Related Research Articles

Blitzkrieg or Bewegungskrieg is a word used to describe a combined arms surprise attack using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with artillery, air assault and close air support, with intent to break through the opponent's lines of defense, dislocate the defenders, unbalance the enemies by making it difficult to respond to the continuously-changing front, and defeat them in a decisive Vernichtungsschlacht: a battle of annihilation.
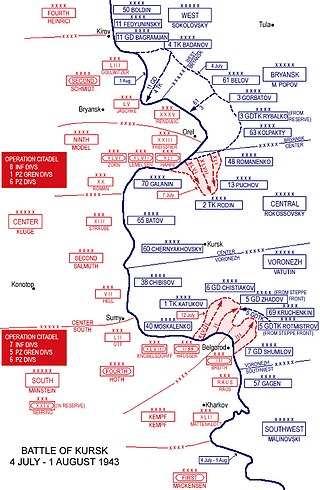
The Battle of Kursk was a major World War II Eastern Front large-scale battle between the forces of Germany and the Soviet Union near Kursk in southwestern Russia during the late summer of 1943; it ultimately became the largest tank battle in history and resulted in a Soviet victory. It is considered by some to be the turning point of the European theatre of war instead of the Battle of Stalingrad several months earlier.

Operation Bagration was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation, a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west, causing Nazi Germany to have to fight on two major fronts at the same time. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of 34 divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. It was the biggest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while 300,000 other German soldiers were cut off in the Courland Pocket.
Deep operation, also known as Soviet Deep Battle, was a military theory developed by the Soviet Union for its armed forces during the 1920s and 1930s. It was a tenet that emphasized destroying, suppressing or disorganizing enemy forces not only at the line of contact but also throughout the depth of the battlefield.
The Battle of Krasny Bor was part of the Soviet offensive Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda in the Eastern Front of World War II. It called for a pincer attack near Leningrad to build on the success of Operation Iskra and completely lift the siege of Leningrad, in the process encircling a substantial part of the German 18th Army. The offensive near the town of Krasny Bor formed the western arm of the pincer. The Soviet offensive began on Wednesday, 10 February 1943, and produced noticeable gains on the first day but rapidly became a stalemate. The strong defense by the Spanish Blue Division and the German SS Polizei Division gave the German forces time to reinforce their positions. By February 13, the Soviet forces had ceased their offensive in this sector.

Operation Iskra, a Soviet military operation in January 1943 during World War II, aimed to break the Wehrmacht's siege of Leningrad. Planning for the operation began shortly after the failure of the Sinyavino Offensive. The German defeat in the Battle of Stalingrad in late 1942 had weakened the German front. By January 1943, Soviet forces were planning or conducting offensive operations across the entire German-Soviet Front, especially in southern Russia; Iskra formed the northern part of the wider Soviet 1942–1943 winter counteroffensive.

The Belgorod–Kharkov strategic offensive operation, or simply Belgorod–Kharkov offensive operation, was a Soviet strategic summer offensive that aimed to recapture Belgorod and Kharkov, and destroy Nazi German forces of the 4th Panzer Army and Army Detachment Kempf. The operation was codenamed Operation Polkovodets Rumyantsev, after the 18th-century Field Marshal Peter Rumyantsev and was conducted by the Voronezh and Steppe Fronts in the southern sector of the Kursk Bulge. The battle was referred to as the Fourth Battle of Kharkov by the Germans.

The Sinyavino offensive was an operation planned by the Soviet Union in the summer of 1942 with the aim of breaking the siege of Leningrad, which had begun the previous summer, and establish a reliable supply line to Leningrad. At the same time, German forces were planning Operation Northern Light to capture the city and link up with Finnish forces. To achieve that heavy reinforcements were arriving from Sevastopol, which the German forces captured in July 1942. Both sides were unaware of the other's preparations, and this made the battle unfold in an unanticipated manner for both sides.
The 40th Guards Rifle Division was one of a series of ten Guards rifle divisions of the Red Army formed from airborne troops in the spring and summer of 1942 in preparation for, or in response to, the German summer offensive. It fought in the Stalingrad area during that battle, eventually in the operations that encircled German 6th Army, and then continued to serve in the several campaigns in the south sector of the front, helping to liberate Ukraine and the Balkans, and ending the war at Vienna.

