Related Research Articles
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.

Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as temporal frequency to emphasize the contrast to spatial frequency, and ordinary frequency to emphasize the contrast to angular frequency. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one (event) per second. The period is the duration of time of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute, its period, T—the time interval between beats—is half a second. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light.

In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant 1000BASE-T is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards.

In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of laser light. This technique enables bidirectional communications over a single strand of fiber, also called wavelength-division duplexing, as well as multiplication of capacity.

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications.
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked".
Liquid crystal on silicon is a miniaturized reflective active-matrix liquid-crystal display or "microdisplay" using a liquid crystal layer on top of a silicon backplane. It is also referred to as a spatial light modulator. LCoS was initially developed for projection televisions but is now used for wavelength selective switching, structured illumination, near-eye displays and optical pulse shaping. By way of comparison, some LCD projectors use transmissive LCD, allowing light to pass through the liquid crystal.

Indium phosphide (InP) is a binary semiconductor composed of indium and phosphorus. It has a face-centered cubic ("zincblende") crystal structure, identical to that of GaAs and most of the III-V semiconductors.
The radio spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies from 3 Hz to 3,000 GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, called radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particularly in telecommunication. To prevent interference between different users, the generation and transmission of radio waves is strictly regulated by national laws, coordinated by an international body, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).

Far infrared (FIR) is a region in the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Far infrared is often defined as any radiation with a wavelength of 15 micrometers (μm) to 1 mm, which places far infrared radiation within the CIE IR-B and IR-C bands. The long-wave side of the FIR spectrum overlaps with so named terahertz radiation. Different sources use different boundaries for the far infrared; for example, astronomers sometimes define far infrared as wavelengths between 25 μm and 350 μm.
The NATO M band is the obsolete designation given to the radio frequencies from 60 to 100 GHz during the cold war period. Since 1992 frequency allocations, allotment and assignments are in line to NATO Joint Civil/Military Frequency Agreement (NJFA).

An optical interleaver is a 3-port passive fiber-optic device that is used to combine (Mux) two sets of dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) channels into a composite signal stream in an interleaving way. For example, optical interleaver takes two multiplexed signals with 100 GHz spacing and interleaves them, creating a denser DWDM signal with channels spaced 50 GHz apart. The process can be repeated, creating even denser composite signals with 25 GHz or 12.5 GHz spacing.
Wavelength selective switching components are used in WDM optical communications networks to route (switch) signals between optical fibres on a per-wavelength basis.
IP over DWDM (IPoDWDM) is a technology used in telecommunications networks to integrate IP routers and network switches in the OTN . A true IPoDWDM solution is implemented only when the IP Routers and Switches support ITU-T G.709. In this way IP devices can monitor the optical path and implement the transport functionality as FEC specified by ITU-T G.709/Y.1331 or Super FEC functionality defined in ITU-T G.975.1.
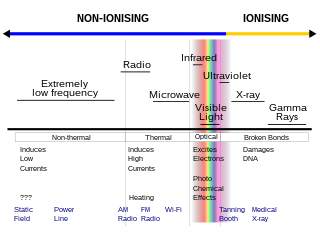
Non-ionizingradiation refers to any type of electromagnetic radiation that does not carry enough energy per quantum to ionize atoms or molecules—that is, to completely remove an electron from an atom or molecule. Instead of producing charged ions when passing through matter, non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation has sufficient energy only for excitation. Non-ionizing radiation can cause some health problems, especially sunburn, and Non ionizing ultraviolet rays(UV-A) can cause melanoma, and non-melanoma skin cancers, but is generally not a significant health risk. In contrast, ionizing radiation has a higher frequency and shorter wavelength than non-ionizing radiation, and can be a serious health hazard: exposure to it can cause burns, radiation sickness, many kinds of cancer, and genetic damage. Using ionizing radiation requires elaborate radiological protection measures, which in general are not required with non-ionizing radiation.
Long Term Evolution (LTE) telecommunications networks use several frequency bands with associated bandwidths.
A super-channel is an evolution in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in which multiple, coherent optical carriers are combined to create a unified channel of a higher data rate, and which is brought into service in a single operational cycle.
The NATO N band is the designation given to the radio frequencies from 100 to 200 GHz used by US armed forces and SACLANT in ITU Region 2.
Submillimeter amateur radio refers to Amateur radio activity in the sub-millimeter region of the electromagnetic spectrum. While no international frequency allocations exist for amateur radio in the sub-millimeter region, a number of administrations permit radio amateurs to experiment on Terahertz frequencies. Amateurs who operate in the region must design and construct their own equipment, and those who do, often attempt to set communication distance records on sub-millimeter frequencies.
Frequency bands for 5G New Radio, which is the air interface or radio access technology of the 5G mobile networks, are separated into two different frequency ranges. First there is Frequency Range 1 (FR1), which includes sub-6 GHz frequency bands, some of which are traditionally used by previous standards, but has been extended to cover potential new spectrum offerings from 410 MHz to 7125 MHz. The other is Frequency Range 2 (FR2), which includes frequency bands from 24.25 GHz to 52.6 GHz.
References
- ↑ ITU-T G.694.1, "Spectral grids for WDM applications: DWDM frequency grid" ITU-T website