Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, where the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned into components attributable to different sources of variation. In its simplest form, ANOVA provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the t-test beyond two means. In other words, the ANOVA is used to test the difference between two or more means.

A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.

Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of variation in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The concept of heritability can be expressed in the form of the following question: "What is the proportion of the variation in a given trait within a population that is not explained by the environment or random chance?"
The statistical power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis when a specific alternative hypothesis is true. It is commonly denoted by , and represents the chances of a "true positive" detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases.
An F-test is any statistical test in which the test statistic has an F-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most often used when comparing statistical models that have been fitted to a data set, in order to identify the model that best fits the population from which the data were sampled. Exact "F-tests" mainly arise when the models have been fitted to the data using least squares. The name was coined by George W. Snedecor, in honour of Sir Ronald A. Fisher. Fisher initially developed the statistic as the variance ratio in the 1920s.
Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) is a general linear model which blends ANOVA and regression. ANCOVA evaluates whether the means of a dependent variable (DV) are equal across levels of a categorical independent variable (IV) often called a treatment, while statistically controlling for the effects of other continuous variables that are not of primary interest, known as covariates (CV) or nuisance variables. Mathematically, ANCOVA decomposes the variance in the DV into variance explained by the CV(s), variance explained by the categorical IV, and residual variance. Intuitively, ANCOVA can be thought of as 'adjusting' the DV by the group means of the CV(s).
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the value of a parameter for a hypothetical population, or to the equation that operationalizes how statistics or parameters lead to the effect size value. Examples of effect sizes include the correlation between two variables, the regression coefficient in a regression, the mean difference, or the risk of a particular event happening. Effect sizes complement statistical hypothesis testing, and play an important role in power analyses, sample size planning, and in meta-analyses. The cluster of data-analysis methods concerning effect sizes is referred to as estimation statistics.

In statistics, an interaction may arise when considering the relationship among three or more variables, and describes a situation in which the effect of one causal variable on an outcome depends on the state of a second causal variable. Although commonly thought of in terms of causal relationships, the concept of an interaction can also describe non-causal associations. Interactions are often considered in the context of regression analyses or factorial experiments.
Linear trend estimation is a statistical technique to aid interpretation of data. When a series of measurements of a process are treated as, for example, a sequences or time series, trend estimation can be used to make and justify statements about tendencies in the data, by relating the measurements to the times at which they occurred. This model can then be used to describe the behaviour of the observed data, without explaining it.
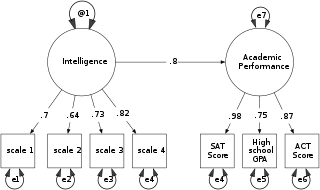
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a label for a diverse set of methods used by scientists in both experimental and observational research across the sciences, business, and other fields. It is used most in the social and behavioral sciences. A definition of SEM is difficult without reference to highly technical language, but a good starting place is the name itself.

In statistics, a mediation model seeks to identify and explain the mechanism or process that underlies an observed relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable via the inclusion of a third hypothetical variable, known as a mediator variable. Rather than a direct causal relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable, a mediation model proposes that the independent variable influences the mediator variable, which in turn influences the dependent variable. Thus, the mediator variable serves to clarify the nature of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
In statistics, one-way analysis of variance is a technique that can be used to compare whether two sample's means are significantly different or not. This technique can be used only for numerical response data, the "Y", usually one variable, and numerical or (usually) categorical input data, the "X", always one variable, hence "one-way".
Repeated measures design is a research design that involves multiple measures of the same variable taken on the same or matched subjects either under different conditions or over two or more time periods. For instance, repeated measurements are collected in a longitudinal study in which change over time is assessed.
In statistics and regression analysis, moderation occurs when the relationship between two variables depends on a third variable. The third variable is referred to as the moderator variable or simply the moderator. The effect of a moderating variable is characterized statistically as an interaction; that is, a categorical or quantitative variable that affects the direction and/or strength of the relation between dependent and independent variables. Specifically within a correlational analysis framework, a moderator is a third variable that affects the zero-order correlation between two other variables, or the value of the slope of the dependent variable on the independent variable. In analysis of variance (ANOVA) terms, a basic moderator effect can be represented as an interaction between a focal independent variable and a factor that specifies the appropriate conditions for its operation.
Psychometric software is software that is used for psychometric analysis of data from tests, questionnaires, or inventories reflecting latent psychoeducational variables. While some psychometric analyses can be performed with standard statistical software like SPSS, most analyses require specialized tools.
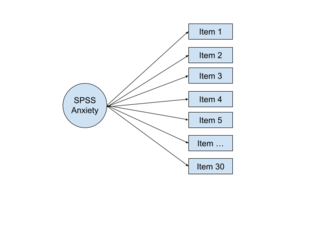
In multivariate statistics, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) is a statistical method used to uncover the underlying structure of a relatively large set of variables. EFA is a technique within factor analysis whose overarching goal is to identify the underlying relationships between measured variables. It is commonly used by researchers when developing a scale and serves to identify a set of latent constructs underlying a battery of measured variables. It should be used when the researcher has no a priori hypothesis about factors or patterns of measured variables. Measured variables are any one of several attributes of people that may be observed and measured. Examples of measured variables could be the physical height, weight, and pulse rate of a human being. Usually, researchers would have a large number of measured variables, which are assumed to be related to a smaller number of "unobserved" factors. Researchers must carefully consider the number of measured variables to include in the analysis. EFA procedures are more accurate when each factor is represented by multiple measured variables in the analysis.
In statistics, one purpose for the analysis of variance (ANOVA) is to analyze differences in means between groups. The test statistic, F, assumes independence of observations, homogeneous variances, and population normality. ANOVA on ranks is a statistic designed for situations when the normality assumption has been violated.
In statistics, the Sobel test is a method of testing the significance of a mediation effect. The test is based on the work of Michael E. Sobel, a statistics professor at Columbia University in New York, NY, and is an application of the delta method. In mediation, the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable is hypothesized to be an indirect effect that exists due to the influence of a third variable. As a result when the mediator is included in a regression analysis model with the independent variable, the effect of the independent variable is reduced and the effect of the mediator remains significant. The Sobel test is basically a specialized t test that provides a method to determine whether the reduction in the effect of the independent variable, after including the mediator in the model, is a significant reduction and therefore whether the mediation effect is statistically significant.
One application of multilevel modeling (MLM) is the analysis of repeated measures data. Multilevel modeling for repeated measures data is most often discussed in the context of modeling change over time ; however, it may also be used for repeated measures data in which time is not a factor.
JASP is a free and open-source program for statistical analysis supported by the University of Amsterdam. It is designed to be easy to use, and familiar to users of SPSS. It offers standard analysis procedures in both their classical and Bayesian form. JASP generally produces APA style results tables and plots to ease publication. It promotes open science by integration with the Open Science Framework and reproducibility by integrating the analysis settings into the results. The development of JASP is financially supported by several universities and research funds.







