
The Flying Yankee was a diesel-electric streamliner built in 1935 for the Maine Central Railroad and the Boston and Maine Railroad by Budd Company and with mechanical and electrical equipment from Electro-Motive Corporation. It was also the name of a passenger train, the third streamliner train in North America. That train ceased passenger service in 1957 and is stored at the Hobo Railroad in New Hampshire. It is owned by the state of New Hampshire, which in 2023 said it wants to sell the train.

The Downeaster is a 145-mile (233 km) passenger train service operated by Amtrak and managed by the Northern New England Passenger Rail Authority (NNEPRA), an agency of the state of Maine. Named for the Down East region of Maine, the train operates five daily round trips between North Station in Boston, Massachusetts, and Brunswick, Maine, with ten intermediate stops.

The Maine Central Railroad was a U. S. class 1 railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to 1,358 miles (2,185 km) when the United States Railroad Administration assumed control in 1917. The main line extended from South Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick, and a Mountain Division extended west from Portland to St. Johnsbury, Vermont, and north into Quebec. The main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a "lower road" through Brunswick and Augusta and a "back road" through Lewiston, which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Branch lines served the industrial center of Rumford, a resort hotel on Moosehead Lake and coastal communities from Bath to Eastport.

Durham–University of New Hampshire station, also known as Durham–UNH station or simply Durham station, is a passenger rail station in Durham, New Hampshire, served by Amtrak's Downeaster line. The historic depot, which now houses the UNH Dairy Bar, is situated just west of downtown Durham on the campus of the University of New Hampshire (UNH). The station is owned by the university, but an adjacent parking area is managed by the town of Durham. On average, about 161 rail passengers board or detrain daily at Durham, making it the third-busiest Amtrak stop in New Hampshire.

The railroad history of Portland, Maine, began in 1842 with the arrival of the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth Railway (PS&P). Most of the rail activity in Portland revolved around agricultural goods bound for export and import freight from Europe. Yet Maine's largest city also enjoyed 125 years of continuous passenger rail service, from 1842 until 1967, and Amtrak began serving the city in 2001. For most of Portland's history, passenger train schedules were designed with intercity travel rather than daily commuting in mind; passenger activities were mostly confined to intercity travel from Portland to Boston, Montreal, Nova Scotia, and points west.

Haverhill station is an intercity and regional rail station located in downtown Haverhill, Massachusetts, United States. It is served by Amtrak's Downeaster service and the MBTA Commuter Rail Haverhill/Reading Line; it is the northern terminus of MBTA service on the line. Haverhill is one of two major hubs for MVRTA local bus service; the Washington Square Transit Center is located 1⁄5 mile (0.32 km) east of the rail station.

Dover Transportation Center is an Amtrak train station in Dover, New Hampshire, United States. The station is served by five daily Downeaster round trips. An average of 150 passengers board or alight at Dover daily, making it the second-busiest stop in New Hampshire.

Wells Regional Transportation Center is an Amtrak train station in Wells, Maine. The station sits next to the Pan Am Railways mainline, formerly the Western Route mainline of the Boston and Maine Railroad.

Saco Transportation Center, also referred to as Saco or Saco–Biddeford in some timetables, is a passenger transportation station in Saco, Maine, served by Amtrak, the national railroad passenger system, and other transportation providers. On average, about 110 passengers daily board or alight Amtrak's Downeaster service at the station, making it the third-busiest stop in Maine. The station is located next to the Pan Am Railways mainline, formerly the Western Route mainline of the Boston & Maine Railroad.

Portland Transportation Center is a bus and train station in Portland, Maine, United States, served and run primarily by Concord Coach Lines and Amtrak Downeaster passenger trains. It is also served by Megabus, as well as the Greater Portland Metro route 1 and BREEZ bus services. The station is open from 4:30 AM to 12:15 AM and from 2:45 AM to 3:15 AM.