The 251st Rifle Division was the seventh of a group of 10 regular rifle divisions formed from cadres of NKVD border and internal troops as standard Red Army rifle divisions, very shortly after the German invasion, in the Moscow Military District. It was largely based on what would become the shtat of July 29, 1941, with several variations. It served under command of 30th Army in an effort to recover Smolensk in late July and in the Dukhovshchina offensives in August and September, and was quickly reduced to a much-weakened state. It was largely encircled in the initial stages of Operation Typhoon but sufficient men and equipment escaped that it was spared being disbanded. In the following two and a half years the division slogged through the difficult and costly battles around Rzhev and Smolensk as part of 20th Army, and later 31st Army, of Western Front, including several abortive offensives toward Orsha and Vitebsk in late 1943 and early 1944. At the start of Operation Bagration in June the 251st was serving in the 39th Army of 1st Baltic Front and it won a battle honor for its part in the liberation of Vitebsk. Following this victory it advanced into the "Baltic Gap" that had formed between Army Groups North and Center, entering Lithuania and winning the Order of the Red Banner for its part in the fighting for Kaunas. The division was transferred to 43rd Army and then 4th Shock Army as the Front advanced on Riga, and two of its rifle regiments received decorations for the battles for the Latvian capital. In the first days of 1945 the 251st was reassigned yet again, to the 2nd Guards Army of 3rd Belorussian Front, and served under this Army for the duration of the war. It, and several of its subunits, received awards during the East Prussian campaign, and ended the war in East Prussia. After the war the 251st was moved into the Caucasus region, and was finally disbanded in early 1947.

