
The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle is a family of light, four-wheel drive, military trucks and utility vehicles produced by AM General. It has largely supplanted the roles previously performed by the original jeep, and others such as the Vietnam War-era M151 jeep, the M561 "Gama Goat", their M718A1 and M792 ambulance versions, the Commercial Utility Cargo Vehicle (CUCV), and other light trucks. Primarily used by the United States military, it is also used by numerous other countries and organizations and even in civilian adaptations. The Humvee saw widespread use in the Gulf War of 1991, where it navigated the treacherous desert terrain; this usage helped to inspire civilian Hummer versions. After going through a replacement process, the Joint Light Tactical Vehicle (JLTV) was chosen as its successor.

The Heavy Expanded Mobility Tactical Truck (HEMTT) is an eight-wheel drive, diesel-powered, 10-short-ton (9,100 kg), tactical truck used by the US military and others. In evolving configurations, it has been in continuous production since 1982. The M977 HEMTT entered service with the U.S. Army as a replacement for the M520 Goer.

A convertible, cabriolet or spyder/spider is a passenger car that can be driven with or without a roof in place. The methods of retracting and storing the roof vary between models. A convertible allows an open-air driving experience, with the ability to provide a roof when required. Potential drawbacks of convertibles are reduced structural rigidity and cargo space.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from inception, through engineering design and manufacture, to service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprise.

Textron Inc. is an American industrial conglomerate based in Providence, Rhode Island. Textron's subsidiaries include Arctic Cat, Bell Helicopter, Textron Aviation, and Lycoming Engines. It was founded by Royal Little in 1923 as the Special Yarns Company. In 2018, Textron employed over 37,000 people worldwide. The company ranked 208th on the 2018 Fortune 500 of the largest United States corporations by revenue.

Zeta was the original name for General Motors' full-size rear-wheel drive automobile platform developed by GM's Australian subsidiary company Holden and was most recently referred to as the "Global RWD Architecture". The GM Zeta replaced the V-body, and debuted with 2006 Holden Commodore (VE) sedan and Holden (VE) Ute. This platform was considered as the replacement for the North American W, H, and K platforms until plans were cancelled due to fuel-economy considerations and GM's financial situation. Although the future of the Zeta program was in doubt at that time, in May 2009, Holden began the development of an improved second version of the platform that went on to form the basis of the 2013 Commodore (VF) and Chevrolet SS.

Robin Hood Engineering Ltd was a British kit car manufacturer based in Mansfield Woodhouse, Nottinghamshire. The factory covered 30,000 square feet (2,800 m2) and was on a one and a half acre site.

Oshkosh Corporation, formerly Oshkosh Truck, is an American industrial company that designs and builds specialty trucks, military vehicles, truck bodies, airport fire apparatus and access equipment. The corporation also owns Pierce Manufacturing, a fire apparatus manufacturer in Appleton, Wisconsin. Based in Oshkosh, Wisconsin, the company employs approximately 16,000 people around the world. It is organized in four primary business groups: access equipment, defense, fire and emergency, and commercial.
Personal Load Carrying Equipment (PLCE) is one of several current tactical webbing systems of the British Armed Forces. Dependent upon the year of design, and the decade of introduction, the webbing system was designated, and is commonly referred to, as either the 85 Pattern, the 90 Pattern or the 95 Pattern webbing.

Parachute cord is a lightweight nylon kernmantle rope originally used in the suspension lines of parachutes. This cord is now used as a general purpose utility cord. This versatile cord was used by astronauts during the 82nd Space Shuttle mission to repair the Hubble Space Telescope.

The Family of Medium Tactical Vehicles (FMTV) is a series of vehicles, based on a common chassis, that vary by payload and mission requirements. The FMTV is derived from the Austrian Steyr 12M18 truck, but substantially modified to meet U.S. Army requirements, these including a minimum 50 per cent U.S. content.

The Palletized Load System (PLS) is a truck-based logistics system that entered service in the United States Army in 1993. It performs line haul, local haul, unit resupply, and other missions in the tactical environment to support modernized and highly mobile combat units. It provides rapid movement of combat configured loads of ammunition and all classes of supply, shelters and containers. It mirrors similar systems in use with the British and other armed forces.
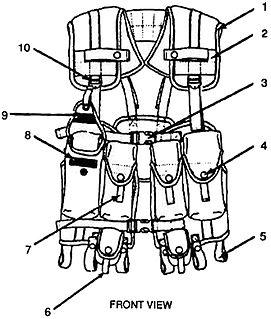
The IIFS was introduced in 1988, to serve as a fighting and existence carrying system - a possible replacement for the All-Purpose Lightweight Individual Carrying Equipment (ALICE) employed and fielded by United States Armed Forces since 1973.
A technical textile is a textile product manufactured for non-aesthetic purposes, where function is the primary criterion. Technical textiles include textiles for automotive applications, medical textiles, geotextiles, agrotextiles, and protective clothing.

IrvinGQ, formerly known as Airborne Systems, is an aerospace manufacturing company based in Llangeinor, Wales, United Kingdom. It specialises in the design, manufacture and supply of a range of parachutes and emergency, rescue and survival equipment for both the military and civilian markets.
Factory Five Racing, Inc. (F.F.R.) is an American automobile company that designs and manufactures assembly kits, chassis, bodies and related components for replicars and sports cars.

The Joint Light Tactical Vehicle (JLTV) is a United States military program to part-replace the Humvee with a family of more survivable vehicles with greater payload. Early studies for the JLTV program were approved in 2006.

The SandCat is a composite armored vehicle designed by the then Plasan Sasa of Israel. The SandCat, which is presented as a single bi-capitalised word, was shown publicly for the first time at AUSA during October 2005. The latest models were shown for the first time at Eurosatory 2018. The SandCat is based on a commercial Ford F-Series chassis. Approximately 700 SandCats have been produced since 2004, and while Plasan has never released complete details, these are known to be in service with at least 16 users across five continents, and in a wide variety of roles that range from Police/internal security to combat/patrol.

The Oshkosh M-ATV is a Mine Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) vehicle developed by the Oshkosh Corporation for the MRAP All Terrain Vehicle (M-ATV) program. Intended to replace M1114 HMMWVs, it is designed to provide the same levels of protection as the larger and heavier previous MRAPs but with improved mobility.

The Oshkosh L-ATV is a light utility/combat multi-role vehicle that won the US military's Army-led Joint Light Tactical Vehicle (JLTV) program. In the very early stages of the program it was suggested that JLTV would replace the AM General High Mobility Multi-purpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV) on a one-for-one basis. It is now suggested that the JLTV will part-replace the HMMWV, not replacing it on a like-for-like basis.

















