
A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as boats rather than ships irrespective of their size.

A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes.

United States naval reactors are nuclear reactors used by the United States Navy aboard certain ships to generate the steam used to produce power for propulsion, electric power, catapulting airplanes in aircraft carriers, and a few more minor uses. Such naval nuclear reactors have a complete power plant associated with them. All U.S. Navy submarines and supercarriers built since 1975 are nuclear-powered by such reactors. There are no commissioned conventional (non-nuclear) submarines or aircraft carriers left in the U.S. Navy, since the last conventional carrier, USS Kitty Hawk, was decommissioned in May 2009. The U.S. Navy had nine nuclear-powered cruisers with such reactors also, but they have since been decommissioned. Reactors are designed by a variety of contractors, then developed and tested at one of several government owned and prime contractor-operated facilities: Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory in West Mifflin, Pennsylvania and its associated Naval Reactors Facility in Idaho, and Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory in Niskayuna, New York and its associated Kesselring site in West Milton, New York, all under the management of the office of Naval Reactors. Sometimes there were full-scale nuclear-powered prototype plants built at the Naval Reactors Facility, Kesselring, and Windsor to test the nuclear plants, which were operated for years to train nuclear-qualified sailors.

A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster and more maneuverable than merchant ships. Unlike a merchant ship, which carries cargo, a warship typically carries only weapons, ammunition and supplies for its crew. Warships usually belong to a navy, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations.

The Tang-class submarines were the first submarines designed and built by the United States Navy after WWII. They incorporated the best features of the high-speed German Type XXI U-boat and the venerable U.S. Navy fleet submarine. The Tang-class, with the fleet submarines converted under the Greater Underwater Propulsion Power (GUPPY) program, had much higher submerged performance than their predecessors, but were quickly surpassed by the nuclear-propelled submarines that entered service beginning in 1954. Six units in total were built.

The V-boats were a group of nine United States Navy submarines built between World War I and World War II from 1921 to 1934 under authorization as the "fleet boat" program.
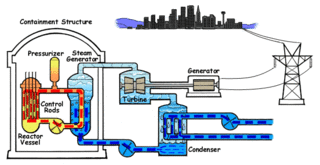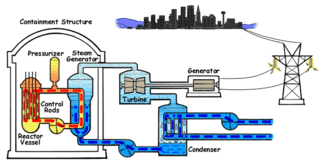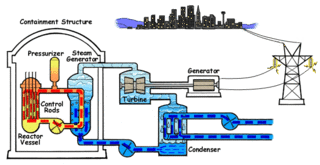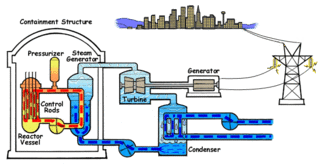
Nuclear propulsion includes a wide variety of propulsion methods that use some form of nuclear reaction as their primary power source. The idea of using nuclear material for propulsion dates back to the beginning of the 20th century. In 1903 it was hypothesized that radioactive material, radium, might be a suitable fuel for engines to propel cars, planes, and boats. H. G. Wells picked up this idea in his 1914 fiction work The World Set Free.

The Sargo-class submarines were among the first United States submarines to be sent into action after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, starting war patrols the day after the attack, having been deployed to the Philippines in late 1941. Similar to the previous Salmon class, they were built between 1937 and 1939. With a top speed of 21 knots, a range of 11,000 nautical miles (20,000 km), and a reliable propulsion plant, along with the Salmons they were an important step in the development of a true fleet submarine. In some references, the Salmons and Sargos are called the "New S Class", 1st and 2nd Groups.

A diesel–electric transmission, or diesel–electric powertrain is a transmission system for vehicles powered by diesel engines in road, rail, and marine transport. Diesel–electric transmission is based on petrol–electric transmission, a very similar transmission system used for petrol engines.
Air-independent propulsion (AIP), or air-independent power, is any marine propulsion technology that allows a non-nuclear submarine to operate without access to atmospheric oxygen. AIP can augment or replace the diesel-electric propulsion system of non-nuclear vessels.
The history of the submarine spans the entire history of human endeavour as mankind has since early civilisation sought to explore and travel under the sea. Humanity has employed a variety of methods to travel underwater for exploration, recreation, research and significantly warfare. While early attempts, such as those by Alexander the Great, were rudimentary, the advent of new propulsion systems, fuels, and sonar, propelled an increase in submarine technology. The introduction of the diesel engine, then the nuclear submarine, saw great expansion in submarine use - and specifically military use - during World War I, World War II, and the Cold War. The Second World War use of the U-Boat by the German Navy against the Royal Navy and commercial shipping, and the Cold War's use of submarines by the United States and Russia, helped solidify the submarine's place in popular culture. The latter conflicts also saw an increasing role for the military submarine as a tool of subterfuge, hidden warfare, and nuclear deterrent. The military use of submarines continues to this day, predominantly by North Korea, China, the United States and Russia.

The S-class or Srednyaya submarines were part of the Soviet Navy's underwater fleet during World War II. Unofficially nicknamed Stalinets, boats of this class were the most successful and achieved the most significant victories among all Soviet submarines. In all, they sank 82,770 gross register tons (GRT) of merchant shipping and seven warships, which accounts for about one-third of all tonnage sunk by Soviet submarines during the war.

Farfadet (Q7) was an early submarine built for the French Navy at the beginning of the 20th century. She was of the Maugas type, and the name ship of her class. Farfadet accidentally sank in July 1905 at Bizerte with the loss of 14 men of her crew; two men survived. She was later refloated and recommissioned as the Follet (Q7). She was stricken in November 1913.

Maxime Laubeuf was a French maritime engineer of the late nineteenth century. He was born on 23 November 1864 at Poissy, Yvelines, and died on 23 December 1939 in Cannes, Alpes-Maritimes.

French submarine Narval (“Narwhal”) was a pioneering vessel of the French Navy, designed by Maxime Laubeuf and built at the end of the 19th century. She was designed in response to a competition set by the French Admiralty and had several revolutionary features which set the pattern for submarines for the next 50 years.
Gaston Romazotti was a French naval engineer of the late 19th and early 20th century, and an early designer of submarines.

The Naïade-class submarines, sometimes referred to as the Perle class were a group of submarines built for the French Navy at the beginning of the 20th century. There were twenty vessels in this class, which was designed by Gaston Romazotti. The class introduced internal combustion engines into French submarine design. They remained in service until just prior to the outbreak of the First World War.

The Farfadet class consisted of four submarines built for the French Navy at the beginning of the 20th century designed by Gabriel Maugas. Two boats were lost in diving accidents. All were disposed of prior to the outbreak of the First World War.
Z51 was the only ship of the Type 1942 destroyer class built for the Kriegsmarine. She was the only destroyer built by the Kriegsmarine to use diesel fuel, which would have given it a longer range and readier access to refueling compared to fuel oil. The Type 1942 destroyer class went through a long period of development, including four total designs. Z51 was ordered on 25 November 1942, and launched on 2 October 1944, far before being finished, likely to clear her slipway for U-boat construction. She was left floating outside Bremen and was sunk in an air raid on 21 March 1945. Germany attempted to communicate the plans for the Type 1942 destroyer to its ally the Empire of Japan using a submarine, U-234, however Germany surrendered before the submarine reached Japan. Z51 was broken up between 1948 and 1949.

The French submarine Z was an experimental submarine built for the French Navy between 1902 and 1905. It was laid down in April 1902, launched in March 1904 and completed in 1905. Designed by Gabriel Maugas, Z was essentially an experimental submarine and it was the first French submarine to be commissioned with a diesel engine although Aigrette was the first to be launched.
















