
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and software that store, manage, analyze, edit, output, and visualize geographic data. Much of this often happens within a spatial database, however, this is not essential to meet the definition of a GIS. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system also to include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, the body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations.

A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems (GIS), and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps. A digital terrain model (DTM) represents specifically the ground surface while DEM and DSM may represent tree top canopy or building roofs.

Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.

The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) in support of national security. Initially known as the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA) from 1996 to 2003, it is a member of the United States Intelligence Community.
A GIS file format is a standard for encoding geographical information into a computer file, as a specialized type of file format for use in geographic information systems (GIS) and other geospatial applications. Since the 1970s, dozens of formats have been created based on various data models for various purposes. They have been created by government mapping agencies, GIS software vendors, standards bodies such as the Open Geospatial Consortium, informal user communities, and even individual developers.

Clip art is a type of graphic art. Pieces are pre-made images used to illustrate any medium. Today, clip art is used extensively and comes in many forms, both electronic and printed. However, most clip art today is created, distributed, and used in a digital form. Since its inception, clip art has evolved to include a wide variety of content, file formats, illustration styles, and licensing restrictions. It is generally composed exclusively of illustrations, and does not include stock photography.
Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland (OSNI) was the official mapping agency of Northern Ireland. The agency ceased to exist separately on 1 April 2008 when it became part of Land and Property Services, an executive agency of the Northern Ireland Department of Finance and Personnel, along with the Rate Collection Agency, the Valuation and Lands Agency, and the Land Registry.
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, analyze, and visualize geographic data, that is, data representing phenomena for which location is important. The GIS software industry encompasses a broad range of commercial and open-source products that provide some or all of these capabilities within various information technology architectures.

In the United States, geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) is intelligence about the human activity on earth derived from the exploitation and analysis of imagery, signals, or signatures with geospatial information. GEOINT describes, assesses, and visually depicts physical features and geographically referenced activities on the Earth. GEOINT, as defined in US Code, consists of imagery, imagery intelligence (IMINT) and geospatial information.
The Digital Chart of the World (DCW) is a comprehensive digital map of Earth. It is the most comprehensive geographical information system (GIS) global database that is freely available as of 2006, although it has not been updated since 1992.
The Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo), is a non-profit non-governmental organization whose mission is to support and promote the collaborative development of open geospatial technologies and data. The foundation was formed in February 2006 to provide financial, organizational and legal support to the broader Free and open-source geospatial community. It also serves as an independent legal entity to which community members can contribute code, funding and other resources.

The Geospatial Data Abstraction Library (GDAL) is a computer software library for reading and writing raster and vector geospatial data formats, and is released under the permissive X/MIT style free software license by the Open Source Geospatial Foundation. As a library, it presents a single abstract data model to the calling application for all supported formats. It may also be built with a variety of useful command line interface utilities for data translation and processing. Projections and transformations are supported by the PROJ library.
MapInfo Pro is a desktop geographic information system (GIS) software product produced by Precisely and used for mapping and location analysis. MapInfo Pro allows users to visualize, analyze, edit, interpret, understand and output data to reveal relationships, patterns, and trends. MapInfo Pro allows users to explore spatial data within a dataset, symbolize features, and create maps.

Web mapping or an online mapping is the process of using maps, usually created through geographic information systems (GIS) on the Internet, more specifically in the World Wide Web. A web map or an online map is both served and consumed, thus, web mapping is more than just web cartography, it is a service where consumers may choose what the map will show.
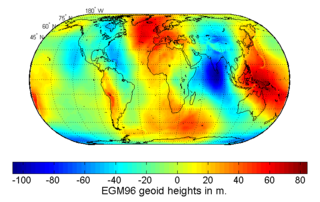
The Earth Gravitational Models (EGM) are a series of geopotential models of the Earth published by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). They are used as the geoid reference in the World Geodetic System.
Wind resource assessment is the process by which wind power developers estimate the future energy production of a wind farm. Accurate wind resource assessments are crucial to the successful development of wind farms.

The SRTM Water Body Data (SWBD) is a geographical dataset (2003) encoding high-resolution worldwide coastline outlines in a vector format, published by NASA and designed for use in geographic information systems and mapping applications. It was created by BAE Systems ADR for the US National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) as a complementary product during editing of the digital elevation model database of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). SWBD data covers the Earth's surface between 56° southern latitude and 60° northern latitude. It is distributed in ESRI shapefile format, divided into 12,229 files, each covering one 1°-by-1° tile of the Earth's surface.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of GIS vector file format. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are based on the stable versions without any add-ons, extensions or external programs.
Geographic information systems (GIS) play a constantly evolving role in geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) and United States national security. These technologies allow a user to efficiently manage, analyze, and produce geospatial data, to combine GEOINT with other forms of intelligence collection, and to perform highly developed analysis and visual production of geospatial data. Therefore, GIS produces up-to-date and more reliable GEOINT to reduce uncertainty for a decisionmaker. Since GIS programs are Web-enabled, a user can constantly work with a decision maker to solve their GEOINT and national security related problems from anywhere in the world. There are many types of GIS software used in GEOINT and national security, such as Google Earth, ERDAS IMAGINE, GeoNetwork opensource, and Esri ArcGIS.

Leo A. Hazlewood was Director of National Photographic Interpretation Center from February 1991 – September 1993), and Deputy Director of National Imagery and Mapping Agency from July 1997 – January 2000. He also served as Deputy Director of Operations at National Imagery and Mapping Agency.