Maine Eastern Railroad was a railroad that operated in coastal Maine, between Brunswick and Rockland, on the former Maine Central Rockland Branch rail line. Maine Eastern passenger trains connected with the Amtrak Downeaster passenger train and Pan Am Railways at Brunswick Maine Street Station. The state of Maine did not renew the operating contract with MERR, which effectively ended operations at the end of 2015.

Brunswick Maine Street Station, or Brunswick station, is a multi-modal, multi-use real estate development in Brunswick, Maine. Located on Maine Street, it consists of commercial offices, service centers, healthcare, retail, restaurants, theater and residential space. Brunswick Station is also a transportation hub for city buses, taxis, and passenger trains.
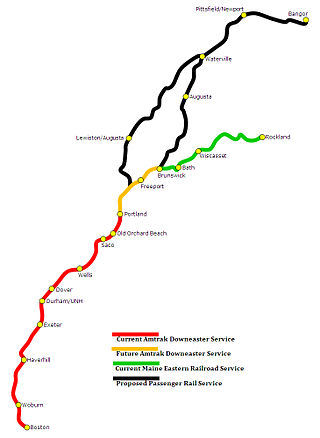
Trainriders Northeast is a non-profit citizens' organization group based out of Portland, Maine, in the United States. It was established in 1989 to advocate for the extension of passenger rail service from Boston to Portland and points north. Today Trainriders Northeast may be most well known for their role in bringing passenger service back to Portland, with the Amtrak Downeaster.

Rockland station is a railway station located at Union and Pleasant Streets in Rockland, Maine. It is the eastern terminus of the Rockland Branch, a state-owned track connecting Rockland and Brunswick. The historic station building was built in 1917 by the Maine Central Railroad, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978 as Rockland Railroad Station. It presently houses a restaurant, and served for a time as Rockland's city hall. The line is presently inactive, having most recently had seasonal passenger service from 2004 to 2015 operated by the now-defunct Maine Eastern Railroad. The line would then be leased to the Central Maine and Quebec Railway (CMQ) from 2015 to 2020, then to Canadian Pacific Railway following its purchase of CMQ in 2020. CMQ originally planned to reintroduce service on the line, but not with excursions.

Yarmouth station of Yarmouth, Maine, is located on the east side of the railroad tracks, just south of Maine State Route 115, the town's Main Street. The railroad station was built in 1906 by the Grand Trunk Railroad, and is a well-preserved example of an early 20th-century passenger rail depot, an increasingly rare sight in the state. The building, which is now in commercial use, was added to the National Register of Historic Places on July 10, 1979.

Union Station was a train station in the Libbytown neighborhood of Portland, Maine, which operated from 1888 to 1960. It was demolished in 1961 and is now the site of a strip mall.

Kennebunk station is a former train station located off Depot Street in Kennebunk, Maine. The station opened in 1873 and closed in 1965; it is now occupied by a private business. Planning began in 2014 to add Kennebunk as a stop on the Amtrak Downeaster route, but the town cancelled the project in 2018.

Yarmouth Junction station was a passenger rail station in Yarmouth, Maine, United States. It stood to the west of East Elm Street at Depot Road, at the junction of the former Grand Trunk Railway and the Maine Central Railroad, around 0.9 miles (1.4 km) north of the town's Railroad Square, where today's 1906-built Grand Trunk station stands. The Amtrak Downeaster utilizes the former Maine Central Railroad line, which passes to the northwest of town. The Yarmouth Junction station building is now gone, but the junction itself is still active.

The Metro Breez is an express bus service in Southern Maine, United States, provided by Greater Portland Metro. It runs thirteen times on weekdays and six times on Saturdays between Portland, the state's largest city, and Brunswick, around 30 miles (48 km) to the northeast, with stops in Yarmouth and Freeport.

Public transportation in Maine is available for all four main modes of transport—air, bus, ferry and rail—assisting residents and visitors without their own vehicle to travel around much of Maine's 31,000 square miles (80,000 km2).





















