
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse generator, or stimulator, is connected to a magnetic coil connected to the scalp. The stimulator generates a changing electric current within the coil which creates a varying magnetic field, inducing a current within a region in the brain itself.

Jennie Kidd Trout was the first woman in Canada to become a licensed medical doctor, on March 11, 1875. Trout was the only woman in Canada licensed to practice medicine until July 1880, when Emily Stowe completed the official qualifications.

Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that implants a neurostimulator and electrodes which sends electrical impulses to specified targets in the brain responsible for movement control. The treatment is designed for a range of movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia, as well as for certain neuropsychiatric conditions like obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and epilepsy. The exact mechanisms of DBS are complex and not entirely clear, but it is known to modify brain activity in a structured way.

Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, depression and insomnia. CES has been suggested as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation, and opiate withdrawal, but there is little evidence of effectiveness for many of these conditions and the evidence for use in acute depression is not sufficient to justify it.

A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is a device that produces mild electric current to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS, by definition, covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents used for nerve excitation, but the term is often used with a more restrictive intent—namely, to describe the kind of pulses produced by portable stimulators used to reduce pain. The unit is usually connected to the skin using two or more electrodes which are typically conductive gel pads. A typical battery-operated TENS unit is able to modulate pulse width, frequency, and intensity. Generally, TENS is applied at high frequency (>50 Hz) with an intensity below motor contraction or low frequency (<10 Hz) with an intensity that produces motor contraction. More recently, many TENS units use a mixed frequency mode which alleviates tolerance to repeated use. Intensity of stimulation should be strong but comfortable with greater intensities, regardless of frequency, producing the greatest analgesia. While the use of TENS has proved effective in clinical studies, there is controversy over which conditions the device should be used to treat.

Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a technique that uses low-energy electrical pulses to artificially generate body movements in individuals who have been paralyzed due to injury to the central nervous system. More specifically, FES can be used to generate muscle contraction in otherwise paralyzed limbs to produce functions such as grasping, walking, bladder voiding and standing. This technology was originally used to develop neuroprostheses that were implemented to permanently substitute impaired functions in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), head injury, stroke and other neurological disorders. In other words, a person would use the device each time he or she wanted to generate a desired function. FES is sometimes also referred to as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES).
Electrotherapy is the use of electrical energy as a medical treatment. In medicine, the term electrotherapy can apply to a variety of treatments, including the use of electrical devices such as deep brain stimulators for neurological disease. The term has also been applied specifically to the use of electric current to speed wound healing. Additionally, the term "electrotherapy" or "electromagnetic therapy" has also been applied to a range of alternative medical devices and treatments.

A spa is a location where mineral-rich spring water is used to give medicinal baths. Spa towns or spa resorts typically offer various health treatments, which are also known as balneotherapy. The belief in the curative powers of mineral waters goes back to prehistoric times. Such practices have been popular worldwide, but are especially widespread in Europe and Japan. Day spas and medspas are also quite popular, and offer various personal care treatments.

Balneotherapy is a method of treating diseases by bathing, a traditional medicine technique usually practiced at spas. Since ancient times, humans have used hot springs, public baths and thermal medicine for therapeutic effects. While it is considered distinct from hydrotherapy, there are some overlaps in practice and in underlying principles. Balneotherapy may involve hot or cold water, massage through moving water, relaxation, or stimulation. Many mineral waters at spas are rich in particular minerals such as silica, sulfur, selenium, and radium. Medicinal clays are also widely used, a practice known as 'fangotherapy'.
Bioelectromagnetics, also known as bioelectromagnetism, is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological entities. Areas of study include electromagnetic fields produced by living cells, tissues or organisms, the effects of man-made sources of electromagnetic fields like mobile phones, and the application of electromagnetic radiation toward therapies for the treatment of various conditions.

Roberts Bartholow or Robert Bartholow was an American physician and a professor at several American medical colleges. He is best known for his experiments involving a 30-year-old patient named Mary Rafferty. Rafferty was admitted to Good Samaritan Hospital in Cincinnati, Ohio in 1874 with a 2-inch-diameter (51 mm) hole in her skull caused by a cancerous ulcer. Bartholow experimented with applying current to Rafferty's exposed dura using needle electrodes. His report detailed the first observations of how electrical stimulation of the brain affects motor functions of the body, but many ethical concerns were raised about the way in which he carried out his experiments. Rafferty went into a coma for three days and then died the day after coming out of the coma from a massive seizure.

Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of neuromodulation that uses constant, low direct current delivered via electrodes on the head. It was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or neuropsychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation, which generally uses alternating current the same way, as well as transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Therapeutic ultrasound refers generally to any type of ultrasonic procedure that uses ultrasound for therapeutic benefit. Physiotherapeutic ultrasound was introduced into clinical practice in the 1950s, with lithotripsy introduced in the 1980s. Others are at various stages in transitioning from research to clinical use: HIFU, targeted ultrasound drug delivery, trans-dermal ultrasound drug delivery, ultrasound hemostasis, cancer therapy, and ultrasound assisted thrombolysis It may use focused ultrasound or unfocused ultrasound.

Electrical brain stimulation (EBS), also referred to as focal brain stimulation (FBS), is a form of electrotherapy used as a technique in research and clinical neurobiology to stimulate a neuron or neural network in the brain through the direct or indirect excitation of its cell membrane by using an electric current. EBS is used for research or for therapeutic purposes.
Electroanalgesia is a form of analgesia, or pain relief, that uses electricity to ease pain. Electrical devices can be internal or external, at the site of pain (local) or delocalized throughout the whole body. It works by interfering with the electric currents of pain signals, inhibiting them from reaching the brain and inducing a response; different from traditional analgesics, such as opiates which mimic natural endorphins and NSAIDs that help relieve inflammation and stop pain at the source. Electroanalgesia has a lower addictive potential and poses less health threats to the general public, but can cause serious health problems, even death, in people with other electrical devices such as pacemakers or internal hearing aids, or with heart problems.
Cortical stimulation mapping (CSM) is a type of electrocorticography that involves a physically invasive procedure and aims to localize the function of specific brain regions through direct electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex. It remains one of the earliest methods of analyzing the brain and has allowed researchers to study the relationship between cortical structure and systemic function. Cortical stimulation mapping is used for a number of clinical and therapeutic applications, and remains the preferred method for the pre-surgical mapping of the motor cortex and language areas to prevent unnecessary functional damage. There are also some clinical applications for cortical stimulation mapping, such as the treatment of epilepsy.
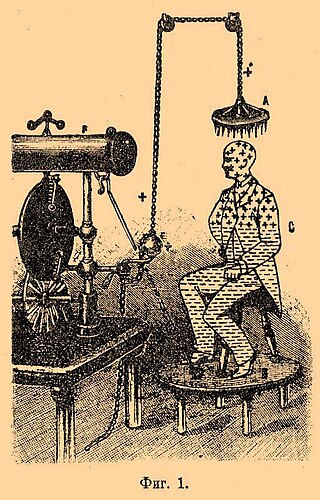
An electric bath is a 19th-century medical treatment in which high-voltage electrical apparatus was used for electrifying patients by causing an electric charge to build up on their bodies. In the US this process was known as Franklinization after Benjamin Franklin. The process became widely known after Franklin described it in the mid-18th century, but after that it was mostly practiced by quacks. Golding Bird brought it into the mainstream at Guy's Hospital in the mid-19th century and it fell into disuse in the early 20th century.
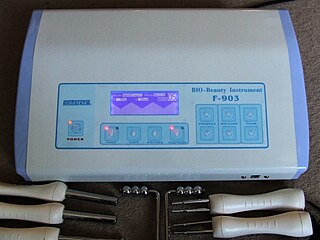
Cosmetic electrotherapy is a range of beauty treatments that uses low electric currents passed through the skin to produce several therapeutic effects such as muscle toning in the body and micro-lifting of the face. It is based on electrotherapy, which has been researched and accepted in the field of rehabilitation, though the "scientific and medical communities have tended to sideline or dismiss the use of electrotherapy for healthy muscles".
Transcranial pulsed ultrasound (TPU) uses low intensity, low frequency ultrasound (LILFU) to stimulate the brain. In 2002, Dr. Alexander Bystritsky first proposed the idea that this methodology contained therapeutic benefits. Beginning in 2008, Dr. William Tyler and his research team from Arizona State University began an investigation and development of this alternative neuromodulation without the harmful effects and risks of invasive surgery. They discovered that this low-power ultrasound is able to stimulate high neuron activity which allows for the manipulation of the brain waves through an external source. Unlike deep brain stimulation or Vagus nerve stimulation, which use implants and electrical impulses, TPU is a noninvasive and focused procedure that does not require the implantation of electrodes that could damage the nervous tissue. Its use is applicable in the various fields including but not limited to medical and military science. Although this technology holds great potential to introducing new and beneficial alternatives to conventional brain manipulation, it is a relatively young science and has certain obstructions to its full development such as a lack of complete understanding and control of every safety measure.
Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation is the application of non-invasive neurostimulation techniques on the cerebellum to modify its electrical activity. Techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can be used. The cerebellum is a high potential target for neuromodulation of neurological and psychiatric disorders due to the high density of neurons in its superficial layer, its electrical properties, and its participation in numerous closed-loop circuits involved in motor, cognitive, and emotional functions.















