 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
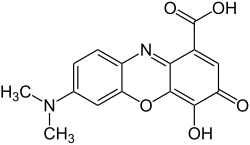
| IUPAC name 7-(Dimethylamino)-4-hydroxy-3-oxo-3H-phenoxazine-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.860 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 300.270 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Gallocyanin is a chemical compound classified as a phenoxazine dye. In combination with certain metals, it is used to prepare gallocyanin stains that are used in identifying nucleic acids. [1]