
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party from 1922 to 1952 and Chairman of the Council of Ministers from 1941 until his death. Initially governing as part of a collective leadership, Stalin consolidated power to become dictator by the 1930s; the totalitarian political system which he established is known as Stalinism.

Kliment Yefremovich Voroshilov, popularly known as Klim Voroshilov, was a prominent Soviet military officer and politician during the Stalin-era. He was one of the original five Marshals of the Soviet Union, the second highest military rank of the Soviet Union, and served as Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet, the nominal Soviet head of state, from 1953 to 1960.

Lavrentiy Pavlovich Beria was a Soviet politician and one of the longest-serving and most influential of Joseph Stalin's secret police chiefs, serving as head of the People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (NKVD) from 1938 to 1946, during the country's involvement in the Second World War.

Nikolay Gerasimovich Kuznetsov was a Soviet naval officer who achieved the rank of Admiral of the Fleet of the Soviet Union and served as People's Commissar of the Navy during the Winter War and the Second World War. The N. G. Kuznetsov Naval Academy and the Russian aircraft carrier Admiral Kuznetsov, as well as the Kuznetsov-class carrier class, are named in his honor.

The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. It was the largest country in the world by area, extending across eleven time zones and sharing land borders with twelve countries.

Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov was a Soviet politician, diplomat, and revolutionary who was a leading figure in the government of the Soviet Union from the 1920s to the 1950s, as one of Joseph Stalin's closest allies. Molotov served as Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars from 1930 to 1941, and as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1939 to 1949 during the era of the Second World War, and again from 1953 to 1956.

The State Flag of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, or simply the Soviet flag, was a red banner with two communist symbols displayed in the canton: a gold hammer and sickle topped off by a red five-point star bordered in gold. The flag's design and symbolism are derived from several sources, but emerged during the Russian Revolution. It has also come to serve as the standard symbol representing communism as a whole, recognized as such in international circles, even after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.

André Léon Blum was a French socialist politician and three-time Prime Minister of France. As a Jew, he was heavily influenced by the Dreyfus affair of the late 19th century. He was a disciple of socialist leader Jean Jaurès; after Jaurès' assassination in 1914, he became his successor.

Andrey Yanuaryevich Vyshinsky was a Soviet politician, jurist and diplomat.

The history of the Soviet Union between 1927 and 1953 covers the period in Soviet history from the establishment of Stalinism through victory in the Second World War and down to the death of Joseph Stalin in 1953. Stalin sought to destroy his enemies while transforming Soviet society with central planning, in particular through the forced collectivization of agriculture and rapid development of heavy industry. Stalin consolidated his power within the party and the state and fostered an extensive cult of personality. Soviet secret-police and the mass-mobilization of the Communist Party served as Stalin's major tools in molding Soviet society. Stalin's methods in achieving his goals, which included party purges, ethnic cleansings, political repression of the general population, and forced collectivization, led to millions of deaths: in Gulag labor camps and during famine.

Edward Hallett Carr was a British historian, diplomat, journalist and international relations theorist, and an opponent of empiricism within historiography. Carr was best known for A History of Soviet Russia, a 14-volume history of the Soviet Union from 1917 to 1929, for his writings on international relations, particularly The Twenty Years' Crisis, and for his book What Is History? in which he laid out historiographical principles rejecting traditional historical methods and practices.

Viktor Platonovich Nekrasov was a Soviet writer, journalist and editor.

FC Chornomorets Odesa is a Ukrainian professional football club based in Odesa.

Choe Yong-gon was the Supreme Commander of the Korean People's Army from 1948 to 1950, North Korean defence minister from 1948 to 1957, and the Chairman of the Standing Committee of the Supreme People's Assembly of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea from 1957 to 1972.

The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, previously known as the Russian Soviet Republic and the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia, was an independent federal socialist state from 1917 to 1922, and afterwards the largest and most populous constituent republic of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1922 to 1991, until becoming a sovereign part of the Soviet Union with priority of Russian laws over Union-level legislation in 1990 and 1991, the last two years of the existence of the USSR. The Russian SFSR was composed of sixteen smaller constituent units of autonomous republics, five autonomous oblasts, ten autonomous okrugs, six krais and forty oblasts. Russians formed the largest ethnic group. The capital of the Russian SFSR and the USSR as a whole was Moscow and the other major urban centers included Leningrad, Stalingrad, Novosibirsk, Sverdlovsk, Gorky and Kuybyshev. It was the first socialist state in the world.

Mehdi Ali oglu Huseynov – famed under the pseudonym Mehdi Huseyn was an Azerbaijani and Soviet writer and critic, laureate of the State Stalin Prize of the third degree (1950) and member of the All-Union Communist Party since 1941.
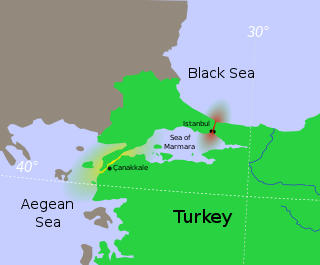
The Turkish Straits crisis was a Cold War-era territorial conflict between the Soviet Union and Turkey. Turkey had remained officially neutral throughout most of the Second World War. After the war ended, Turkey was pressured by the Soviet government to institute joint military control of passage through Turkish Straits, which connected the Black Sea to the Mediterranean. When the Turkish government refused, tensions in the region rose, leading to a Soviet show of force and demands for territorial concessions along the Georgia–Turkey border.

Oleksandr Yevdokymovych Korniychuk was a Soviet and Ukrainian playwright, literary critic and state official.

The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs, abbreviated as NKVD, was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) secret police organization, and thus had a monopoly on intelligence and state security functions. The NKVD is known for carrying out political repression and the Great Purge under Joseph Stalin, as well as counterintelligence and other operations on the Eastern Front of World War II. The head of the NKVD was Genrikh Yagoda from 1934 to 1936, Nikolai Yezhov from 1936 to 1938, Lavrentiy Beria from 1938 to 1946, and Sergei Kruglov in 1946.

The Order of Lenin was an award named after Vladimir Lenin, the leader of the October Revolution. It was established by the Central Executive Committee on 6 April 1930. The order was the highest civilian decoration bestowed by the Soviet Union. The order was awarded to:



















