Roman or Romans most often refers to:

Vercingetorix was a king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Despite having willingly surrendered to Caesar, he was executed in Rome.

Gaul was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, and parts of Northern Italy, the Netherlands, and Germany, particularly the west bank of the Rhine. It covered an area of 494,000 km2 (191,000 sq mi). According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of Gaul in his campaigns of 58 to 51 BC.

Commentarii de Bello Gallico, also Bellum Gallicum, is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting the Celtic and Germanic peoples in Gaul that opposed Roman conquest.

Germania, also called Magna Germania, Germania Libera, or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-central Europe during the Roman era, which was associated by Roman authors with the Germanic peoples. The region stretched roughly from the Middle and Lower Rhine in the west to the Vistula in the east. It also extended as far south as the Upper and Middle Danube and Pannonia, and to the known parts of Scandinavia in the north. Archaeologically, these peoples correspond roughly to the Roman Iron Age of those regions. While apparently dominated by Germanic peoples, Magna Germania was also inhabited by Celts.
Colonia Copia Claudia Augusta Lugdunum was an important Roman city in Gaul, established on the current site of Lyon. The city was founded in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus. It served as the capital of the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis and was an important city in the western half of the Roman Empire for centuries. Two emperors, Claudius and Caracalla, were born in Lugdunum. In the period AD 69–192 the city's population may have numbered 50,000 to 100,000, and possibly up to 200,000 inhabitants.

The Remi were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the Aisne, Vesle and Suippe river valleys during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Their territory roughly corresponded the modern Marne and Ardennes and parts of the Aisne and Meuse departments.
The Volcae were a Gallic tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedonia c. 270 BC and fought the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC. Tribes known by the name Volcae were found simultaneously in southern Gaul, Moravia, the Ebro valley of the Iberian Peninsula, and Galatia in Anatolia. The Volcae appear to have been part of the late La Tène material culture, and a Celtic identity has been attributed to the Volcae, based on mentions in Greek and Latin sources as well as onomastic evidence. Driven by highly mobile groups operating outside the tribal system and comprising diverse elements, the Volcae were one of the new ethnic entities formed during the Celtic military expansion at the beginning of the 3rd century BC. Collecting in the famous excursion into the Balkans, ostensibly, from the Greek point of view, to raid Delphi, a branch of the Volcae split from the main group on the way into the Balkans and joined two other tribes, the Tolistobogii and the Trocmi, to settle in central Anatolia and establish a new identity as the Galatians.

Louis Laurent Gabriel de Mortillet, French archaeologist and anthropologist, was born at Meylan, Isère.

Roman Gaul refers to Gaul under provincial rule in the Roman Empire from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD.
The name France comes from Latin Francia.

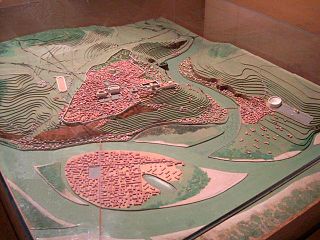
Alesia was the capital of the Mandubii, one of the Gallic tribes allied with the Aedui. The Celtic oppidum was conquered by Julius Caesar during the Gallic Wars and afterwards became a Gallo-Roman town. Modern understanding of its location was controversial for a long time; however, it is now thought to have been located on Mont-Auxois, near Alise-Sainte-Reine in Burgundy, France.

Alise-Sainte-Reine (Alise-Ste-Reine) is a commune in the Côte-d'Or department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region of eastern France.

The Gallic rooster is an official national symbol of France as a nation, as opposed to Marianne representing France as a state and its values: the Republic. The rooster is also the symbol of the Wallonia region and the French Community of Belgium.
Antenor is the name of several historical and mythological Ancient Greek people. In modern times, the name is mainly attested in Latin America and the Caribbean. It may refer to:
The various names used since classical times for the people known today as the Celts are of disparate origins.

Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gaulish peoples under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context. The well-studied meld of cultures in Gaul gives historians a model against which to compare and contrast parallel developments of Romanization in other, less-studied Roman provinces.

The Gauls were a group of Celtic peoples of Continental Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period. The area they originally inhabited was known as Gaul. Their Gaulish language is a Continental Celtic language.
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul. In a wider sense, it also comprises varieties of Celtic that were spoken across much of central Europe ("Noric"), parts of the Balkans, and Anatolia ("Galatian"), which are thought to have been closely related. The more divergent Lepontic of Northern Italy has also sometimes been subsumed under Gaulish.












