
Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi) and a population of 2.3 million people. There are coastal plains, mountains, and a savanna in the east. Libreville is the country's capital and largest city.
Little is known of the history of Gabon before European contact. Bantu migrants settled the area beginning in the 14th century. Portuguese explorers and traders arrived in the area in the late 15th century. The coast subsequently became a centre of the transatlantic slave trade with European slave traders arriving to the region in the 16th century. In 1839 and 1841, France established a protectorate over the coast. In 1849, captives released from a captured slave ship founded Libreville. In 1862–1887, France expanded its control including the interior of the state, and took full sovereignty. In 1910 Gabon became part of French Equatorial Africa and in 1960, Gabon became independent.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in North America.

An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.

The SS Richard Montgomery is a wrecked American Liberty cargo ship that was built during World War II. She was named after Richard Montgomery, an Irish officer who fought in the American Revolutionary War.

The River Blackwater is a river in Essex, England. It rises as the River Pant in the northwest of the county, just east of Saffron Walden, and flows in a generally southeast direction to Bocking, near Braintree, via Great Sampford and Great Bardfield. At Bocking, it becomes the River Blackwater, and veers east to flow past Bradwell Juxta Coggeshall and Coggeshall. It then veers south, flowing past Kelvedon and Witham, before reaching Maldon. There, it veers east again and empties into the Blackwater Estuary, which in turn meets the North Sea at Mersea Island.

PS Tattershall Castle is a floating pub and restaurant moored on the River Thames at Victoria Embankment. It was a passenger ferry across the Humber estuary from 1934 to 1973, before being towed to London in 1976.

The Blackwater Estuary is the estuary of the River Blackwater between Maldon and West Mersea in Essex. It is a 5,538 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI). An area of 4,395 hectares is also designated a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance, and a Special Protection Area 1,099 hectares is a National Nature Reserve. Tollesbury Wick and part of Abbotts Hall Farm, both nature reserve managed by the Essex Wildlife Trust, are in the SSSI.

The Muni is an estuary of several rivers of Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. Part of its length form part of the border with Gabon. It is from this estuary that the former name for this part of Equatorial Guinea, Río Muni was taken.
The Kingdom of Orungu was a small, pre-colonial state of what is now Gabon in Central Africa. Through its control of the slave trade in the 18th and 19th centuries, it was able to become the most powerful of the trading centers that developed in Gabon during that period.
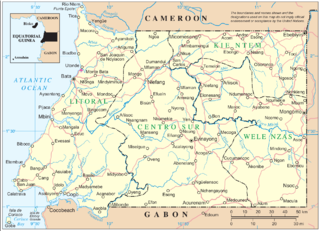
The Mitimele is a river of southwestern mainland Equatorial Guinea. It forms part of the Muni Estuary along with the Mitong River, Mandyani River, Congue River, Utamboni River and Mven River. The river becomes the Utamboni River along the border with Gabon.

The Utamboni is a river of southwestern mainland Equatorial Guinea. It flows along the border with Gabon and forms part of the Muni Estuary along with the Mitimele River, Mitong River, Mandyani River, Congue River, and Mven River. The river becomes the Utamboni River along the border with Gabon.

The Dove is a Grade II listed public house at 19 Upper Mall, Hammersmith, London W6 9TA.

The Crouch and Roach Estuaries are a 1729 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) at the mouth of the Crouch and Roach rivers in Essex. The Crouch part of the SSSI stretches from near Battlesbridge to Foulness Island, and the Roach from Rochford to the junction with the Crouch. Part of the site is in the Mid-Essex Coast Special Protection Area under the EC Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds, and a Ramsar wetland site of international importance. It is also part of the Essex Estuaries Special Area of Conservation. An area of 65 hectares is managed by the Essex Wildlife Trust as the Lion Creek and Lower Raypits nature reserve and 8 hectares at Woodham Fen, both of which are managed by the Essex Wildlife Trust. A small area is also a geological SSSI, The Cliff, Burnham-on-Crouch.

Foulness SSSI is a 10,702 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest covering the shoreline between Southend-on-Sea and the Crouch estuary in Essex.

Mucking Flats and Marshes is a 311.6 biological Site of Special Scientific Interest east of Tilbury in Essex. It is part of the Thames Estuary and Marshes Ramsar site. and Special Protection Area

Holehaven Creek is a 272.9-hectare (674-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) between Canvey Island and Corringham in Essex.

Woodham Fen is an 8.1-hectare (20-acre) nature reserve in South Woodham Ferrers in Essex. It is managed by the Essex Wildlife Trust. It is part of the Crouch and Roach Estuaries Site of Special Scientific Interest.

Medway Estuary and Marshes is a 4,748.8-hectare (11,735-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest which stretches along the banks of the River Medway between Gillingham and Sheerness in Kent. It is a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I, a Ramsar internationally important wetland site, and a Special Protection Area under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds.

South Thames Estuary and Marshes is a 5,289-hectare (13,070-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest which stretches between Gravesend and the mouth of the River Medway in Kent. Part of it is a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I, and part is a Royal Society for the Protection of Birds nature reserve. It is part of the Thames Estuary and Marshes Ramsar internationally important wetland site and Special Protection Area under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds.

















