Related Research Articles

BibTeX is reference management software for formatting lists of references. The BibTeX tool is typically used together with the LaTeX document preparation system. Within the typesetting system, its name is styled as . The name is a portmanteau of the word bibliography and the name of the TeX typesetting software.

An archive is an accumulation of historical records – in any media – or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity.

An archivist is an information professional who assesses, collects, organizes, preserves, maintains control over, and provides access to records and archives determined to have long-term value. The records maintained by an archivist can consist of a variety of forms, including letters, diaries, logs, other personal documents, government documents, sound and/or picture recordings, digital files, or other physical objects.

Library and Archives Canada is a federal institution tasked with acquiring, preserving and making Canada's documentary heritage accessible. It is the fourth-largest library in the world. LAC reports to Parliament through Steven Guilbeault, the Minister of Canadian Heritage since November 20, 2019.
In archival science, a fonds is a group of documents that share the same origin and that have occurred naturally as an outgrowth of the daily workings of an agency, individual, or organization. An example of a fonds could be the writings of a poet that were never published or the records of an institution during a specific period.
Archival science, or archival studies, is the study and theory of building and curating archives, which are collections of documents, recordings and data storage devices.

A finding aid, in the context of archival science, is a tool containing detailed, indexed, and processed information about a specific collection of records within an archive. Finding aids often consist of a documentary inventory and description of the materials, their source, and their structure. The finding aid for a collection is usually compiled by the collection's entity of origin, provenance, or by an archivist or librarian during archival processing. The finding aid serves the purpose of locating specific information within the collection. The finding aid can also help the archival repository manage their materials and resources.

In library and archival science, preservation is a set of activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record, book, or object while making as few changes as possible. Preservation activities vary widely and may include monitoring the condition of items, maintaining the temperature and humidity in collection storage areas, writing a plan in case of emergencies, digitizing items, writing relevant metadata, and increasing accessibility. Preservation, in this definition, is practiced in a library or an archive by a librarian, archivist, or other professional when they perceive a record is in need of care.

The Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL) is a consortium of natural history and botanical libraries that cooperate to digitize and make accessible the legacy literature of biodiversity held in their collections and to make that literature available for open access and responsible use as a part of a global "biodiversity commons". The BHL consortium works with the international taxonomic community, rights holders, and other interested parties to ensure that this biodiversity heritage is made available to a global audience through open access principles. In partnership with the Internet Archive and through local digitization efforts, the BHL has digitized millions of pages of taxonomic literature, representing tens of thousands of titles and more than 100,000 volumes.
Digital curation is the selection, preservation, maintenance, collection and archiving of digital assets. Digital curation establishes, maintains and adds value to repositories of digital data for present and future use. This is often accomplished by archivists, librarians, scientists, historians, and scholars. Enterprises are starting to use digital curation to improve the quality of information and data within their operational and strategic processes. Successful digital curation will mitigate digital obsolescence, keeping the information accessible to users indefinitely. Digital curation includes digital asset management, data curation, digital preservation, and electronic records management.

Europeana is a web portal created by the European Union containing digitalised museum collections of more than 3,000 institutions across Europe. It includes records of over 10 million cultural and scientific artefacts, brought together on a single platform and presented in a variety of ways relevant to modern users. The prototype for Europeana was the European Digital Library Network (EDLnet), launched in 2008.

The Digital Library Federation (DLF) is a program of the Council on Library and Information Resources (CLIR) that brings together a consortium of college and university libraries, public libraries, museums, and related institutions with the stated mission of "advanc[ing] research, learning, social justice, and the public good through digital library technologies." It was formed in 1995.

Smithsonian Libraries (SIL), formerly known as Smithsonian Institution Libraries, is a library system comprising 20 branch libraries serving the various Smithsonian Institution museums and research centers, as well as central support services which include a Book Conservation Laboratory and an Imaging Center. The Libraries serve Smithsonian Institution staff as well as the scholarly community and general public with information and reference support. Its collections number over 1.5 million volumes including 40,000 rare books and 2,000 manuscripts. The Libraries also holds the United States' largest trade literature collection, which includes over 300,000 commercial catalogs dating from the early nineteenth century and representing more than 30,000 companies.

