorder carbonate thermometer", is a new approach for paleoclimate reconstruction, based on the temperature dependence of the clumping of 13C and 18O into bonds within the carbonate mineral lattice. This approach has the advantage that the 18O ratio in water is not necessary (different from the δ18O approach), but for precise paleotemperature estimation, it also needs very large and uncontaminated samples, long analytical runs, and extensive replication. Commonly used sample sources for paleoclimatological work include corals, otoliths, gastropods, tufa, bivalves, and foraminifera. Results are usually expressed as Δ47 (said as "cap 47"), which is the deviation of the ratio of isotopologues of CO2 with a molecular weight of 47 to those with a weight of 44 from the ratio expected if they were randomly distributed.

Janne Blichert-Toft is a geochemist, specializing in the use of isotopes with applications in understanding planetary mantle-crust evolution, as well as the chemical composition of matter in the universe. To further this research, Blichert-Toft has developed techniques for high-precision Isotope-ratio mass spectrometry measurements.
The δ34S value is a standardized method for reporting measurements of the ratio of two stable isotopes of sulfur, 34S:32S, in a sample against the equivalent ratio in a known reference standard. Presently, the most commonly used standard is Vienna-Canyon Diablo Troilite (VCDT). Results are reported as variations from the standard ratio in parts per thousand, per mil or per mille, using the ‰ symbol. Heavy and light sulfur isotopes fractionate at different rates and the resulting δ34S values, recorded in marine sulfate or sedimentary sulfides, have been studied and interpreted as records of the changing sulfur cycle throughout the earth's history.
Robert Norman Clayton was a Canadian-American chemist and academic. He was the Enrico Fermi Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus of Chemistry at the University of Chicago. Clayton studied cosmochemistry and held a joint appointment in the university's geophysical sciences department. He was a member of the National Academy of Sciences and was named a fellow of several academic societies, including the Royal Society.

Jiwchar Ganor is a professor in the Department of Geological and Environmental Sciences at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, and currently serves as Dean of the Faculty of Natural Sciences.
Dorothy Carroll (1907–1970) was an Australian geologist.

Hadean zircon is the oldest-surviving crustal material from the Earth's earliest geological time period, the Hadean eon, about 4 billion years ago. Zircon is a mineral that is commonly used for radiometric dating because it is highly resistant to chemical changes and appears in the form of small crystals or grains in most igneous and metamorphic host rocks.
Carbonate-associated sulfates (CAS) are sulfate species found in association with carbonate minerals, either as inclusions, adsorbed phases, or in distorted sites within the carbonate mineral lattice. It is derived primarily from dissolved sulfate in the solution from which the carbonate precipitates. In the ocean, the source of this sulfate is a combination of riverine and atmospheric inputs, as well as the products of marine hydrothermal reactions and biomass remineralisation. CAS is a common component of most carbonate rocks, having concentrations in the parts per thousand within biogenic carbonates and parts per million within abiogenic carbonates. Through its abundance and sulfur isotope composition, it provides a valuable record of the global sulfur cycle across time and space.
CM chondrites are a group of chondritic meteorites which resemble their type specimen, the Mighei meteorite. The CM is the most commonly recovered group of the 'carbonaceous chondrite' class of meteorites, though all are rarer in collections than ordinary chondrites.
Jane Selverstone is a geologist known for her research into tectonic processes, especially as they apply to the Eastern Alps.
In stable isotope geochemistry, the Urey–Bigeleisen–Mayer equation, also known as the Bigeleisen–Mayer equation or the Urey model, is a model describing the approximate equilibrium isotope fractionation in an isotope exchange reaction. While the equation itself can be written in numerous forms, it is generally presented as a ratio of partition functions of the isotopic molecules involved in a given reaction. The Urey–Bigeleisen–Mayer equation is widely applied in the fields of quantum chemistry and geochemistry and is often modified or paired with other quantum chemical modelling methods to improve accuracy and precision and reduce the computational cost of calculations.
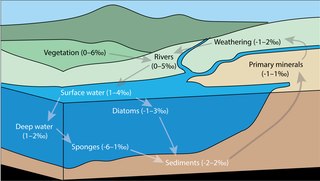
Silicon isotope biogeochemistry is the study of environmental processes using the relative abundance of Si isotopes. As the relative abundance of Si stable isotopes varies among different natural materials, the differences in abundance can be used to trace the source of Si, and to study biological, geological, and chemical processes. The study of stable isotope biogeochemistry of Si aims to quantify the different Si fluxes in the global biogeochemical silicon cycle, to understand the role of biogenic silica within the global Si cycle, and to investigate the applications and limitations of the sedimentary Si record as an environmental and palaeoceanographic proxy.
Keiko Hattori is a geochemist and mineralogist. She is Distinguished University Professor of Geochemistry and Mineral Deposits in the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences at the University of Ottawa.
John Williams Valley is an American geochemist and petrologist. He is an expert on stable isotope geochemistry, especially as applied to understanding the evolution of the Earth's crust.
Hugh Pettingill Taylor Jr. was an American geochemist.







