Related Research Articles

Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator, was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was censor in 230 BC. His agnomen, Cunctator, usually translated as "the delayer", refers to the strategy that he employed against Hannibal's forces during the Second Punic War. Facing an outstanding commander with superior numbers, he pursued a then-novel strategy of targeting the enemy's supply lines, and accepting only smaller engagements on favourable ground, rather than risking his entire army on direct confrontation with Hannibal himself. As a result, he is regarded as the originator of many tactics used in guerrilla warfare.
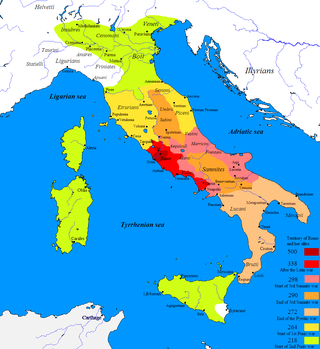
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.
Gaius Marcius Rutilus was the first plebeian dictator and censor of ancient Rome, and was consul four times.
Agrarian laws were laws among the Romans regulating the division of the public lands, or ager publicus. In its broader definition, it can also refer to the agricultural laws relating to peasants and husbandmen, or to the general farming class of people of any society.
Land reform in the Roman republic was a system first attempted in the Roman Republic in 486 BC under the consulships of Spurius Cassius Vecellinus, and Proculus Verginius Tricostus Rutilus.

The gens Marcia, occasionally written Martia, was one of the oldest and noblest houses at ancient Rome. They claimed descent from the second and fourth Roman Kings, and the first of the Marcii appearing in the history of the Republic would seem to have been patrician; but all of the families of the Marcii known in the later Republic were plebeian. The first to obtain the consulship was Gaius Marcius Rutilus in 357 BC, only a few years after the passage of the lex Licinia Sextia opened this office to the plebeians.
The gens Sempronia was one of the most ancient and noble houses of ancient Rome. Although the oldest branch of this gens was patrician, with Aulus Sempronius Atratinus obtaining the consulship in 497 BC, the thirteenth year of the Republic, but from the time of the Samnite Wars onward, most if not all of the Sempronii appearing in history were plebeians. Although the Sempronii were illustrious under the Republic, few of them attained any importance or notice in imperial times.
The gens Verginia or Virginia was a prominent family at ancient Rome, which from an early period was divided into patrician and plebeian branches. The gens was of great antiquity. It frequently filled the highest honors of the state during the early years of the Republic. The first of the family who obtained the consulship was Opiter Verginius Tricostus in 502 BC, the seventh year of the Republic. The plebeian members of the family were also numbered amongst the early tribunes of the people.
The Roman–Volscian wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Volsci, an ancient Italic people. Volscian migration into southern Latium led to conflict with that region's old inhabitants, the Latins under leadership of Rome, the region's dominant city-state. By the late 5th century BC, the Volsci were increasingly on the defensive and by the end of the Samnite Wars had been incorporated into the Roman Republic. The ancient historians devoted considerable space to Volscian wars in their accounts of the early Roman Republic, but the historical accuracy of much of this material has been questioned by modern historians.
Gaius Plautius Venox was a Roman statesman and general who served as consul in 347 and 341 BC. Plautius was a member of the family of the Plautii, a relatively undistinguished plebeian gens who had only achieved their first consulship in 358 BC. Plautius' father and grandfather were both named Lucius and may have had a son named Gaius, who was the father of Gaius Plautius Venox, Censor in 312 BC.
Gaius Plautius Decianus was a Roman general and politician who served as consul once in 329 BC. Plautius was from a plebeian family whose first consul, Gaius Plautius Proculus, had only attained the position in 358 BC, meaning that Plautius, and his family as of large, lacked the same kind of political clout which was held by more prominent patrician families. As for his exact lineage, nothing is known other than that both his father and grandfather were named Publius.
The Roman-Aequian wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their eastern neighbours, the Aequi.
Lucius Papirius Crassus was a Roman politician. He was appointed dictator in 340 BC, and consul in 336 BC and 330 BC. Lucius Papirius was from the Papiria gens (family) in Rome.
Gaius Julius Iulus was a member of the Roman gens Julia, and was nominated dictator in 352 BC.

The gens Plautia, sometimes written Plotia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens first appear in history in the middle of the fourth century BC, when Gaius Plautius Proculus obtained the consulship soon after that magistracy was opened to the plebeian order by the Licinio-Sextian rogations. Little is heard of the Plautii from the period of the Samnite Wars down to the late second century BC, but from then to imperial times they regularly held the consulship and other offices of importance. In the first century AD, the emperor Claudius, whose first wife was a member of this family, granted patrician status to one branch of the Plautii.
Publius Cornelius Rutilus Cossus was a statesman and military commander from the early Roman Republic who served as Dictator in 408 BC.
Spurius Nautius Rutilus was a consul of the Roman Republic in 411 and a consular tribune in 419, 416 and 404 BC.
Gaius Valerius Potitus Volusus was a consul in 410 BC and consular tribune in 415, 407 and 404 BC of the Roman Republic.
Lucius Valerius Potitus was a five time consular tribune, in 414, 406, 403, 401 and 398 BC, and two times consul, in 393 and 392 BC, of the Roman Republic.
References
- ↑ Nicola Terrenato, "Private Vis, Public Virtus: Family agendas during the early Roman expansion", in Roman Republican Colonization New Perspectives from Archaeology and Ancient History, edited by Tesse D. Stek and Jeremia Pelgrom (Rome: Papers of the Royal Netherlands Institute in Rome, 2014), pp. 48f
- 1 2 Terrenato, "Private Vis", p. 49