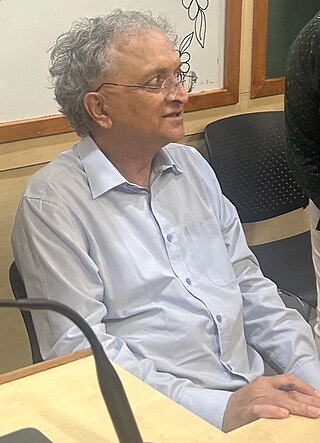Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule. He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world.

Chakravarti Rajagopalachari BR, popularly known as Rajaji or C.R., also known as Mootharignar Rajaji, was an Indian statesman, writer, lawyer, and Indian independence activist. Rajagopalachari was the last Governor-General of India, as when India became a republic in 1950 the office was abolished. He was also the only Indian-born Governor-General, as all previous holders of the post were British nationals. He also served as leader of the Indian National Congress, Premier of the Madras Presidency, Governor of West Bengal, Minister for Home Affairs of the Indian Union and Chief Minister of Madras state. Rajagopalachari founded the Swatantra Party and was one of the first recipients of India's highest civilian award, the Bharat Ratna. He vehemently opposed the use of nuclear weapons and was a proponent of world peace and disarmament. During his lifetime, he also acquired the nickname 'Mango of Salem'.

Amitav Ghosh is an Indian writer. He won the 54th Jnanpith award in 2018, India's highest literary honour. Ghosh's ambitious novels use complex narrative strategies to probe the nature of national and personal identity, particularly of the people of India and South Asia. He has written historical fiction and non-fiction works discussing topics such as colonialism and climate change.

Kasturba Mohandas Gandhi was an Indian political activist who was involved in the Indian independence movement during British India. She was married to Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mahatma Gandhi. National Safe Motherhood Day is observed in India annually on April 11, coinciding with Kasturba's birthday.

Harilal Mohandas Gandhi was the eldest son of Mahatma Gandhi and Kasturba Gandhi. He had three younger brothers: Manilal Gandhi, Ramdas Gandhi and Devdas Gandhi.
Mahatma Gandhi (1869–1948) is widely regarded as the main icon of the Indian independence movement.

Kaba Gandhi No Delo is a house in Rajkot, Gujarat, India. It was Indian independence leader Mahatma Gandhi's primary family home from 1881 to 1915. It is built in the traditional Saurashtrian architectural style and houses a permanent pictorial exhibition called Gandhi Smriti.

Madeleine Slade, also known as Mirabehn or Meera Behn, was a British supporter of the Indian Independence Movement who in the 1920s left her home in England to live and work with Mahatma Gandhi. She devoted her life to human development and the advancement of Gandhi's principles.
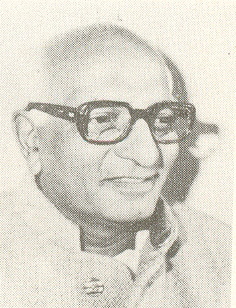
Madhu Dandavate was an Indian physicist and socialist politician, who served as Minister of Railways in the Morarji Desai ministry, and as Minister of Finance in the V P Singh ministry.
The Poona Pact of 1932 was a negotiated settlement between Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar that significantly shaped the political representation of the depressed classes, now known as Scheduled Castes (SC). The Poona Pact was an agreement between Hindus and the Depressed Classes and was signed by 23 people including Madan Mohan Malaviya, on behalf of Hindus and Dr Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar on behalf of The Depressed Classes.
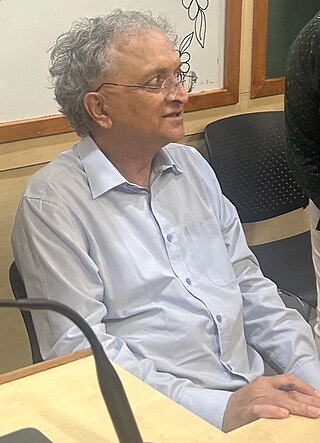
Ramachandra "Ram" Guha is an Indian historian, environmentalist, writer and public intellectual whose research interests include social, political, contemporary, environmental and cricket history, and the field of economics. He is an important authority on the history of modern India.

India After Gandhi: The History of the World's Largest Democracy is a non-fiction book by Indian historian Ramachandra Guha. First published by HarperCollins in August 2007.
Peter Heehs is an American historian living in Puducherry, India who writes on modern Indian history, spirituality and religion. Much of his work focuses on the Indian freedom fighter and spiritual leader Sri Aurobindo. His publications include twelve books and more than sixty articles in journals and magazines.
Richard Symonds was an English academic and civil servant.

Enuga Sreenivasulu Reddy, also known as E. S. Reddy, was an Indian-born diplomat at the United Nations who led the anti-apartheid efforts at the UN's Special Committee Against Apartheid and its Centre Against Apartheid. He also served as director of the UN Trust Fund for South Africa and the Educational and Training Programme for Southern Africa. During his time in these roles, he campaigned for economic boycott of the then Government of South Africa, advancing anti-apartheid actions including a combination of economic and social measures. He also lobbied for the release of the imprisoned leader Nelson Mandela.

Gandhi Before India is a 2013 book by the Indian historian Ramachandra Guha, the first part of a two-volume biography of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. The book deals with Gandhi's life up to his return to India following a 21-year period as a lawyer and civil-rights activist in South Africa. During this period in South Africa, Gandhi experienced discrimination that all coloured people there faced, including the Indian community he became a part of. In response to the government's policies he developed Satyagraha, a form of protest that translates loosely to "truth force".
Herbert Fischer (1914–2006) was a German diplomat, indologist and the ambassador of the erstwhile German Democratic Republic to India from 1972 to 1976. Fischer was born on 10 April 1914 in Herrnhut, in East Germany to a craftsman. He migrated to western Europe in 1933, where he completed his studies. Fischer moved to India in 1936, which gave him the opportunity to get acquainted with Mahatma Gandhi. After Indian independence in 1947, he returned to the German Democratic Republic, where he joined the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1956. He served as the Chief of the East German Trade Mission in the late 1960s, before becoming the East German ambassador to India in 1972. He was the author of many Indological books, including Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, a biography of the Indian leader. He was a recipient of the Patriotic Order of Merit III Class. In 2003, the Government of India awarded him the Padma Bhushan, their third highest civilian honour, for his contributions to public affairs.

A Corner of a Foreign Field: The Indian History of a British Sport is a 2002 book by Indian historian Ramachandra Guha that offers a historical account of cricket in the Indian subcontinent. Some critics have called it one of the finest books on cricket.

Putlibai Karamchand Gandhi was the mother of Indian independence leader Mahatma Gandhi.

Makers of Modern India is a non-fiction book written by Indian historian-scholar Ramachandra Guha and published by Penguin India in 2010. The book features profiles of selected personalities that laid the foundation of modern India: Ram Mohan Roy, Syed Ahmad Khan, Khuda Bakhsh, Jotirao Phule, Gopal Krishna Gokhale, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Tarabai Shinde, Mahatma Gandhi, Rabindranath Tagore, B. R. Ambedkar, Mohammad Ali Jinnah, Periyar, Kamala Devi Chattopadhyay, Jawaharlal Nehru, M. S. Golwalkar, Rammanohar Lohia, Jayaprakash Narayan, C. Rajagopalachari, Verrier Elwin, and Hamid Dalwai.