
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the 3+1⁄2-mile (5.6-kilometre) wide, 295-foot deep Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; the two are geologically a single lake.

The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to Landsat 1 in 1975. The most recent, Landsat 9, was launched on 27 September 2021.

A pole of inaccessibility with respect to a geographical criterion of inaccessibility marks a location that is the most challenging to reach according to that criterion. Often it refers to the most distant point from the coastline, implying a maximum degree of continentality or oceanity. In these cases, a pole of inaccessibility can be defined as the center of the largest circle that can be drawn within an area of interest without encountering a coast. Where a coast is imprecisely defined, the pole will be similarly imprecise.
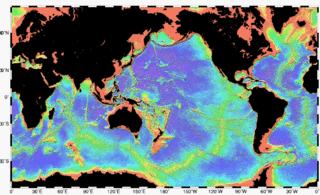
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors, lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetric charts, are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines and selected depths (soundings), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a global relief model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwater depths.

Generic Mapping Tools (GMT) are an open-source collection of computer software tools for processing and displaying xy and xyz datasets, including rasterization, filtering and other image processing operations, and various kinds of map projections. The software stores 2-D grids as COARDS-compliant netCDF files and comes with a comprehensive collection of free GIS data, such as coast lines, rivers, political borders and coordinates of other geographic objects. Users convert further data from other sources and import them. GMT stores the resulting maps and diagrams in PostScript (PS) or Encapsulated PostScript (EPS) format.
The Vector Map (VMAP), also called Vector Smart Map, is a vector-based collection of geographic information system (GIS) data about Earth at various levels of detail. Level 0 (low resolution) coverage is global and entirely in the public domain. Level 1 (global coverage at medium resolution) is only partly in the public domain.

NOAA-19, known as NOAA-N' before launch, is the last of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) series of weather satellites. NOAA-19 was launched on 6 February 2009. NOAA-19 is in an afternoon Sun-synchronous orbit and is intended to replace NOAA-18 as the prime afternoon spacecraft.

NOAA-15, also known as NOAA-K before launch, is an operational, polar-orbiting of the NASA-provided Television Infrared Observation Satellite (TIROS) series of weather forecasting satellite operated by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-15 was the latest in the Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) series. It provided support to environmental monitoring by complementing the NOAA/NESS Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite program (GOES).
NOAA-13, also known as NOAA-I before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-I continued the operational, polar orbiting, meteorological satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite System (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-I continued the series (fifth) of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983. NOAA-I was in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and was intended to replace the NOAA-11 (NOAA-H) as the prime afternoon (14:00) spacecraft.

NOAA-7, known as NOAA-C before launch, was an American operational weather satellite for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for the support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978-1984. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment. An earlier launch, NOAA-B, was scheduled to become NOAA-7, however NOAA-B failed to reach its required orbit.
NOAA-6, known as NOAA-A before launch, was an American operational weather satellite for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for the support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978-1984. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
Pål Wessel, pronounced as, and also known as, Paul Wessel, is a professor of the Department of Geology and Geophysics at the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) at the University of Hawaii. He has taught as a visiting professor at Sydney University in Australia and University of Oslo in Norway. Dr. Wessel is a Fellow of the Geological Society of America.

Sandy Island is a non-existent island that was charted for over a century as being located near the French territory of New Caledonia between the Chesterfield Islands and Nereus Reef in the eastern Coral Sea. The island was included on many maps and nautical charts from as early as the late 19th century. It was removed from French hydrographic charts in 1974. The island gained wide media and public attention in November 2012 when the R/V Southern Surveyor, an Australian research ship, passed through the area and "undiscovered" it. The island was quickly removed from many maps and data sets, including those of the National Geographic Society and Google Maps.

NOAA-20, designated JPSS-1 prior to launch, is the first of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System. NOAA-20 was launched on 18 November 2017 and joined the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite in the same orbit. NOAA-20 operates about 50 minutes behind Suomi NPP, allowing important overlap in observational coverage. Circling the Earth from pole-to-pole, it crosses the equator about 14 times daily, providing full global coverage twice a day. This gives meteorologists information on "atmospheric temperature and moisture, clouds, sea-surface temperature, ocean color, sea ice cover, volcanic ash, and fire detection" so as to enhance weather forecasting including hurricane tracking, post-hurricane recovery by detailing storm damage and mapping of power outages.
NOAA-8, known as NOAA-E before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was first of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.

NOAA-9, known as NOAA-F before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was the second of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-10, known as NOAA-G before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was the third of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-11, known as NOAA-H before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978–1984. It was the fourth of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-12, also known as NOAA-D before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an operational meteorological satellite for use in the National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service (NESDIS). The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
Walter H. F. Smith is a geophysicist, currently working in NOAA's Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry. He was formerly Chair of the scientific and technical sub-committee of GEBCO from 2003 to 2013.












