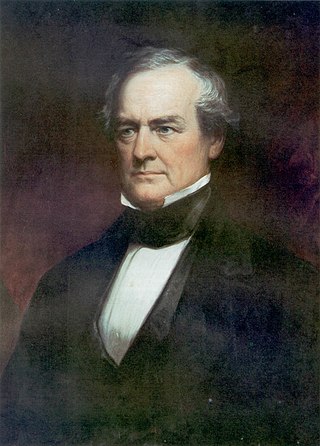John Quincy Adams was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diplomatic and political career, Adams served as an ambassador and also as a member of the United States Congress representing Massachusetts in both chambers. He was the eldest son of John Adams, who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801, and First Lady Abigail Adams. Initially a Federalist like his father, he won election to the presidency as a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, and later, in the mid-1830s, became affiliated with the Whig Party.

The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that temporarily defused tensions between slave and free states in the years leading up to the American Civil War. Designed by Whig senator Henry Clay and Democratic senator Stephen A. Douglas, with the support of President Millard Fillmore, the compromise centered on how to handle slavery in recently acquired territories from the Mexican–American War (1846–48).

Daniel Webster was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the 14th and 19th U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, and Millard Fillmore. Webster was one of the most prominent American lawyers of the 19th century, arguing over 200 cases before the United States Supreme Court in his career. During his life, Webster had been a member of the Federalist Party, the National Republican Party, and the Whig Party. He was among the three members of the Great Triumvirate along with Henry Clay and John C. Calhoun.

Langdon Cheves was an American politician, lawyer and businessman from South Carolina. He represented the city of Charleston in the United States House of Representatives from 1810 to 1815, where he played a key role on the home front of the War of 1812. Cheves was a leader among the War Hawk faction of the House. He served as chairman of the Committees on Naval Affairs and Ways and Means under Speaker of the House Henry Clay, then succeeded Clay as Speaker in the war's final stages. After leaving the House, he served as President of the Second Bank of the United States from 1819 to 1823.

Simon Cameron was an American businessman and politician who represented Pennsylvania in the United States Senate and served as United States Secretary of War under President Abraham Lincoln at the start of the American Civil War.

William Harris Crawford was an American politician and judge during the early 19th century. He served as US Secretary of War and US Secretary of the Treasury before he ran for US president in the 1824 election.

John Jordan Crittenden was an American statesman and politician from the U.S. state of Kentucky. He represented the state in the U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate and twice served as United States Attorney General in the administrations of William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, and Millard Fillmore. He was also the 17th governor of Kentucky and served in the state legislature. Although frequently mentioned as a potential candidate for the U.S. presidency, he never consented to run for the office.

John Middleton Clayton was an American lawyer and politician from Delaware. He was a member of the Whig Party who served in the Delaware General Assembly, and as U.S. Senator from Delaware and U.S. Secretary of State.

Thomas Ewing Sr. was a National Republican and Whig politician from Ohio. He served in the U.S. Senate as well as serving as the fourteenth secretary of the treasury and the first secretary of the interior. He is also known as the foster father of famous American Civil War general William Tecumseh Sherman.

Jacob Collamer was an American politician from Vermont. He served in the U.S. House of Representatives, as Postmaster General in the cabinet of President Zachary Taylor, and as a U.S. Senator.
George Walker Crawford was a licensed attorney turned politician from Columbia County, Georgia. Crawford was appointed attorney general for the state in 1827, by Governor John Forsyth, serving in that capacity until 1831. Crawford also served five years in the General Assembly's lower house as a representative of Richmond County on a platform of states' rights.

Howell Cobb was an American and later Confederate political figure. A southern Democrat, Cobb was a five-term member of the United States House of Representatives and the speaker of the House from 1849 to 1851. He also served as the 40th governor of Georgia (1851–1853) and as a secretary of the treasury under President James Buchanan (1857–1860).

William Morris Meredith was an American lawyer and politician from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He served as the United States Secretary of the Treasury, during President Zachary Taylor's Administration.

The presidency of Millard Fillmore began on July 9, 1850, when Millard Fillmore became President of the United States upon the death of President Zachary Taylor, and ended on March 4, 1853. Fillmore had been Vice President of the United States for 1 year, 4 months when he became the 13th United States president. Fillmore was the second president to succeed to the office without being elected to it, after John Tyler. He was the last Whig president. His presidency ended after losing the Whig nomination at the 1852 Whig National Convention. Fillmore was succeeded by Democrat Franklin Pierce.

The Big Four or the Four Nations refer to the four top Allied powers of World War I and their leaders who met at the Paris Peace Conference in January 1919. The Big Four is also known as the Council of Four. It was composed of Georges Clemenceau of France, David Lloyd George of the United Kingdom, Vittorio Emanuele Orlando of Italy, and Woodrow Wilson of the United States.

Zachary Taylor was the 12th president of the United States, serving from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States Army, rising to the rank of major general and becoming a national hero for his victories in the Mexican–American War. As a result, he won election to the White House despite his vague political beliefs. His top priority as president was to preserve the Union. He died 16 months into his term from a stomach disease. Taylor had the third-shortest presidential term in U.S. history.
The Province of Georgia was a significant battleground in the American Revolution. Its population was at first divided about exactly how to respond to revolutionary activities and heightened tensions in other provinces. Georgia was the only colony not present in the First Continental Congress in 1774. When violence broke out in 1775, radical Patriots took control of the provincial government, and drove many Loyalists out of the province. Georgia subsequently took part to the Second Continental Congress with the other colonies. In 1776 and 1778, Georgia served as the staging ground for several important raids into British-controlled Florida. The British army captured Savannah in 1778, and the American and French forces failed to recapture the city during the Siege of Savannah in 1779. Georgia remained under British control until their evacuation from Savannah in 1782.
George Galphin (1708–1780) was an American businessman specializing in Indian Trade, an Indian Commissioner, and plantation owner who lived and conducted business in the colonies of Georgia and South Carolina, primarily around the area known today as Augusta, Georgia.

During Ulysses S. Grant's two terms as president of the United States (1869–1877) there were several executive branch investigations, prosecutions, and reforms carried-out by President Grant, Congress, and several members of his cabinet, in the wake of several revelations of fraudulent activities within the administration. Grant's cabinet fluctuated between talented individuals or reformers and those involved with political patronage or party corruption. Some notable reforming cabinet members were persons who had outstanding abilities and made many positive contributions to the administration. These reformers resisted the Republican Party's demands for patronage to select efficient civil servants. Although Grant traditionally is known for his administration scandals, more credit has been given to him for his appointment of reformers.
The history of the United States Whig Party lasted from the establishment of the Whig Party early in President Andrew Jackson's second term (1833–1837) to the collapse of the party during the term of President Franklin Pierce (1853–1857). This article covers the party in national politics. For state politics see Whig Party.