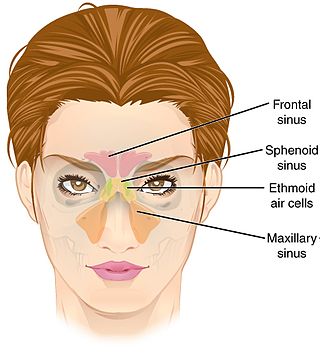
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes. The sinuses are named for the facial bones and sphenoid bone in which they are located. Their role is disputed.

The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a family of nonvenomous snakes primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anaconda of South America being the heaviest and second-longest snake known; in general, adults are medium to large in size, with females usually larger than the males. Six subfamilies comprising 15 genera and 54 species are currently recognized.

The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones, and ear ossicles. Two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium (braincase) and the viscerocranium that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans, these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.

Colubridae is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest fossil species of the family date back to the Late Eocene epoch, with earlier origins suspected. Colubrid snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica.

In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is a unpaired bone which consists of two portions. These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word frons.
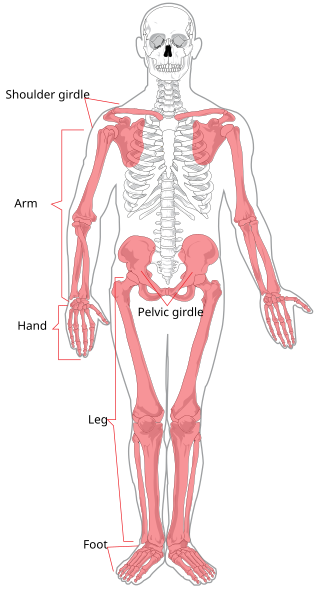
The appendicular skeleton is the portion of the vertebrate endoskeleton consisting of the bones and cartilages that support the paired appendages. In most terrestrial vertebrates, the appendicular skeleton and the associated skeletal muscles are the predominant locomotive structures.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is about 28 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

A snake skeleton consists primarily of the skull, vertebrae, and ribs, with only vestigial remnants of the limbs.

Adelospondyli is an order of elongated, presumably aquatic, Carboniferous amphibians. They have a robust skull roofed with solid bone, and orbits located towards the front of the skull. The limbs were almost certainly absent, although some historical sources reported them to be present. Despite the likely absence of limbs, adelospondyls retained a large part of the bony shoulder girdle. Adelospondyls have been assigned to a variety of groups in the past. They have traditionally been seen as members of the subclass Lepospondyli, related to other unusual early tetrapods such as "microsaurs", "nectrideans", and aïstopods. Analyses such as Ruta & Coates (2007) have offered an alternate classification scheme, arguing that adelospondyls were actually far removed from other lepospondyls, instead being stem-tetrapod stegocephalians closely related to the family Colosteidae.

The frontalis muscle is a muscle which covers parts of the forehead of the skull. Some sources consider the frontalis muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle along with the occipitalis muscle.
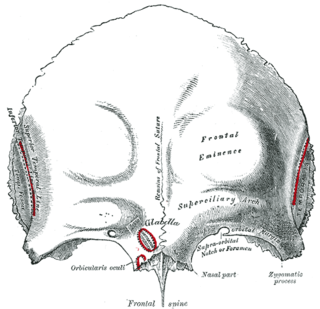
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates and some other animals. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin.

The occipitofrontalis muscle is a muscle which covers parts of the skull. It consists of two parts or bellies: the occipital belly, near the occipital bone, and the frontal belly, near the frontal bone. It is supplied by the supraorbital artery, the supratrochlear artery, and the occipital artery. It is innervated by the facial nerve. In humans, the occipitofrontalis helps to create facial expressions.

Chrysopelea ornata is a mildly venomous opisthoglyphous (rear-fanged) colubrid snake found in both South and Southeast Asia. It is commonly known as the golden tree snake, ornate flying snake, and golden flying snake. Along with the other species in the Chrysopelea genus, the golden tree snake is very unusual, as it is capable of a type of gliding "flight" —mainly utilised during the pursuit of prey animals—from tree-to-tree. This action is also used to great effect for the snake to flee its own potential predators. Currently, three subspecies are recognised. The snake's striking looks, and potential for gliding, have made it a coveted choice for captivity.

Hydrophis cyanocinctus, commonly called the annulated sea snake or the blue-banded sea snake, is a species of venomous sea snake in the family Elapidae.

Causus is a genus of vipers found only in sub-Saharan Africa. It is a group considered to be among the most primitive members of the family Viperidae based on head scalation, oviparity, venom apparatus, and because they have round pupils. However, this is contradicted by recent molecular studies. Seven species are currently recognized. They are commonly known as night adders. Like all other vipers, they are venomous.

Snakes, like other reptiles, have skin covered in scales. Snakes are entirely covered with scales or scutes of various shapes and sizes, known as snakeskin as a whole. A scale protects the body of the snake, aids it in locomotion, allows moisture to be retained within, alters the surface characteristics such as roughness to aid in camouflage, and in some cases even aids in prey capture. The simple or complex colouration patterns are a property of the underlying skin, but the folded nature of scaled skin allows bright skin to be concealed between scales then revealed in order to startle predators.

Parietal scales are the scales of a snake located on the snake's head and are connected to the frontals towards the posterior. These plate-like scales are analogous to and take their name from the parietal bone, which forms the roof and sides of the cranium in humans.

Coelognathus helena monticollaris is subspecies of nonvenomous constricting snake in the family Colubridae. The subspecies is native to the Western ghats of India.

The calvaria is the top part of the skull. It is the superior part of the neurocranium and covers the cranial cavity containing the brain. It forms the main component of the skull roof.

In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton.




