Archival research is a type of research which involves seeking out and extracting evidence from archival records. These records may be held either in collecting institutions, such as libraries and museums, or in the custody of the organization that originally generated or accumulated them, or in that of a successor body. Archival research can be contrasted with (1) secondary research, which involves identifying and consulting secondary sources relating to the topic of enquiry; and (2) with other types of primary research and empirical investigation such as fieldwork and experiment.

Trove is an Australian online library database aggregator and service which includes full text documents, digital images, bibliographic and holdings data of items which are not available digitally, and a free faceted-search engine as a discovery tool. The database includes archives, images, newspapers, official documents, archived websites, manuscripts and other types of data. Hosted by the National Library of Australia in partnership with content providers, including members of the National and State Libraries Australia, it is one of the most well-respected and accessed GLAM services in Australia, with over 70,000 daily users.
A memory institution is an organization maintaining a repository of public knowledge, a generic term used about institutions such as libraries, archives, heritage institutions, aquaria and arboreta, and zoological and botanical gardens, as well as providers of digital libraries and data aggregation services which serve as memories for given societies or mankind. Memory institutions serve the purpose of documenting, contextualizing, preserving and indexing elements of human culture and collective memory. These institutions allow and enable society to better understand themselves, their past, and how the past impacts their future. These repositories are ultimately preservers of communities, languages, cultures, customs, tribes, and individuality. Memory institutions are repositories of knowledge, while also being actors of the transitions of knowledge and memory to the community. These institutions ultimately remain some form of collective memory. Increasingly such institutions are considered as a part of a unified documentation and information science perspective.
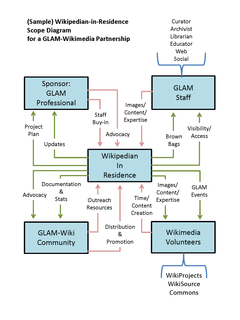
A Wikipedian in residence or Wikimedian in residence (WiR) is a Wikipedia editor, a Wikipedian, who accepts a placement with an institution, typically an art gallery, library, archive, or museum, learned society, or institute of higher education to facilitate Wikipedia entries related to that institution's mission, encourage and assist it to release material under open licences, and to develop the relationship between the host institution and the Wikimedia community. A Wikipedian in residence generally helps to coordinate Wikipedia-related outreach events between the GLAM and the general public such as editathons.
Elizabeth Yakel is an archivist, researcher, and educator in information science. Yakel is known for work advancing archival practice, the use of primary sources in archives education, studies of data reuse practices, and digital curation. Yakel is the Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and a Professor at the University of Michigan School of Information, where she has been on the faculty since 2000. She is the former coordinator of the Preservation of Information specialization in the Master of Science in Information program and teaches in the Archives and Record Management area. She specializes in digital archives and digital preservation and has developed five such graduate level courses at UM, including "Economics of Sustainable Digital Information" and "Practical Engagement Workshop in Digital Preservation."
Social Networks and Archival Context (SNAC) is an online project for discovering, locating, and using distributed historical records in regard to individual people, families, and organizations.

Helen Ruth Tibbo is an American archivist, professor and author writing about digital preservation in the archival profession. At the University of North Carolina, she created and directed the first American master's degree on digital curation. She is a past President of the Society of American Archivists
References
- ↑ Australian Society of Archivists, Australian Society of Archivists Annual Conference - GLAM, 17–20 September 2003, Hilton, Adelaide.
- ↑ "GLAM - CC Wiki". Creative Commons. Retrieved 29 October 2011.
- ↑ "2017 Conference - Australian Society of Archivists". www.archivists.org.au. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ↑ BibSI. "On the LAM: Library, Archive, and Museum Collections in the Creation and Maintenance of Knowledge Communities | BibSI". Bibsi.cms.si.umich.edu. Archived from the original on 2014-03-05. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ↑ "Internet Archive Wayback Machine". 2008-12-22. Archived from the original on May 1, 2009. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ↑ Jim Michalko (2005-08-04). "LAM DNA". hangingtogether.org. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ↑ Information Retrieval & Library Automation. Lomond Systems. 1997.
- ↑ "GLAM Peak — Digital Access to Collections". digitalcollections.org.au. Retrieved 10 Jun 2019.
- ↑ "National Digital Forum". ndf.org.nz. Retrieved 10 Jun 2019.
- ↑ Marcum, Deanna (2014-01-01). "Archives, Libraries, Museums: Coming Back Together?". Information & Culture: A Journal of History. 49 (1): 74–89. doi:10.1353/lac.2014.0001. ISSN 2166-3033. S2CID 144095412.