
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size, and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix.

Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs as well as organism structure and function. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.

Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.

Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into organology, the study of organs, histology, the study of tissues, and cytology, the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms.
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions.
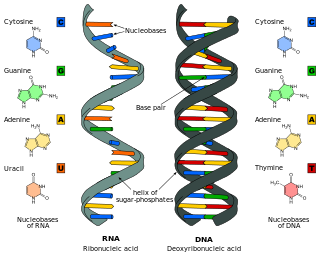
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA.

Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is a technique widely used in biochemistry, forensic chemistry, genetics, molecular biology and biotechnology to separate biological macromolecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, according to their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic mobility is a function of the length, conformation, and charge of the molecule. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used to analyze RNA samples. When polyacrylamide gel is denatured after electrophoresis, it provides information on the sample composition of the RNA species.

Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids is an analytical technique to separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules are placed on a gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the positively charged anode. The molecules separate as they travel through the gel based on the each molecule's size and shape. Longer molecules move more slowly because the gel resists their movement more forcefully than it resists shorter molecules. After some time, the electricity is turned off and the positions of the different molecules are analyzed.

A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set dyes on fabrics. It does this by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric. It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in cell or tissue preparations. Although mordants are still used, especially by small batch dyers, they have been largely displaced in industry by directs.

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology, in cytology, and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.
The Bradford protein assay was developed by Marion M. Bradford in 1976. It is a quick and accurate spectroscopic analytical procedure used to measure the concentration of protein in a solution. The reaction is dependent on the amino acid composition of the measured proteins.

Papanicolaou stain is a multichromatic (multicolored) cytological staining technique developed by George Papanicolaou in 1942. The Papanicolaou stain is one of the most widely used stains in cytology, where it is used to aid pathologists in making a diagnosis. Although most notable for its use in the detection of cervical cancer in the Pap test or Pap smear, it is also used to stain non-gynecological specimen preparations from a variety of bodily secretions and from small needle biopsies of organs and tissues. Papanicolaou published three formulations of this stain in 1942, 1954, and 1960.

An electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) or mobility shift electrophoresis, also referred as a gel shift assay, gel mobility shift assay, band shift assay, or gel retardation assay, is a common affinity electrophoresis technique used to study protein–DNA or protein–RNA interactions. This procedure can determine if a protein or mixture of proteins is capable of binding to a given DNA or RNA sequence, and can sometimes indicate if more than one protein molecule is involved in the binding complex. Gel shift assays are often performed in vitro concurrently with DNase footprinting, primer extension, and promoter-probe experiments when studying transcription initiation, DNA gang replication, DNA repair or RNA processing and maturation, as well as pre-mRNA splicing. Although precursors can be found in earlier literature, most current assays are based on methods described by Garner and Revzin and Fried and Crothers.
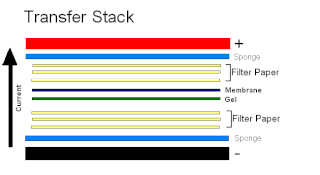
Electroblotting is a method in molecular biology/biochemistry/immunogenetics to transfer proteins or nucleic acids onto a membrane by using PVDF or nitrocellulose, after gel electrophoresis. The protein or nucleic acid can then be further analyzed using probes such as specific antibodies, ligands like lectins, or stains. This method can be used with all polyacrylamide and agarose gels. An alternative technique for transferring proteins from a gel is capillary blotting.

Toluidine blue, also known as TBO or tolonium chloride (INN) is a blue cationic (basic) dye used in histology and sometimes clinically.

Alcian blue is any member of a family of polyvalent basic dyes, of which the Alcian blue 8G has been historically the most common and the most reliable member. It is used to stain acidic polysaccharides such as glycosaminoglycans in cartilages and other body structures, some types of mucopolysaccharides, sialylated glycocalyx of cells etc. For many of these targets it is one of the most widely used cationic dyes for both light and electron microscopy. Use of alcian blue has historically been a popular staining method in histology especially for light microscopy in paraffin embedded sections and in semithin resin sections. The tissue parts that specifically stain by this dye become blue to bluish-green after staining and are called "Alcianophilic". Alcian blue staining can be combined with H&E staining, PAS staining and van Gieson staining methods. Alcian blue can be used to quantitate acidic glycans both in microspectrophotometric quantitation in solution or for staining glycoproteins in polyacrylamide gels or on western blots. Biochemists had used it to assay acid polysaccharides in urine since the 1960s for diagnosis of diseases like mucopolysaccharidosis but from 1970's, partly due to lack of availability of Alcian and partly due to length and tediousness of the procedure, alternative methods had to be developed e.g. Dimethyl methylene blue method.
Virus quantification is counting or calculating the number of virus particles (virions) in a sample to determine the virus concentration. It is used in both research and development (R&D) in academic and commercial laboratories as well as in production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable that must be monitored. For example, the production of virus-based vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors, and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually monitor and/or modify the process in order to optimize product quality and production yields and to respond to ever changing demands and applications. Other examples of specific instances where viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization, and adaptation of methods to cell culture.

Luxol fast blue stain, abbreviated LFB stain or simply LFB, is a commonly used stain to observe myelin under light microscopy, created by Heinrich Klüver and Elizabeth Barrera in 1953. LFB is commonly used to detect demyelination in the central nervous system (CNS), but cannot discern myelination in the peripheral nervous system.

GelRed is an intercalating nucleic acid stain used in molecular genetics for agarose gel DNA electrophoresis. GelRed structurally consists of two ethidium subunits that are bridged by a linear oxygenated spacer.
Model organism databases (MODs) are biological databases, or knowledgebases, dedicated to the provision of in-depth biological data for intensively studied model organisms. MODs allow researchers to easily find background information on large sets of genes, efficiently plan experiments, integrate their data with existing knowledge, and formulate new hypotheses. They allow users to analyse results and interpret datasets, and the data they generate are increasingly used to describe less well studied species. Where possible, MODs share common approaches to collect and represent biological information. For example, all MODs use the Gene Ontology (GO) to describe functions, processes and cellular locations of specific gene products. Projects also exist to enable software sharing for curation, visualization and querying between different MODs. Organismal diversity and varying user requirements however mean that MODs are often required to customize capture, display, and provision of data.
















