Related Research Articles
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or other organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information.

Marketing is the act of satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of business management and commerce.

Sales are activities related to selling or the number of goods sold in a given targeted time period. The delivery of a service for a cost is also considered a sale. A period during which goods are sold for a reduced price may also be referred to as a "sale".
Marketing research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of qualitative and quantitative data about issues relating to marketing products and services. The goal is to identify and assess how changing elements of the marketing mix impacts customer behavior.
New product development (NPD) or product development in business and engineering covers the complete process of launching a new product to the market. Product development also includes the renewal of an existing product and introducing a product into a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design. New product development is the realization of a market opportunity by making a product available for purchase. The products developed by an commercial organisation provide the means to generate income.
Marketing management is the strategic organizational discipline that focuses on the practical application of marketing orientation, techniques and methods inside enterprises and organizations and on the management of marketing resources and activities. Compare marketology, which Aghazadeh defines in terms of "recognizing, generating and disseminating market insight to ensure better market-related decisions".
Market penetration refers to the successful selling of a good or service in a specific market. It involves using tactics that increase the growth of an existing product in an existing market. It is measured by the amount of sales volume of an existing good or service compared to the total target market for that product or service. Market penetration is the key for a business growth strategy stemming from the Ansoff Matrix (Richardson, M., & Evans, C.. H. Igor Ansoff first devised and published the Ansoff Matrix in the Harvard Business Review in 1957, within an article titled "Strategies for Diversification". The grid/matrix is utilized across businesses to help evaluate and determine the next stages the company must take in order to grow and the risks associated with the chosen strategy. With numerous options available, this matrix helps narrow down the best fit for an organization.

Proof of concept, also known as proof of principle, is a realization of a certain idea, method or principle in order to demonstrate its feasibility, or viability, or a demonstration in principle with the aim of verifying that some concept or theory has practical potential. A proof of concept is usually small and may or may not be complete.
Database marketing is a form of direct marketing that uses databases of customers or potential customers to generate personalized communications in order to promote a product or service for marketing purposes. The method of communication can be any addressable medium, as in direct marketing.
International business refers to the trade of Goods and service goods, services, technology, capital and/or knowledge across national borders and at a global or transnational scale.
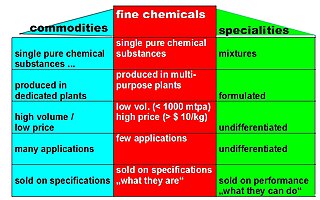
In chemistry, fine chemicals are complex, single, pure chemical substances, produced in limited quantities in multipurpose plants by multistep batch chemical or biotechnological processes. They are described by exacting specifications, used for further processing within the chemical industry and sold for more than $10/kg. The class of fine chemicals is subdivided either on the basis of the added value, or the type of business transaction, namely standard or exclusive products.
Business marketing is a marketing practice of individuals or organizations. It allows them to sell products or services to other companies or organizations, who either resell them, use them in their products or services, or use them to support their work.
The target audience is the intended audience or readership of a publication, advertisement, or other message catered specifically to the previously intended audience. In marketing and advertising, the target audience is a particular group of consumer within the predetermined target market, identified as the targets or recipients for a particular advertisement or message.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to marketing:
A target market, also known as serviceable obtainable market (SOM), is a group of customers within a business's serviceable available market at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. A target market is a subset of the total market for a product or service.
Product planning is the ongoing process of identifying and articulating market requirements that define a product's feature set. It serves as the basis for decision-making about price, distribution and promotion. Product planning is also the means by which companies and businesses can respond to long-term challenges within the business environment, often achieved by managing the product throughout its life cycle using various marketing strategies, including product extensions or improvements, increased distribution, price changes and promotions. It involves understanding the needs and wants of core customer groups so products can target key customer desires and allows a firm to predict how a product will be received within a market upon launch.

The purchase funnel, or purchasing funnel, is a consumer-focused marketing model that illustrates the theoretical customer journey toward the purchase of a good or service.
Marketing automation refers to software platforms and technologies designed for marketing departments and organizations automate repetitive tasks and consolidate multi-channel interactions, tracking and web analytics, lead scoring, campaign management and reporting into one system. It often integrates with customer relationship management (CRM) and customer data platform (CDP) software.
Product strategy defines the high-level plan for developing and marketing a product, how the product supports the business strategy and goals, and is brought to life through product roadmaps. A product strategy describes a vision of the future with this product, the ideal customer profile and market to serve, go-to-market and positioning (marketing), thematic areas of investment, and measures of success. A product strategy sets the direction for new product development. Companies utilize the product strategy in strategic planning and marketing to set the direction of the company's activities. The product strategy is composed of a variety of sequential processes in order for the vision to be effectively achieved. The strategy must be clear in terms of the target customer and market of the product in order to plan the roadmap needed to achieve strategic goals and give customers better value.
Rural marketing is the process of developing, pricing, promoting and distributing rural specific products and services leading to consumer satisfaction and achievement of organizational objectives. It aims to improve standard of living of rural consumers by providing them greater awareness and accessibility to new products and services.
References
- Jolly, Vijay K.(1997): Commercializing New Technologies: Getting from Mind to Market; Harvard Business School Press. [Note: a new edition was due in early 2009.]