Galvanic (after Luigi Galvani) may refer to:

An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ACID, for "anode current into device". The direction of conventional current in a circuit is opposite to the direction of electron flow, so electrons flow from the anode of a galvanic cell, into an outside or external circuit connected to the cell. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a "+" is the cathode.
Cell most often refers to:
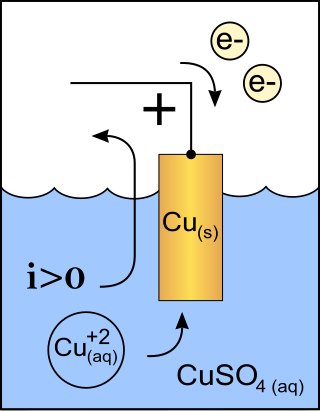
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic CCD for Cathode Current Departs. A conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. Electrons have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is opposite to that of the conventional current flow. Consequently, the mnemonic cathode current departs also means that electrons flow into the device's cathode from the external circuit. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode.

Luigi Galvani was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher, who studied animal electricity. In 1780, using a frog, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when struck by an electrical spark. This was an early study of bioelectricity, following experiments by John Walsh and Hugh Williamson.

Electrology is the practice of electrical hair removal to permanently remove human hair from the body. Electrolysis is the actual process of removing hair using electricity.

Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion.

A galvanic anode, or sacrificial anode, is the main component of a galvanic cathodic protection system used to protect buried or submerged metal structures from corrosion.
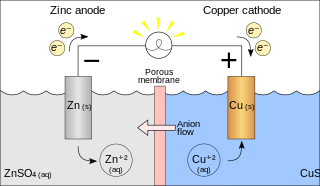
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell, named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta, respectively, is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous oxidation–reduction reactions. An example of a galvanic cell consists of two different metals, each immersed in separate beakers containing their respective metal ions in solution that are connected by a salt bridge or separated by a porous membrane.

Cathodic protection is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded "sacrificial metal" to act as the anode. The sacrificial metal then corrodes instead of the protected metal. For structures such as long pipelines, where passive galvanic cathodic protection is not adequate, an external DC electrical power source is used to provide sufficient current.
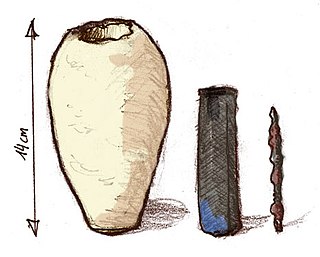
The Baghdad Battery is the name given to a set of three artifacts which were found together: a ceramic pot, a tube of copper, and a rod of iron. It was discovered in present-day Khujut Rabu, Iraq in 1936, close to the metropolis of Ctesiphon, the capital of the Parthian and Sasanian empires, and it is believed to date from either of these periods.
Isolation is the near or complete lack of social contact by an individual.
Electrodermal activity (EDA) is the property of the human body that causes continuous variation in the electrical characteristics of the skin. Historically, EDA has also been known as skin conductance, galvanic skin response (GSR), electrodermal response (EDR), psychogalvanic reflex (PGR), skin conductance response (SCR), sympathetic skin response (SSR) and skin conductance level (SCL). The long history of research into the active and passive electrical properties of the skin by a variety of disciplines has resulted in an excess of names, now standardized to electrodermal activity (EDA).
The galvanic series determines the nobility of metals and semi-metals. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experience galvanic corrosion. The rate of corrosion is determined by the electrolyte, the difference in nobility, and the relative areas of the anode and cathode exposed to the electrolyte. The difference can be measured as a difference in voltage potential: the less noble metal is the one with a lower electrode potential than the nobler one, and will function as the anode within the electrolyte device functioning as described above. Galvanic reaction is the principle upon which batteries are based.
GVS may refer to:

Galvanic isolation is a principle of isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flow; no direct conduction path is permitted.
Power cell may refer to:
O'Reilly v. Morse, 56 U.S. 62 (1853), also known as The Telegraph Patent Case, is an 1854 decision of the United States Supreme Court that has been highly influential in the development of the law of patent-eligibility in regard to claimed inventions in the field of computer-software related art. It holds, essentially, that an abstract idea, apart from its implementation, is not patent-eligible.
Galvanic urticaria has been described after exposure to a galvanic (electrical) device used to treat hyperhidrosis.
Cosmetic electrotherapy is a range of beauty treatments that uses low electric currents passed through the skin to produce several therapeutic effects such as muscle toning in the body and micro-lifting of the face. It is based on electrotherapy, which has been researched and accepted in the field of rehabilitation, though the "scientific and medical communities have tended to sideline or dismiss the use of electrotherapy for healthy muscles".

Galvanic corrosion is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. This phenomenon is named after Italian physician Luigi Galvani (1737–1798).