The 293rd Rifle Division began service as a Red Army rifle division shortly after the German invasion. It was largely based on what would become the shtat of July 29, 1941. The division was initially assigned to 40th Army of Southwestern Front when that Army was formed on August 26. It served in several clashes with the German 2nd Panzer Group in the vicinity of Korop and was therefore outside the area encircled by 2nd and 1st Panzer Groups in September, spending the winter along the front near Kursk. It fought in the unsuccessful Soviet offensive on Kharkiv in May, 1942 as part of 21st Army, suffering significant casualties in the process. During June and July the remnants of the division fought along the Don River against the German summer offensive until it was pulled back into the Reserve of the Supreme High Command for rebuilding. It returned to the front in October, again as part of 21st Army, near Stalingrad, where it played a leading role in the encirclement and destruction of German 6th Army in January 1943, for which it was raised to Guards status as the 66th Guards Rifle Division as the battle was still ongoing.
The 399th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army. Partially raised in 1941, this formation was abandoned until a second formation began in February 1942, this time in the far east of Siberia. The formation lasted until July, after which it was moved west to join the Stalingrad Front in the great bend of the Don River. Badly mauled in its first actions, it was rebuilt west of the Don in late July, and went on to contest the German advance right into the center of the city. The remnants of the division were pulled out and sent north to Bryansk Front, and the once-again rebuilt division went on to serve in the winter offensive against the German forces in the salient around Oryol. It was present on the right flank of the Kursk salient during the German offensive in July 1943 but saw little action until the Soviet forces went on the counterattack later that month. During the advance into western Russia it earned a battle honor. Through the winter of 1943-44 it helped to make incremental gains against the forces of Army Group Center, setting the stage for the summer offensive, during which the division would win its first decoration. Later that year it advanced into Poland and in early 1945 it took part in the battles for East Prussia, and won the Order of the Red Banner for its efforts. The division was disbanded shortly thereafter.
The 64th Guards Rifle Division was created on January 19, 1943, from the 327th Rifle Division, in recognition of that division's distinguished combat record in the Second Siniavino Offensive and Operation Iskra. It was one of a relatively small number of formations raised to Guards status in the northern sector of the Soviet-German Front. As such, it was employed as an assault division in the subsequent fighting, particularly in the final defeat of the German forces before Leningrad, and the final offensive against Finland. The division ended the war in Lithuania, helping to contain the enemy forces trapped in the Courland Pocket, and went on to serve well into the postwar era, still in the Leningrad/St. Petersburg area.
The 378th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army that began forming in August 1941 in the Siberian Military District, before being sent to the vicinity of Leningrad, where it spent most of the war. The soldiers of this division fought until early 1944 to break the siege and drive off the besieging German forces, distinguishing themselves in the liberation of Novgorod. Finally, the division was redeployed to advance into the Baltic states in 1944 and into East Prussia in the winter of 1945. As the war was ending the 378th was disbanded to provide replacements for other divisions. Nevertheless, it had compiled a very creditable combat record for any rifle division.
The 364th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army during World War II.
The 19th Guards Rifle Division was formed from the first formation of the 366th Rifle Division on March 17, 1942. At this time it was in the 52nd Army of Volkhov Front, taking part in the Lyuban Offensive Operation, which was planned to encircle and defeat the enemy forces laying siege to Leningrad. However, just at that time the German 18th Army was in the process of cutting off the Soviet Lyuban grouping in a pocket, and over the following months the division was nearly destroyed. Enough survivors emerged from the swamps in June and July to rebuild the unit, and it fought in the Second Sinyavino Offensive before it was shifted south into Kalinin Front to take part in the battle and siege of Velikiye Luki in December. In the summer of 1943 the 19th Guards fought in the battles for Smolensk, and won its first battle honor, "Rudnya". in September. During the offensive in the summer of 1944 it was awarded the Order of the Red Banner for its successes in the fighting around Vitebsk. It was further honored in February, 1945, with the Order of Lenin for its role in the victories in East Prussia. In the summer the division was moved by rail with its 39th Army to the Far East and saw action in the Soviet invasion of Manchuria in August, winning its second battle honor, "Khingan", for its services. The division continued to see service well into the postwar era.
The 374th Rifle Division was raised in 1941 as an infantry division of the Red Army, and served for the duration of the Great Patriotic War in that role. It began forming in August 1941 in the Siberian Military District. It joined the fighting front in December with the new 59th Army along the Volkhov River and it continued to serve in the fighting near Leningrad until early 1944. The dismal fighting on this front gave little opportunity for a unit to distinguish itself, and the division did not finally earn a battle honor until late January 1944, during the Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive. It continued to serve in the summer and autumn offensive through the Baltic States, becoming so reduced in strength that its remaining infantry was consolidated into a single understrength regiment which nevertheless won a battle honor in the liberation of Riga. The 374th ended the war in Latvia, helping to contain and reduce the German forces trapped in the Courland Pocket, and was disbanded shortly thereafter.
The 219th Rifle Division was formed as an infantry division of the Red Army after a motorized division of that same number was redesignated about 10 weeks after the start of the German invasion of the Soviet Union. Due to a chronic lack of vehicles, and especially tanks, the division had been effectively serving as a motorized rifle brigade since June 22, so the redesignation was a formality and it was soon destroyed in the encirclement battle east of Kiev.
The 222nd Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army, originally formed in the months just before the start of the German invasion, based on the shtat of September 13, 1939. It was formed at Starodub and was considered a "sister" to the 217th Rifle Division. It first saw action in July 1941 as part of 28th Army in the fighting between Smolensk and Roslavl and the division took heavy casualties when it was partly encircled and forced to abandon the latter city in early August. It was again encircled during Operation Typhoon but managed to escape complete destruction and soon came under command of 33rd Army, where it remained for almost the entire length of the war.
The 239th Rifle Division was formed as an infantry division of the Red Army after a motorized division of that same number was reorganized in the first weeks of the German invasion of the Soviet Union. It was based on the shtat of July 29, 1941, and remained forming up and training in Far Eastern Front until early November when the strategic situation west of Moscow required it to be moved by rail to Tula Oblast where it became encircled in the last throes of the German offensive and suffered losses in the following breakout. When Western Front went over to the counteroffensive in the first days of December the division was in the second echelon of 10th Army and took part in the drive to the west against the weakened 2nd Panzer Army. As the offensive continued it took part in the fighting for Belyov and Sukhinichi before being subordinated to the 1st Guards Cavalry Corps in January 1942 to provide infantry support. It then became involved in the complicated and costly battles around the Rzhev salient as part of 50th, 10th and 31st Armies until December. It was then moved north to Volkhov Front, and took part in several operations to break the siege of Leningrad, mostly as part of 2nd Shock and 8th Armies. As part of 59th Army it helped to drive Army Group North away from the city and was rewarded with the Order of the Red Banner in January 1944. During the following months it continued to advance through northwestern Russia but was halted by the defenses of the Panther Line in April. The division took part in the advance through the Baltic states in the summer of 1944 but in February 1945 it was transferred to 1st Ukrainian Front, rejoining 59th Army as part of 93rd Rifle Corps and fought in upper Silesia. In the last weeks of the war the 239th was advancing on Prague, but despite its distinguished record it was selected as one of the many divisions to be disbanded during the summer of 1945.
References
- Glantz, David, Soviet military operational art: in pursuit of deep battle, Frank Cass, London, 1991 ISBN 0-7146-4077-8
- Simpkin, Richard, Red Armour: An examination of the Soviet mobile force concept, Brassey's Defence Publishers, London, 1984