
Potsdam is the capital and largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some 25 kilometres southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin.

Lake Elgygytgyn, also transcripted El'gygytgyn, is a crater lake in Anadyrsky District, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in northeast Siberia, about 150 km (93 mi) southeast of Chaunskaya Bay.
The Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres is the largest scientific organisation in Germany. It is a union of 18 scientific-technical and biological-medical research centers. The official mission of the Association is "solving the grand challenges of science, society and industry". Scientists at Helmholtz therefore focus research on complex systems which affect human life and the environment. The namesake of the association is the German physiologist and physicist Hermann von Helmholtz.

The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth (SAFOD) was a research project that began in 2002 aimed at collecting geological data about the San Andreas Fault for the purpose of predicting and analyzing future earthquakes. The site consists of a 2.2 km pilot hole and a 3.2 km main hole. Drilling operations ceased in 2007. Located near the town of Parkfield, California, the project installed geophone sensors and GPS clocks in a borehole that cut directly through the fault. This data, along with samples collected during drilling, helped shed new light on geochemical and mechanical properties around the fault zone.
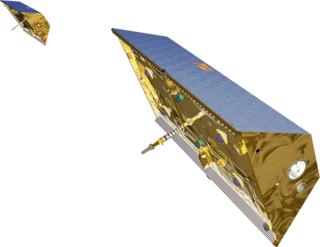
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) was a joint mission of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Twin satellites took detailed measurements of Earth's gravity field anomalies from its launch in March 2002 to the end of its science mission in October 2017. The two satellites were sometimes called Tom and Jerry, a nod to the famous cartoon. The GRACE Follow-On (GRACE-FO) is a continuation of the mission on near-identical hardware, launched in May 2018. On March 19, 2024, NASA announced that the successor to GRACE-FO would be Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment-Continuity (GRACE-C), to be launched in or after 2028.

The Göttingen State and University Library is the library for Göttingen University as well as for the Göttingen Academy of Sciences and is the state library for the German State of Lower Saxony. One of the largest German academic libraries, it has numerous national as well as international projects in librarianship and in the provision of research infrastructure services. In the year 2002, the SUB Göttingen won the German Library of the Year award. Its current director is Wolfram Horstmann.

Challenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP) was a German satellite launched July 15, 2000 from Plesetsk, Russia and was used for atmospheric and ionospheric research, as well as other geoscientific applications, such as GPS radio occultation, gravity field determination, and studying the Earth's magnetic field.

The Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize, or Leibniz Prize, is awarded by the German Research Foundation to "exceptional scientists and academics for their outstanding achievements in the field of research". Since 1986, up to ten prizes have been awarded annually to individuals or research groups working at a research institution in Germany or at a German research institution abroad. It is considered the most important research award in Germany.

The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region is one of the most prolific centers of higher education and research in the world. It is the largest concentration of universities and colleges in Germany. The city has four public research universities and 27 private, professional and technical colleges (Hochschulen), offering a wide range of disciplines. Access to the German university system is tuition free.
The Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology is a German research institute for molecular plant physiology, based in the Golm district of Potsdam, Brandenburg. Founded on 1 January 1994, the MPIMP focuses on the study of the dynamics of plant metabolism and how that relates to the entire plant system. The institution is one of the 80 institutes in the Max Planck Society (Max-Planck-Gesellschaft).

The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association in Berlin is one of the 18 institutions that make up the Helmholtz Association. It combines basic molecular biology research with clinical research and is dedicated to the research foci of systems medicine and cardiovascular diseases. The research center is named after the Berlin-born biophysicist and Nobel laureate Max Delbrück. The center is headed by Maike Sander.
The Leibniz Centre for Contemporary History Potsdam is an interdisciplinary research institute focusing on the contemporary history of Europe, especially Germany, and member of the Leibniz Association.

The Albert Einstein Science Park is located on the Telegrafenberg hill in Potsdam, Germany. The park was named after the physicist Albert Einstein. The best known buildings in the park are the Einstein Tower, an astrophysical observatory that was built to perform checks of Einstein's theory of General Relativity; and the Great Refractor of Potsdam, which today belong to the Astrophysical Institute Potsdam. These buildings, along with various astronomical, meteorological, and geophysical observatories were integrated into an English-style country garden.
The Deutsches Klima-Konsortium e. V. is located in Berlin, Germany, and represents the leading players of German climate and climate impact research encompassing 26 renowned research organisations. The federation is also an important international partner acting as a guidepost, strategic partner, project partner and information broker.
Paul Hermann Otto Eggert was a German surveyor and professor of Gdańsk University of Technology. He was also dean of the Faculty of Civil Engineering from 1909 to 1910 and from 1919 to 1920 and the first head of the Department of Geodesy at the Technical University of Gdańsk (1904-1921).

The Research Institute for Sustainability (RIFS) in Potsdam conducts research with the aim of investigating, identifying, and advancing development pathways for transformation processes towards sustainability in Germany and abroad. The Institute joined the Helmholtz Association in 2023 and is affiliated with the Helmholtz Centre Potsdam – GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences. Its research approach is transdisciplinary, transformative, and co-creative. The Institute cooperates with partners in science, political and administrative institutions, the business community, and civil society to develop solutions for sustainability challenges that enjoy broad public support. Its central research topics include the energy transition, climate change and socio-technical transformations, as well as sustainable governance and participation, and cultures of transformation in the Anthropocene. A strong network of national and international partners and a Fellow Programme supports the work of the Institute.

Professor Günter Blöschl is an Austrian hydrologist, engineer and academic.
Mioara Mandea is Head "Science Coordination" Department, Strategy Directorate at the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales. Mioara Mandea’s research has had a broader significance and a huge impact in the community. One of her accomplishments of incalculable importance is the assembling of the geomagnetic time series at Paris, opening the path to other long magnetic series as Munich and Bucharest and dedicated studies. Over her entire career, she has been focused on the geomagnetic field and its variations, using data derived from magnetic observatories and satellites participating in elaborating useful models, such as the IGRF series. With GRACEFUL, a Synergy project of the European Research Council in the framework of the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Mioara Mandea continues her precursory work related to the dynamical processes in Earth's fluid core seen by both magnetic and gravity variations.

Michael Kellner is a German politician who has been serving as a Member of the Bundestag representing electoral constituency Uckermark – Barnim I since 2021.
Bettina Hörstrup is a German lawyer and administrative director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) since 2020. Together with the scientific directors Ottmar Edenhofer and Johan Rockström, she forms the board of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research.




















